Published online May 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3108
Revised: April 16, 2008
Published online: May 21, 2008
AIM: To discuss the variations and distributions of authors who published their papers in World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) during 2001-2007 and evaluate the development of WJG and gastroenterology core journals in recent years by comparing the contributions of the authors.
METHODS: WJG articles published in 2001-2007 were searched from MEDLINE database (by ISI Web of Knowledge). The variations (cooperation degree, cooperation rate) and distributions of the first authors were analyzed with bibliometric methods. SCIE was used to collect articles published in Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology, Scand J Gastroenterol and WJG in 2007, and comparison of the data was made. Comparison indicators included the article number of annual journals, cooperation degree of authors, cooperation rate, mean number of articles published in each WJG issue, number of countries of the first WJG authors, geographical distribution and article contribution ratio of all WJG authors and domestic authors.
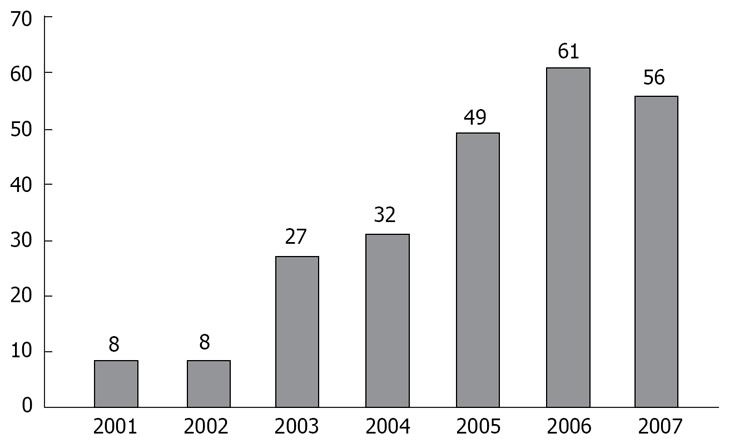
RESULTS: Of the 5851 articles covered in MEDLINE, 173, 236, 633, 826, 1496, 1382 and 1105 articles were cited from 2001 to 2007. The cooperation degree was 5.11, 5.56, 5.75, 5.76, 6.31, 5.90 and 5.64 respectively. The cooperation rates was 94.80%, 99.15%, 98.89%, 98.55%, 99.13%, 96.67% and 95.66%, respectively. The mean number of articles published in each WJG issue from 2001 to 2007 was 28, 39, 52, 34, 31, 28 and 23, respectively. The number of countries of the first WJG authors was 8, 8, 27, 32, 49, 61 and 56, respectively. The first authors of WJG came from 3 continents in 2001 and covered 6 continents in 2006-2007. The number of articles written by Asian authors was 136 (79.07%), 227 (96.19%), 575 (90.98%), 713 (87.81%), 1111 (75.32%), 712 (53.98%) and 555 (53.21%), respectively in 2001-2007. The number of articles written by European & American authors increased from 36 (20.93%) and 8 (3.39%) in 2001-2002 to 563 (42.68%) and 452(43.34%) in 2006-2007. The number of countries except for China contributing papers was increased. The number of articles written by first authors of Japan rose from 0 (0%) in 2001-2002 to 287 (12.15%) in 2006-2007. The number of articles written by American authors increased from 6 (1.47%) in 2001-2002 to 158 (6.69%) in 2006-2007. The number of articles written by Chinese authors was 136 (79.07%), 227 (96.19%), 548 (86.71%), 669 (82.39%), 884 (59.93%), 380 (28.81%) and 320 (30.68%), respectively, in 2001 to 2007. The number of articles published in Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology, Scand J Gastroenterol and WJG was 565, 586, 238 and 1118, respectively in 2007. The cooperation degree was 4.77, 6.14, 5.95 and 5.64, respectively, in 2007. The cooperation rate was 95.40%, 84.18%, 96.63% and 95.66%, respectively, in 2007. The number of countries of authors contributing papers was 44, 35, 42 and 62, respectively, in 2007.
CONCLUSION: The geographical distribution of WJG authors is wide for the past 2 years. WJG has made a step onto international publishing, and drawn even more attentions from gastroenterology researchers. Its authors are distributed over 74 countries in 6 global continents, and the journal has become the main intermediary for international gastroenterology researchers to demonstrate their research accomplishments.
