Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 15, 2003; 9(1): 9-15
Published online Jan 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.9
Published online Jan 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.9
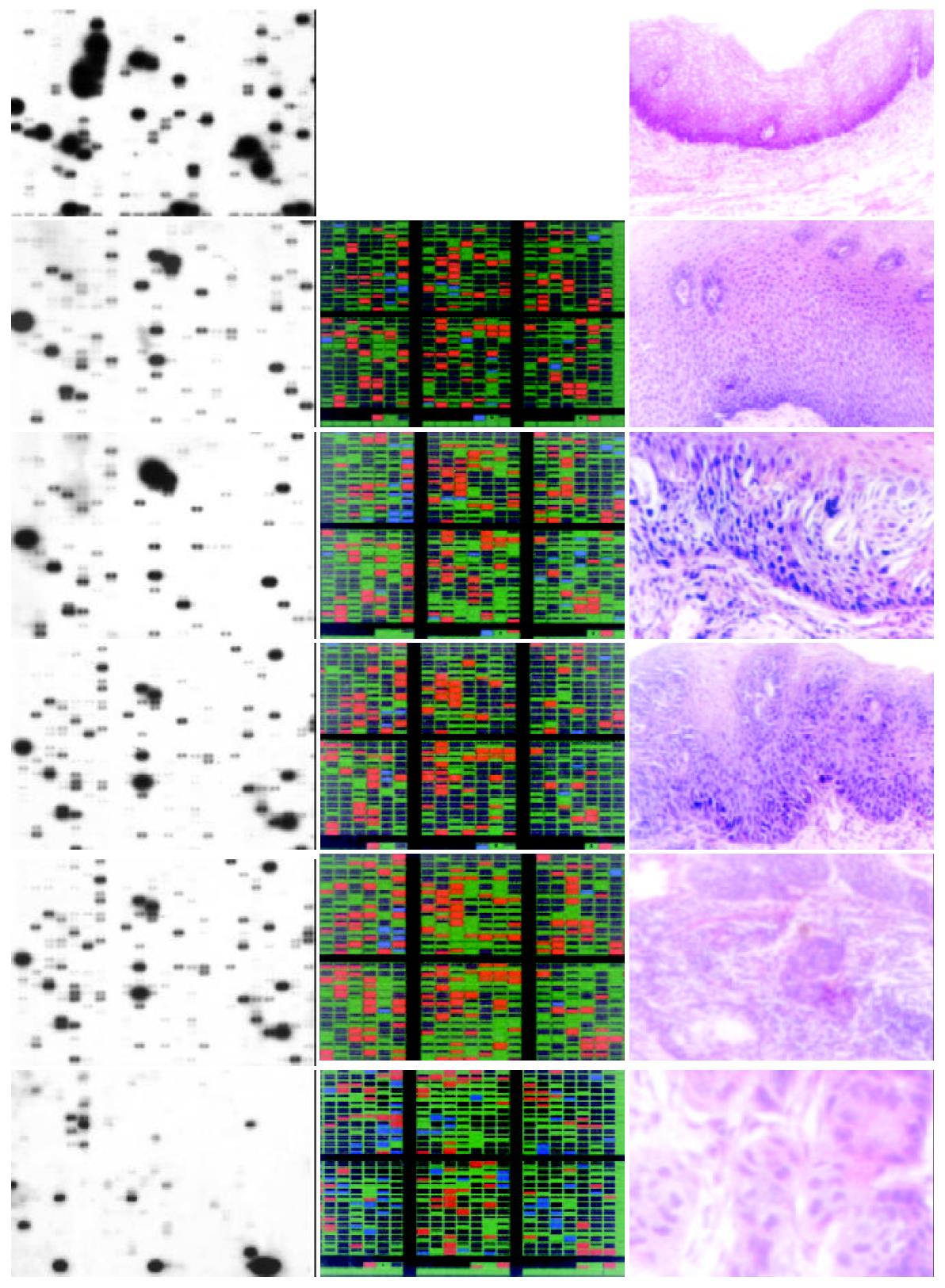
Figure 1 Expression patterns of genes in esophageal tissue of normal, basal cell hyperplasia, high-grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, early and advanced cancer.
