Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2002; 8(4): 746-751
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.746
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.746
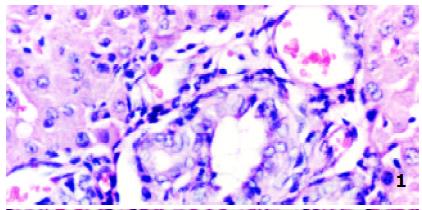
Figure 1 Liver tissue from isograft (Group I) complicated with subhepatic abscess of cholangiojejunal fistula at 14 d post-transplantation and with pneumonia at 94 d post-transplantation.
HE × 66
Figure 2 Liver tissue from isograft (Group I) complicated with subhepatic abscess of cholangiojejunal fistula at 14 d post-transplantation and with pneumonia at 94 d post-transplantation.
HE × 66
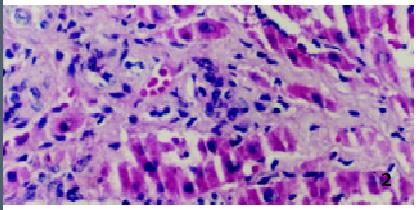
Figure 3 Liver tissue from acutely rejecting liver xenograft (Group II) at 7 d post-transplant HE × 66
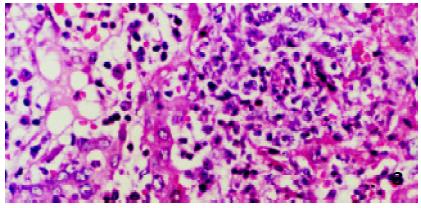
Figure 4 Liver tissue from xenograft (Group V) with double immunosuppressive action at 14 d post-transplantation.
HE × 33
Figure 5 NADPH diaphorase histochemocal staining in acutely rejecting liver xenografts (Group II) at 2, 7 d post-transplantation.
NADPH-d × 33, × 66
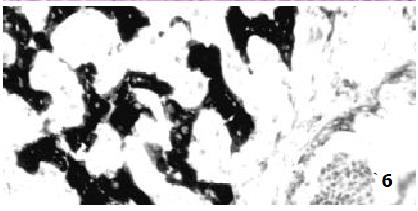
Figure 6 NADPH diaphorase histochemocal staining in acutely rejecting liver xenografts (Group II) at 2, 7 d post-transplantation.
NADPH-d × 33, × 66
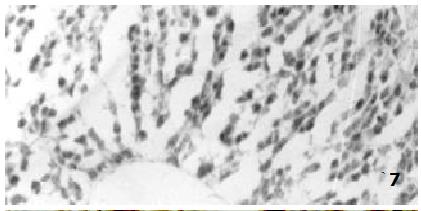
Figure 7 NO synthase in liver xenograft (Group V) with double immunosuppressive action at 14 d post-transplantation, showing negative NO synthase.
NADPH-d × 33
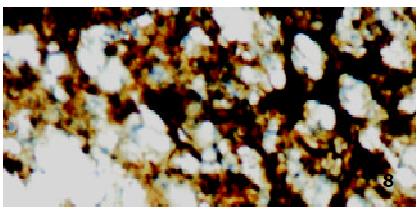
Figure 8 iNOS and cNOS in acutely rejecting rat orthotopic liver xenograft (Group II) at 7 d post-transplantation.
ABC × 66
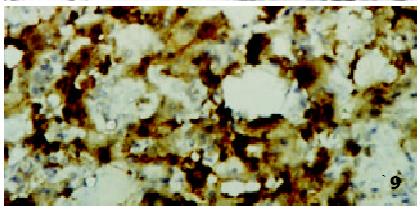
Figure 9 iNOS and cNOS in acutely rejecting rat orthotopic liver xenograft (Group II) at 7 d post-transplantation.
ABC × 66
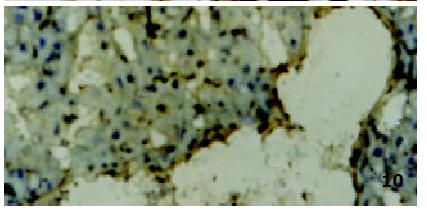
Figure 10 cNOS in liver xenograft (Group V) with double immunosuppressive action at 14 d post-transplantation.
ABC × 33
- Citation: Diao TJ, Yuan TY, Li YL. Immunologic role of nitric oxide in acute rejection of golden hamster to rat liver xenotransplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(4): 746-751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i4/746.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.746