Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2022; 28(25): 2994-3000
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2994
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2994
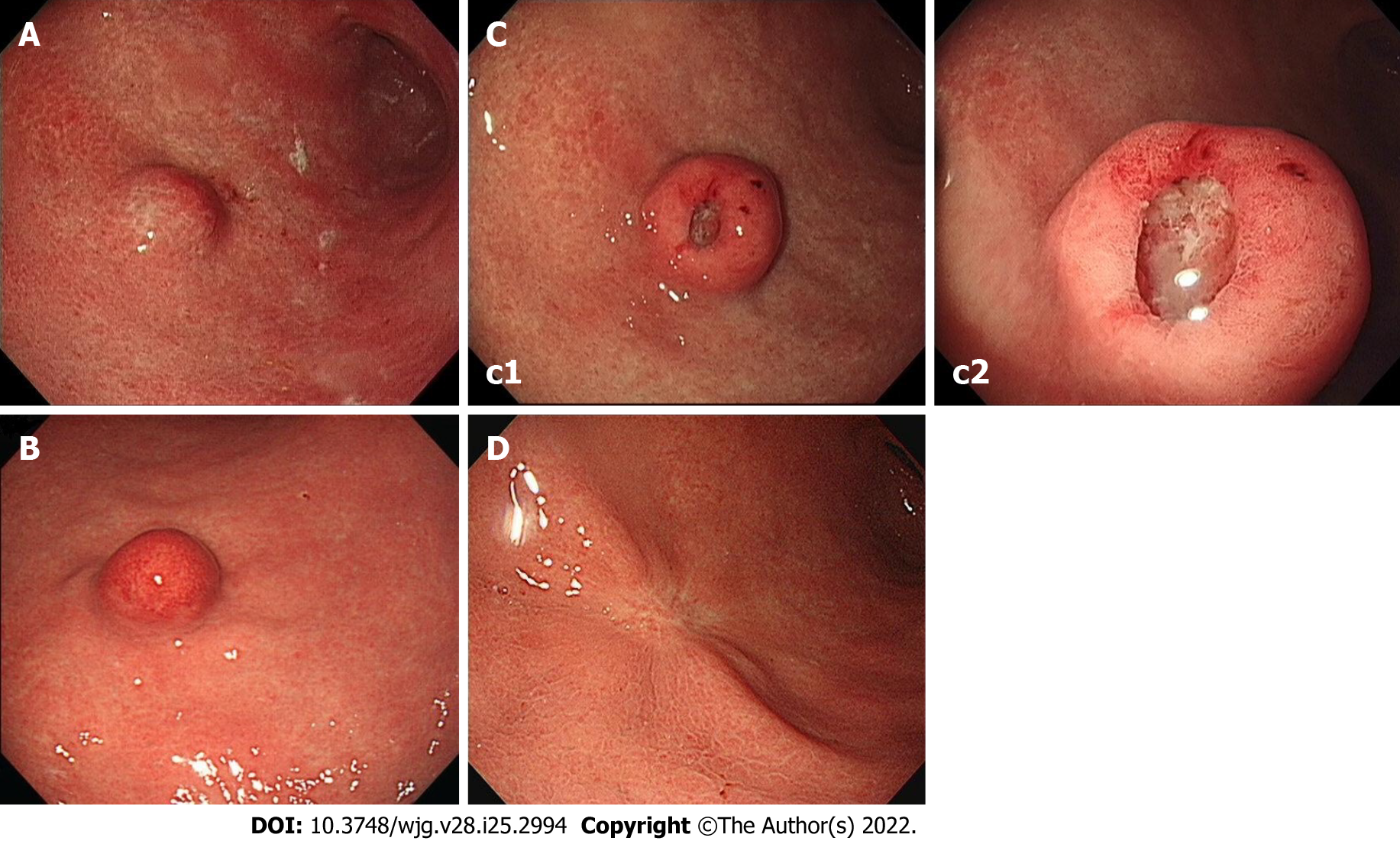
Figure 1 Endoscopy images.