-
Citation: Yang H, Zhao YY. Variations of author origins in
World Journal of Gastroenterology during 2001-2007. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(19): 3108-3111 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i19/3108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3108
World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) was first published in 1995. This English journal is edited and published by The WJG Press and can be retrieved with the following citation tools: Current Contents®/Clinical Medicine, Science Citation Index Expanded (also known as SciSearch®) and Journal Citation Reports/Science Edition, Index Medicus, MEDLINE and PubMed, Chemical Abstracts, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Abstracts Journals, Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology and Hepatology, CAB Abstracts and Global Health, etc. In recent years, Ma et al[1] has analyzed the articles covered in SCIE during 1998-2004, claiming that the self-citation rate is decreased. However, the citation rate by others is increased and the journal citation status is improved. The variations of WJG authors’ data in 2001 to 2007 were comparatively analyzed. The cooperation degree, cooperation rate, number of countries and author publishing ratios of domestic journal issues in American Journal of Gastroenterology, Gastroenterology, Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, were also comparatively analyzed using the SCIE database.
A bibliometric analysis of the variations in distributions of authors was made to show the improvements and shortcomings of WJG and speed up its development.
WJG articles were searched from MEDLINE (by ISI Web of Knowledge)[2] in 2001-2007. Variations (cooperation degree, cooperation rate) and distributions of the first authors were analyzed with biliometric methods. Articles published in Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology, Scand J Gastroenterol and WJG covered in SCIE[3] in 2007 were analyzed using Web of Science (meeting summaries were not covered). The authors, titles, addresses and other relevant data of the four journals in 2007 were processed through the SCIE’s ‘Refine Results’ function, and countries of authors, WJG authors, research institutions and their distribution were closely consistent with the current status and authors of articles published in WJG experienced difficulties.
WJG was published bimonthly in 2001-2002, monthly in 2003, semimonthly in 2004, and weekly from 2006. In 2001 -2007, 173, 236, 633, 826, 1496, 1382 and 1105 articles published in WJG were covered in MEDLINE. The number of articles published in each issue of WJG was 28, 39, 52, 34, 31, 28 and 23, respectively, in 2001-2007.
A total of 5851 articles published in WJG during 2001-2007 were cited. The number of authors of these papers was 34415 and the cooperation degree was 5.11, 5.56, 5.75, 5.76, 6.31, 5.90 and 5.64, respectively, with a mean cooperation degree of 5.88. The number of articles written by a single author was 137, accounting for 2.34% of all articles. The number of co-author articles published in 2001-2007 was 5714 and the cooperation rate was 94.80%, 99.15%, 98.89%, 98.55%, 99.13%, 96.67% and 95.66% respectively, with a mean cooperation rate of 97.66%. The cooperation degree was slightly increased from 2001 to 2005 (Table 1).
| Yr | Distribution of co-author articles | Total (articles) | Authors | Cooperation degree | Cooperation rate (%) | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | > 11 | |||||
| 2001 | 9 | 18 | 20 | 33 | 26 | 20 | 20 | 14 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 173 | 884 | 5.11 | 94.80 |
| 2002 | 2 | 20 | 23 | 44 | 35 | 39 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 2 | 11 | 236 | 1313 | 5.56 | 99.15 |
| 2003 | 7 | 30 | 65 | 88 | 131 | 110 | 79 | 55 | 25 | 22 | 21 | 633 | 3637 | 5.75 | 98.89 |
| 2004 | 12 | 47 | 82 | 112 | 146 | 154 | 105 | 71 | 43 | 25 | 29 | 826 | 4755 | 5.76 | 98.55 |
| 2005 | 13 | 59 | 113 | 188 | 243 | 273 | 202 | 154 | 86 | 56 | 109 | 1496 | 9434 | 6.31 | 99.13 |
| 2006 | 46 | 111 | 149 | 169 | 210 | 191 | 150 | 119 | 74 | 57 | 106 | 1382 | 8160 | 5.90 | 96.67 |
| 2007 | 48 | 107 | 129 | 148 | 158 | 139 | 120 | 83 | 48 | 59 | 66 | 1105 | 6232 | 5.64 | 95.66 |
| Total | 137 | 392 | 581 | 782 | 949 | 926 | 706 | 516 | 291 | 223 | 348 | 5851 | 34415 | 5.88 | 97.66 |
Only addresses of the first authors were marked in MEDLINE, and 5851 articles published in WJG were retrieved in 2001-2007, in which only 5689 articles had available addresses. The number of countries with their articles covered in MEDLINE was 8, 8, 27, 32, 49, 61 and 56, respectively (Figure 1). The geographical distribution of WJG authors was increasingly broadened, especially in 2006 and 2007 during which the number of countries increased multiple folds.