Total RNAs were isolated from these tissues, reverse-transcribed into 32P-labeled cDNAs and hybridized to AtlasTM Human Cancer cDNA expression arrays. A complete list of names and location of the arrayed gene can be found in the instruction manual and website from Clontech. Data was analyzed by AtlasImageTM 1.01 software. A, B, C, D, E, F showed hybridization result of normal cells, basal cell hyperplasia, high-grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, early and advanced cancer; G, H, I, J, K showed the color charts indicating up-regulated genes with red, down-regulated genes with blue, and non-changed genes with green in the later 5 stages when compared to normal tissue; L, M, N, O, P showed the pathological image of normal, basal cell hyperplasia, high-grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, early and advanced cancer respectively.
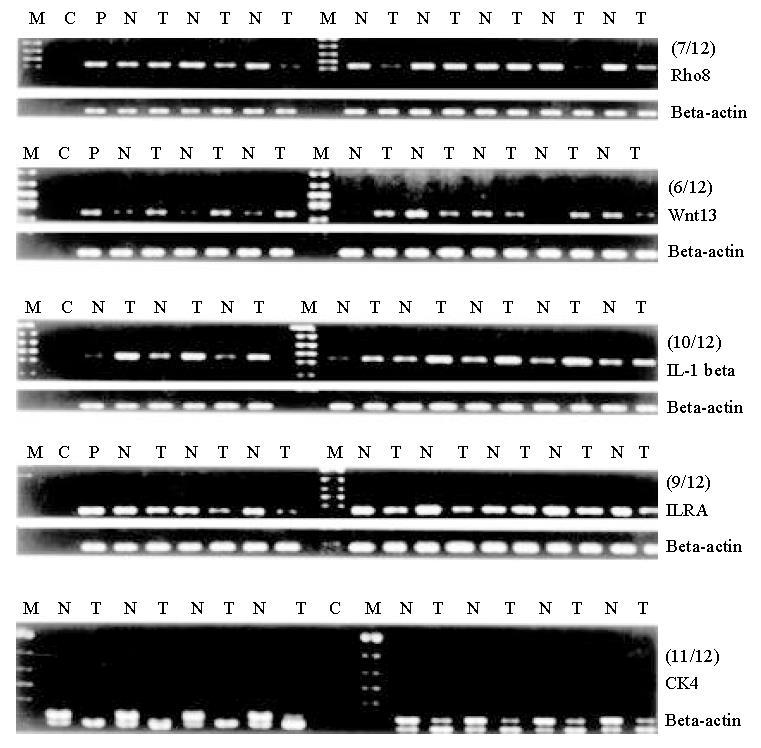
Figure 2 Validation of array data with RT-PCR: Rho8, Wnt 13, IL-1 beta, IL-1 receptor antagonist and cytokeratin 4 were chosen to further investigate the reliability of the array data using RT-PCR.
The figures showed part of the RT-PCR results of five genes in cancer (designated T) and matched almost normal tissues(designated N). P means positive control.
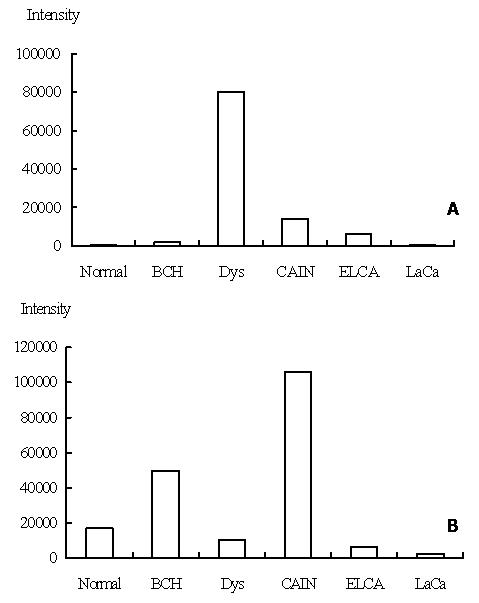
Figure 3 Expression level of p160ROCK (3A) and JNK2 (3B) in 6 different stages, p160ROCK peaked its expression at stage of high-grade dysplasia and JNK2 peaked its expression at stage of carcinoma in situ.
The column chart indicated expression levels of p160ROCK and JNK2 in stages of normal mucosa (designated normal), basal cell hyperplasia II (designated BCH), high grade dysplasia (designated Dys), squamous cell carcinoma in situ (designated CAIN), early cancer (designated ELCA) and late cancer (designated LaCa).
- Citation: Zhou J, Zhao LQ, Xiong MM, Wang XQ, Yang GR, Qiu ZL, Wu M, Liu ZH. Gene expression profiles at different stages of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(1): 9-15
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i1/9.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.9