A: Initial endoscopic image showing a 15 mm-sized submucosal tumor-like elevated lesion with normally appearing mucosa at the great curvature side of the proximal part of gastric antrum; B: Endoscopic image obtained 3 years later showing the tumor had not changed in size but that marked erythema had developed on overlying mucosa; C: Endoscopic image (c2 shows a higher magnification image of the mass) obtained 4 years after initial examination [immediately before endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)] showing the tumor had increased in size to 18 mm and developed a 5-mm-sized central ulcer and overlying reddish mucosa of fine granularity; D: Endoscopic image obtained approximately 2.5 years after ESD showing post-ESD scarring.
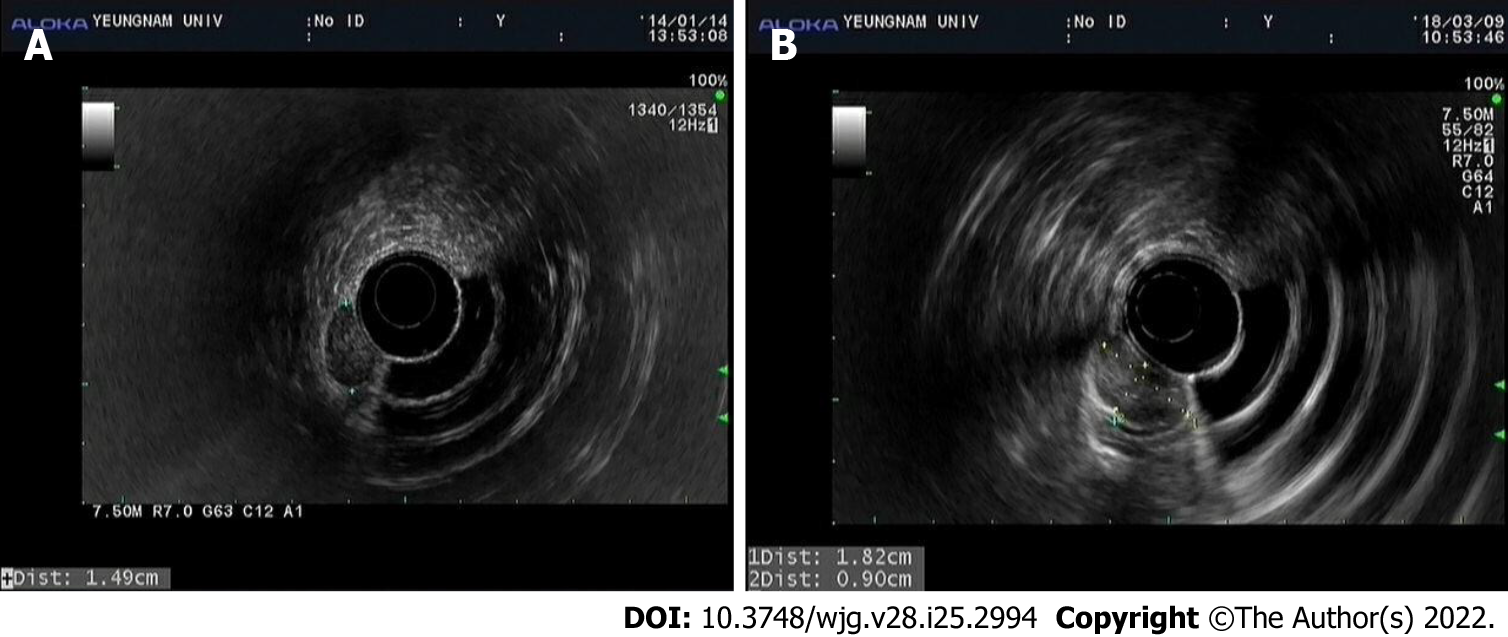
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound images.
