Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2002; 8(6): 976-981
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.976
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.976
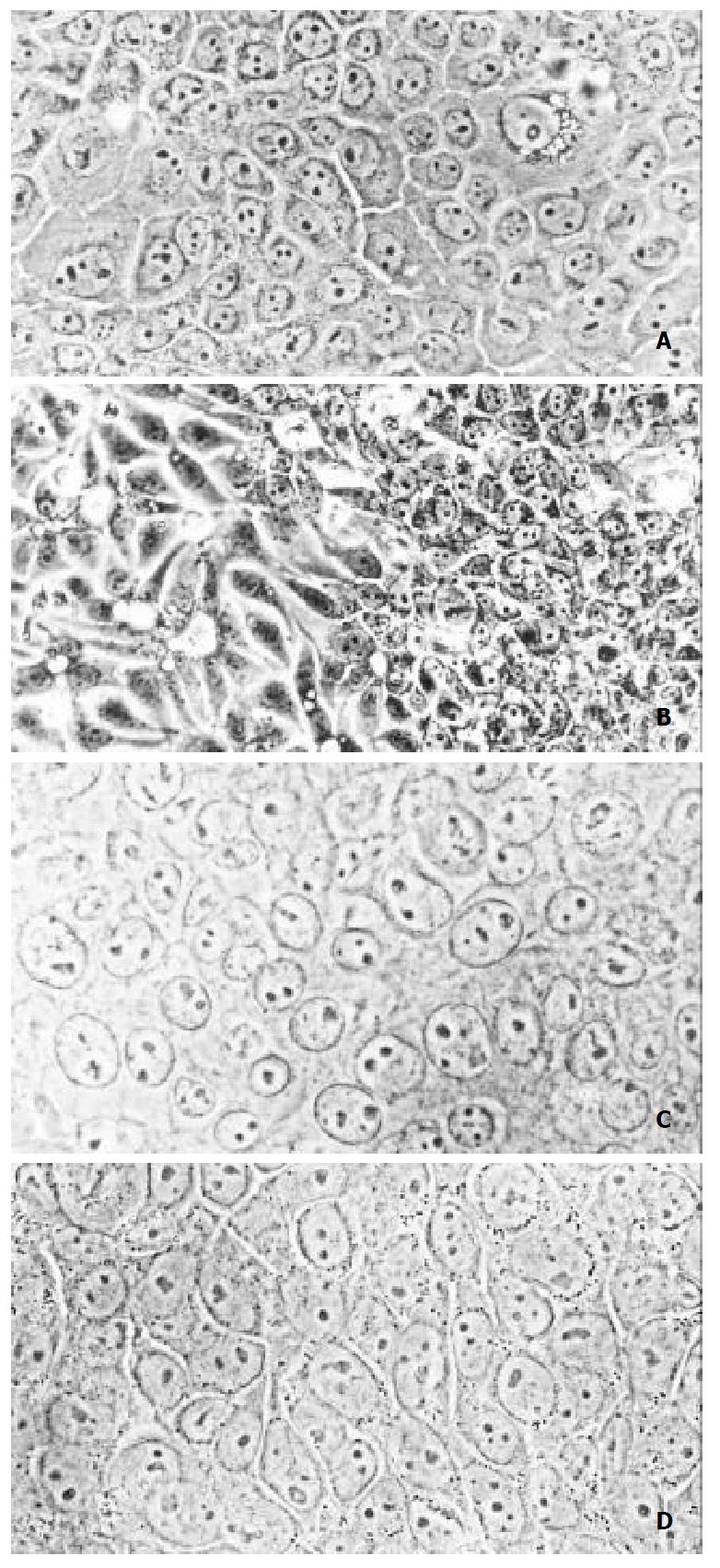
Figure 1 Morphology of SHEE cell (photographs of phase con-trast microscope).
A, SHEE10, good differentiation (× 400); B, SHEE31, differentiated to two directions, well differentiated (left), and poorly differentiated (right) (× 200); C, SHEE60, poor differentiation (× 400); D, SHEE85 shows different shape and size with larger nucleolus (× 400)
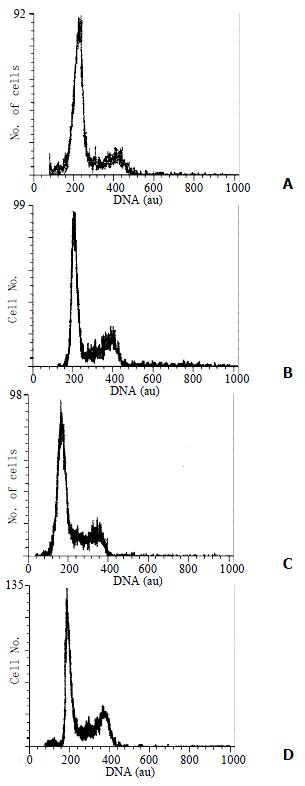
Figure 2 DNA histograms of SHEE.