The geographical distribution of the authors with addresses in 5689 articles was categorized into 6 continents (Table 2). During 2001-2005, the majority authors were from Asia, accounting for136 (79.07%), 227 (96.19%), 575 (90.98%), 713 (87.81%) and 1111 (75.32%), respectively. During 2006-2007, the number of authors from Asia was 712 (53.98%), 555 (53.21%) respectively, showing that the number of Asian authors is declining. During 2006-2007, the geographical distribution of WJG authors covered all the 6 continents and the number of European and North America authors increased from 36 (20.93%) and 8 (3.39%) in 2001-2002 to 563 (42.68%) and 452 (43.34%) in 2006-2007 respectively.
| Yr | Distribution of the authors in 6 continents | |||||
| Africa | Asia | Europe | North America | Oceania | South America | |
| 2001 | 0 | 136 | 32 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 2002 | 0 | 227 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 2003 | 1 | 575 | 45 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
| 2004 | 3 | 713 | 85 | 6 | 0 | 5 |
| 2005 | 7 | 1111 | 314 | 28 | 4 | 11 |
| 2006 | 11 | 712 | 453 | 110 | 10 | 23 |
| 2007 | 9 | 555 | 359 | 93 | 13 | 14 |
In order to reflect the geographical distributions of authors, a comparison of the distribution of WJG authors was performed. The number of articles contributed to WJG by the top 15 countries (Table 3) was 5167 (90.82%), the number of articles contributed to WJG by Chinese authors was 136 (79.07%), 227 (96.19%), 548 (86.71%), 669 (82.39%), 884 (59.93%), 380 (28.81%) and 320 (30.68%), respectively, in 2001-2007. The number of articles contributed by Japanese authors increased from 0 (0%) in 2001-2002 to 287 (12.15%) in 2006-2007, the number of articles contributed by the American authors was also increased from 6 (1.47%) in 2001-2002 to 158 (6.69%) in 2006-2007. All countries, except for China showed an increased number of contributed articles. Among the top 15 countries, 7 are in Asia, 7 in Europe, and 1 in North America.
| Country name | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | Total |
| China | 136 | 227 | 548 | 669 | 884 | 380 | 320 | 3164 |
| Japan | 6 | 19 | 133 | 170 | 117 | 445 | ||
| Germany | 10 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 68 | 92 | 66 | 252 |
| Italy | 9 | 15 | 56 | 79 | 56 | 215 | ||
| United States | 4 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 19 | 77 | 81 | 194 |
| Turkey | 17 | 24 | 31 | 43 | 62 | 177 | ||
| South Korea | 5 | 9 | 37 | 53 | 38 | 142 | ||
| Greece | 2 | 6 | 34 | 45 | 31 | 118 | ||
| United Kingdom | 18 | 3 | 1 | 16 | 28 | 22 | 88 | |
| India | 5 | 2 | 7 | 35 | 30 | 79 | ||
| Spain | 1 | 2 | 13 | 34 | 21 | 71 | ||
| Poland | 1 | 2 | 6 | 31 | 17 | 4 | 61 | |
| Hungary | 2 | 12 | 20 | 20 | 5 | 59 | ||
| Iran | 2 | 2 | 7 | 25 | 18 | 54 | ||
| Thailand | 1 | 4 | 14 | 16 | 13 | 48 |
The articles of Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology and Scand J Gastroenterol were selected to compare with those of WJG. Am J Gastroenterol is an official publication of the American College of Gastroenterology, and its IF was 5.608 in 2006, ranking 5th in Journal Citation Report(JCR). Gastroenterology is the official journal of the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) and its IF was 12.457 in 2006, ranking 1st in JCR. Scand J Gastroenterol published by Taylor & Francis Group is the membership journal of the Gastroenterologic Societies of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden, and its IF was 1.869 in 2006. These four journals are most typical of all journals related to the field of gastroenterology. The number of articles published in Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology, Scand J Gastroenterol and WJG covered in SCIE was 565, 586, 238 and 1118, respectively, in 2007. The cooperation degree of authors was 4.77, 6.14, 5.95 and 5.64, respectively; the cooperation rate was 95.40%, 84.18%, 96.63% and 95.66% respectively, in 2007. The geographical distribution of authors’ was 44, 35, 42 and 62, respectively (Table 4). In 2007, The number of American authors contributing to Am J Gastroenterol and Gastroenterology accounted for 47.43% and 50.85% respectively, the number of Swedish authors contributing to Scand J Gastroenterol accounted for 18.07%, the number of Northern Europe authors contributing to Scand J Gastroenterol accounted for 45.38%, the number of Chinese authors contributing to WJG accounted for 30.4%.