A: Initial endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) image showing a well-circumscribed homogeneous and hypoechogenic mass measuring about 15 mm × 7 mm originating from the second sonographic layer with associated subtle obliteration of the third sonographic layer; B: EUS image obtained 4 years after the initial examination showing a well-circumscribed, hypoechogenic mass of greater size (18 mm × 9 mm) with slightly more heterogeneous echogenicity, and that the mass originated from the second sonographic layer with associated subtle obliteration of the third sonographic layer.
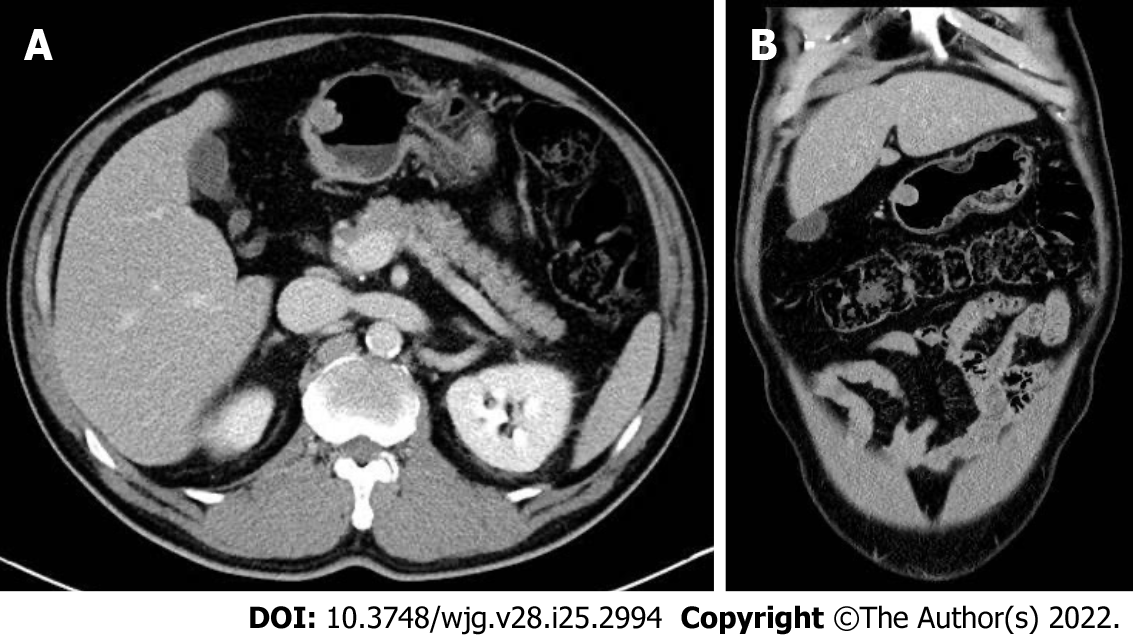
Figure 3 Abdominal computed tomography images.
Initial axial (A) and coronal (B) computed tomography images showing a 15 mm protruding intraluminal mass at gastric antrum.
