Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2003; 9(4): 808-812
Published online Apr 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.808
Published online Apr 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.808
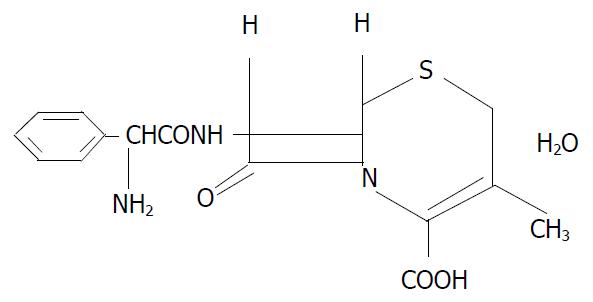
Figure 1 Structure of cephalexin used in this study.
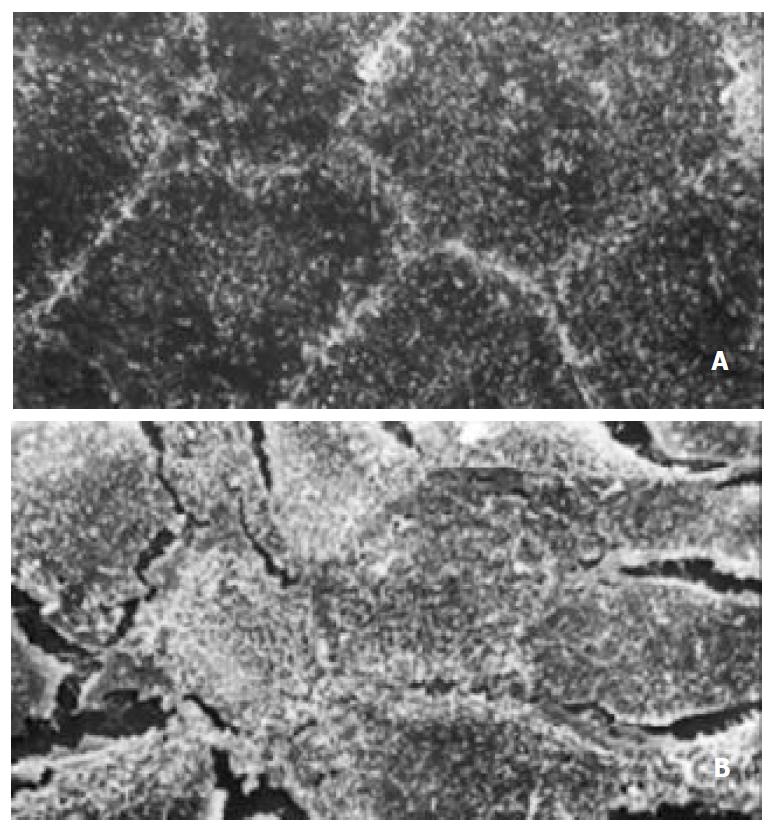
Figure 2 Appearance of scan electronic microscopy of Caco-2 cells.
(A) Tight junction formation of normal Caco-2 cells. × 1000; (B) Tight junction of A/R Caco-2 cells was destroyed partially. × 1000.
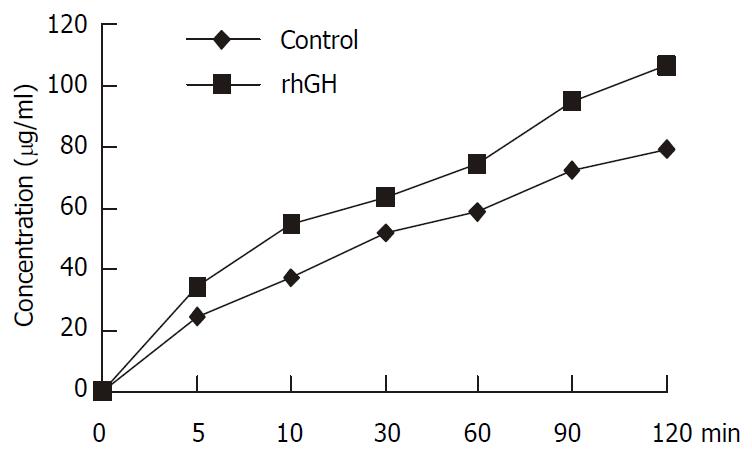
Figure 3 Transport of 1 mM cephalexin in Caco-2 cells.
Caco-2 cells were cultured with rhGH in apical side for 4 d. The controls were incubated with PH7.0 culture medium without rhGH both in apical side and basolateral side. All the mono-layers were washed in each experiment. The apical chambers were then filled with 1.5 ml solution containing 1 mM cephalexin. Transport was examined within the time range of 0, 5, 10, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. At the end of the incubation period, the inserts of Transwell were removed and the trans-port samples were obtained from the basolateral chambers. The concentrations of cephalexin of the transport samples were determined by HPLC. The apical-to-basolateral transport of cephalexin was significantly increased compared with the con-trols (P = 0.0045).