| Journal name | Articles published in 2007 | Cooperation degree in 2007 | Cooperation rate in 2007 | Geographical distribution of authors | Ratio of articles contributed by domestic authors (%) |
| Am J Gastroenterol | 565 | 4.77 | 95.40 | 44 | United States 47.43 |
| Gastroenterology | 586 | 6.14 | 84.18 | 35 | United States 50.85 |
| Scand J Gastroenterol | 238 | 5.95 | 96.63 | 42 | Sweden 18.07 |
| WJG | 1118 | 5.64 | 95.66 | 62 | China 30.4 |
In 2001-2007, the number of articles covered in MEDLINE was 173, 236, 633, 826, 1496, 1382 and 1105 respectively, the mean number of articles published in each issue was 28, 39, 52, 34, 31, 28 and 23 respectively. The number of articles published increased by 932 (638.73%) in 2007 compared to 2001.
In 2001-2007, the cooperation degree was 5.11, 5.56, 5.75, 5.76, 6.31, 5.90 and 5.64 respectively (mean 5.88), the cooperation rate was 94.80%, 99.15%, 98.89%, 98.55%, 99.13%, 96.67% and 95.66% respectively (mean 97.66%). The mean number of co-authors and single authors showed a tendency to increase from 2001 to 2005, while slightly decreased in 2006 to 2007.
The geographical distributions of authors in WJG were expanded from 4 continents in 2001 to the 6 continents in 2006-2007, the number of countries increased in multiple folds. The number of authors from Europe and North America increased while that from Asia decreased. The number of countries increased from 8, 8, 27, 32 and 49 in 2001-2005 to 61 and 56 in 2006-2007.
The number of Chinese authors accounted for 79.07%, 96.19%, 86.71%, 82.39%, 59.93%, 28.81% and 30.68% respectively, in 2001-2007, showing a maximum decrease of 67.38%. The number of Japanese, American, German and Italian authors increased greatly, showing an increasing trend of international authors contributing to WJG.
When compared with Am J Gastroenterol, Gastroenterology, Scand J Gastroenterol, the geographical distribution of authors in WJG was greatly expanded in the order of China, Asia and 6 continents. The mean number of published articles in each issue showed a prominent decrease, which may improve the quality of articles published in WJG. The cooperation degree and rate were reasonable, and the number of Chinese authors was slightly increased in 2007.
In conclusion, the geographical distribution of WJG authors is worldwide. WJG has made a step onto international level, thus drawing more attentions from gastroenterology researchers. The journal has become the main intermediary for international researchers in gastroenterology to demonstrate their research accom-plishments.
| 1. | Ma LS, Pan BR, Li WZ, Guo SY. Improved citation status of World Journal Gastroenterology in 2004: Analysis of all reference citations by WJG and citations of WJG articles by other SCI journals during 1998-2004. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:1-6. |
| 2. | MEDLINE. Available from: URL: http://apps.isiknowledge.com/. |
| 3. | SCIE. Available from: URL: http://www.isinet.com/cgi-bin/jrnlst/jlsubcatg.cgi?PC=D. |