Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 15, 2001; 7(1): 22-27
Published online Feb 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i1.22
Published online Feb 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i1.22
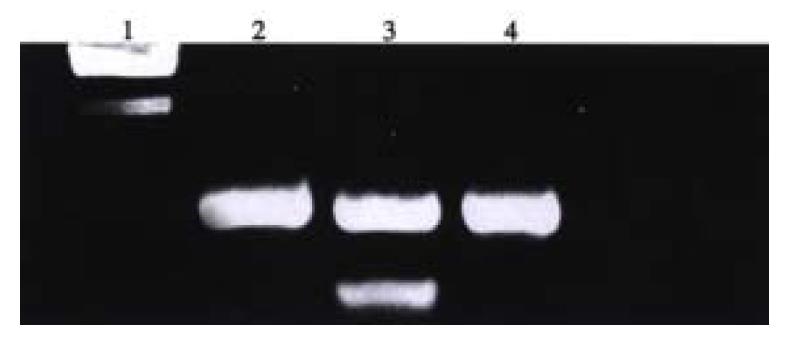
Figure 1 Electrophoresis pattern of pLXSN-U6 sense, antisense VEGF plasmid digested by Bam HI.
Lane 1: λ DNA Hind III Marker; Lane 2: pLXSN digested by Bam HI; Lane 3: pLXSN-U6 sense VEGF digested by Bam HI; Lane 4: pLXSN-U6 antisense VEGF digested by Bam HI.
Figure 2 Detection of antisense VEGF RNA expression by RNase protection assay.
Lane 1: Hybridization with total RNA from SMMC-7721 antisense clone showed 200 bp antisenseVEGF RNA; Lane 2: Hybridization with total RNA from SMMC-7721 sense clone showed no positive band; Lane 3: Hybridization with total RNA from SMMC-7721 cells showed no positive band.
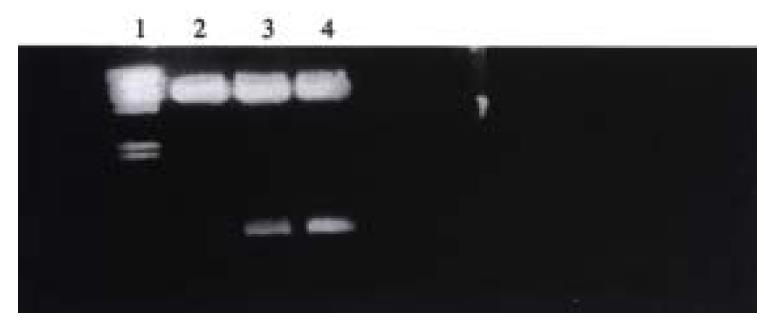
Figure 3 PCR amplification of genomic DNA from SMMC-7721 antisense, sense VEGF clone.
Lane 1: Marker; Lane 2: SMMC-7721/sense VEGF clone showed of neo gene 790 bp; Lane 3: SMMC-7721/antisense VEGF clone showed neo gene 790 bp, U6 cassette 260 bp; Lane 4: SMMC-7721/pLXSN clone showed neo gene 790 bp
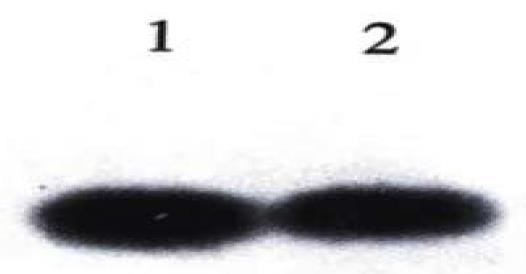
Figure 4 Genomic analysis of SMMC-7721/U6 antisense VEGF, SMMC-7721/U6 sense VEGF clones.
Lane 1: SMMC-7721/U6 sense VEGF clone; Lane 2: SMMC-7721/U6 antisense VEGF clone.
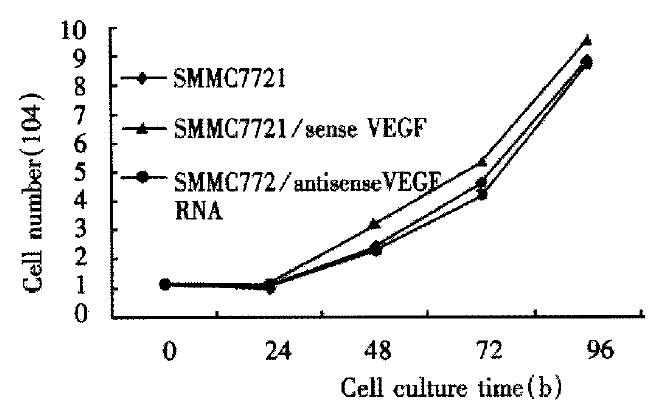
Figure 5 Proliferation curves of parental SMMC-7721 cells and antisense-VEGF, sense-VEGF cell lines.
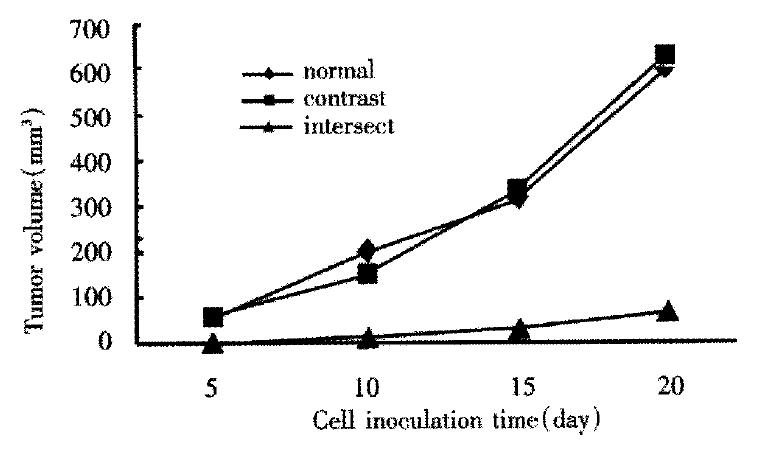
Figure 6 Tumorgenicity of antisense VEGF SMMC-7721 in nude mice.
- Citation: Tang YC, Li Y, Qian GX. Reduction of tumorigenicity of SMMC-27721 hepatoma cells by vascular endothelial growth factor antisense gene therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(1): 22-27
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i1/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i1.22