A, SHEE10; B, SHEE31; C, SHEE60; D, SHEE85; au, arbitrary unit.
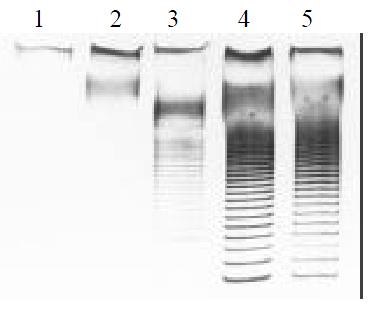
Figure 3 Activity of telomerase SHEE series.
1, normal esoph-ageal epithelium; 2, SHEE10; 3, SHEE31; 4, SHEE60; 5, SHEE85.
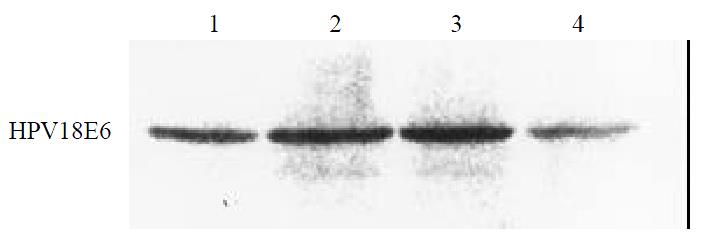
Figure 4 Western blot analysis of protein of HPV18E6 in SHEE 1, SHEE10; 2, SHEE31; 3, SHEE60; 4, SHEE85.
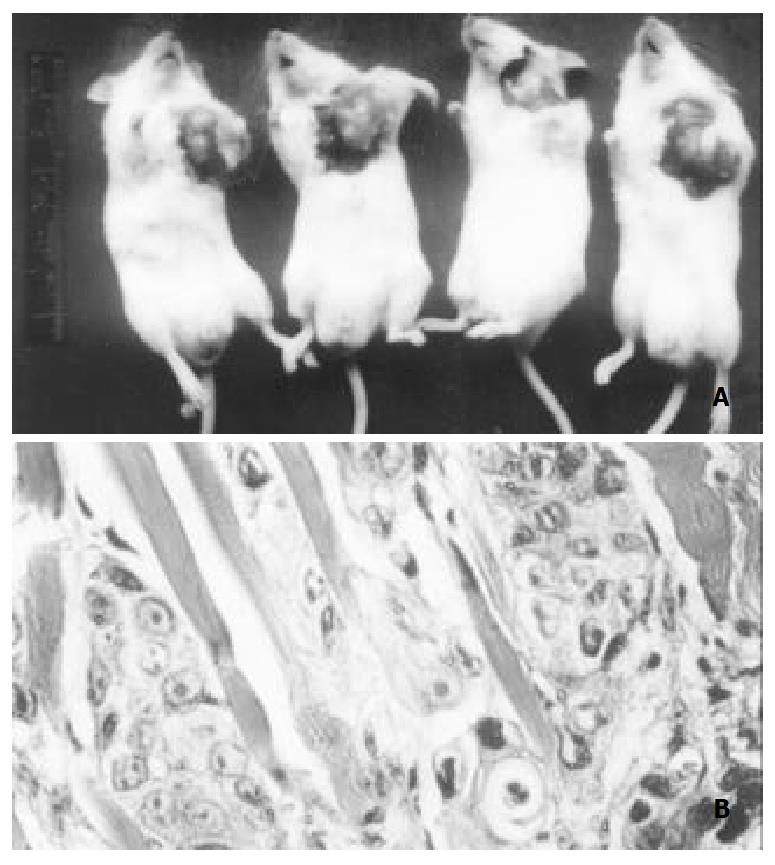
Figure 5 Heterotransplanting SHEE85 cells into SCID mice Tumors in right axiua (arrow) of SCID mice are found (A).
In-vasion of tumor cells is found in muscular layer (B). HE, × 400
- Citation: Shen ZY, Xu LY, Chen MH, Shen J, Cai WJ, Zeng Y. Progressive transformation of immortalized esophageal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(6): 976-981
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i6/976.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.976