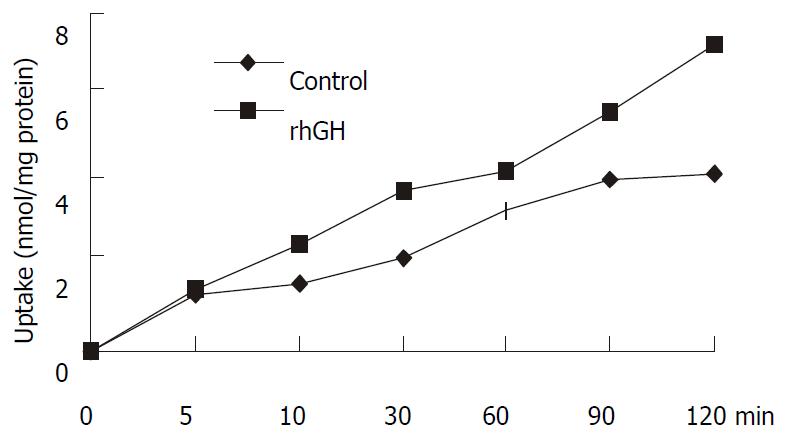
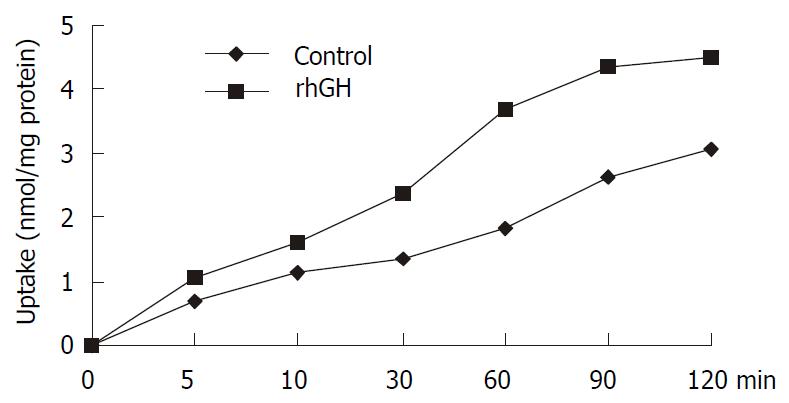
Figure 4 Uptake of 1 mM cephalexin in Caco-2 cells.
Caco-2 cells cultured in the multiwell dishes (24 pore) were cultured for 4 d with 34 nM rhGH. After washing the monolayers, the transport medium with 1 mM cephalexin was added to the pores and uptake was measured at 0, 5, 10, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. At the end of the incubation period, cell monolayers were washed with PH7.4 PBS to remove any extracellular cephalexin. Accumulated concentrations of cephalexin were determined by HPLC after the cells were lysed. The differences were significant (P = 0.0223).
Figure 5 Uptake of 1 mM cephalexin in Caco-2 cells with an-oxia/reoxygenation injury.
Caco-2 monolayers were initially subjected to a 90-minute period of anoxia followed by a 30-minute period of reoxygenation. The effect of the presence of rhGH on cephalexin uptake via the PepT1 of anoxia/reoxygenation Caco-2 cells was examined. The differences were significant (P = 0.0116).
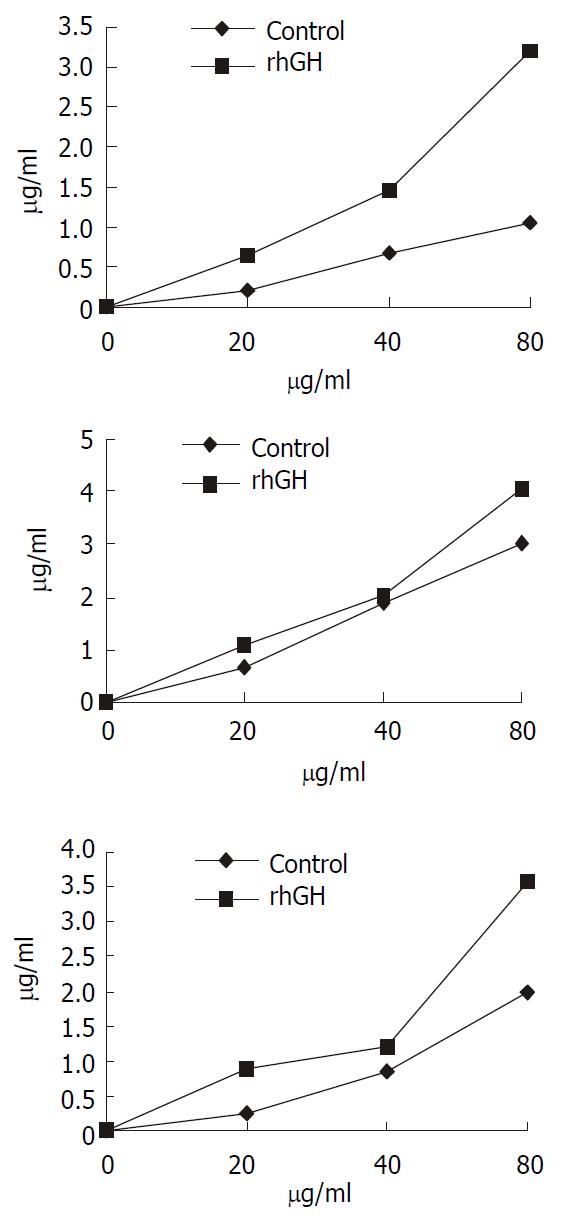
Figure 6 Concentration-dependent transport of cephalexin.
The kinetics of cephalexin transport by rhGH-treated Caco-2 cells showed that the transport level of Caco-2 cells was in ac-cordance with the concentration of cephalexin. The concentra-tions of cephalexin range of 20 to 80 µg·ml-1 were used. Trans-port was determined at the different time-point (a, 15 min; b, 30 min; c, 45 min). The extent of upregulation of rhGH on the transport was greater than the controls followed the increase of the concentration of cephalexin.
- Citation: Sun BW, Zhao XC, Wang GJ, Li N, Li JS. Hormonal regulation of dipeptide transporter (PepT1) in Caco-2 cells with normal and anoxia/reoxygenation management. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(4): 808-812
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i4/808.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.808