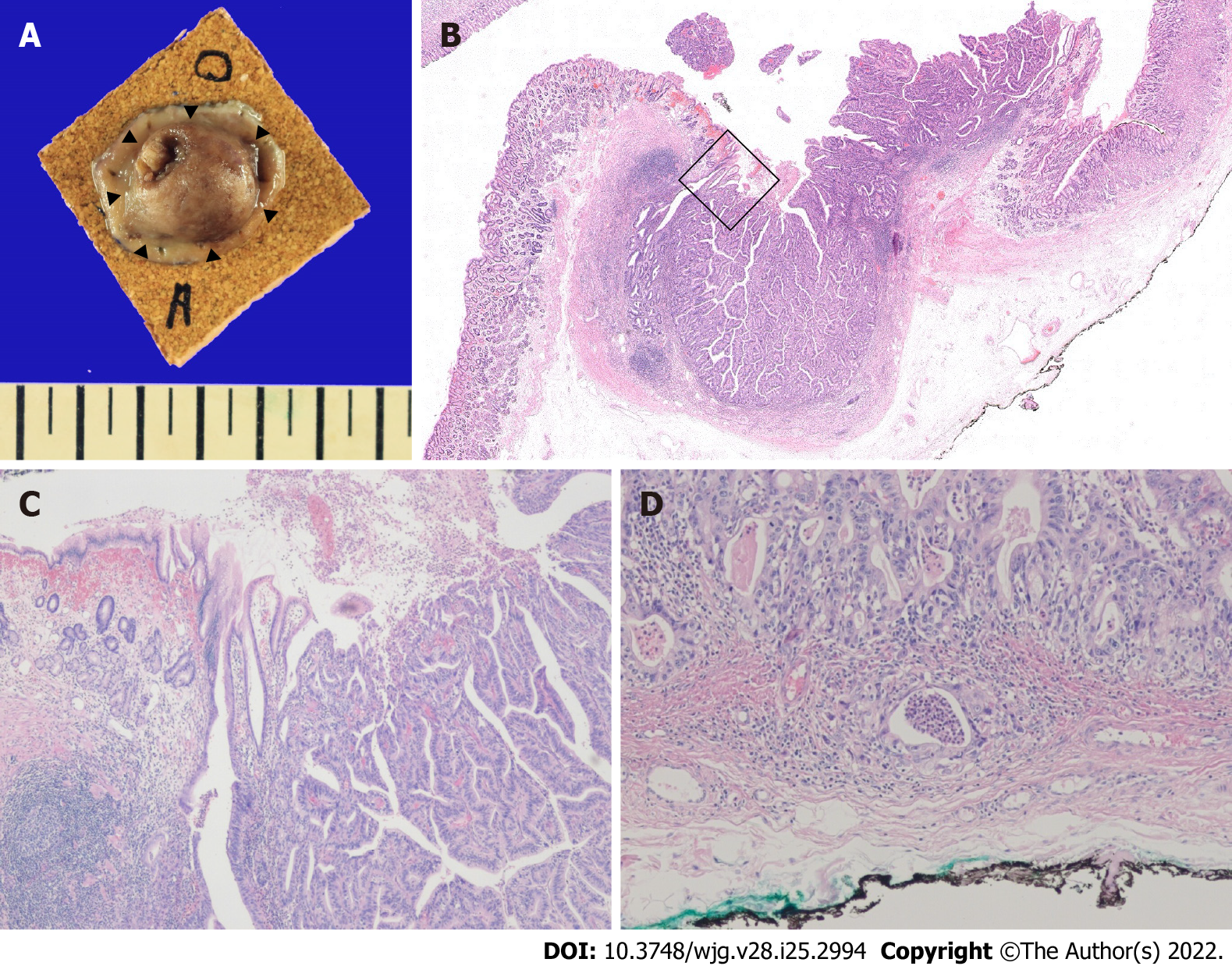
Figure 4 Pathology of the endoscopically resected lesion.
A: Gross appearance of the resected lesion, which had negative lateral margins. The black triangles indicate the border of the cancerous region; B: Hematoxylin & eosin stained section showing gastric wall mucosal layer elevation by the adenocarcinoma, central erosion, and exposed tumor cells (original magnification × 10); C: Microscopic finding of the boxed area in Figure B showing the periphery of the tumor mass, which demonstrated moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (original magnification × 40); D: Microscopic finding of the vertical resection margin showing penetration of the muscularis mucosa and minute invasion of submucosa (depth of invasion 169 μm) by tumor cells (original magnification × 100).
- Citation: Cho JH, Lee SH. Early gastric cancer presenting as a typical submucosal tumor cured by endoscopic submucosal dissection: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(25): 2994-3000
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i25/2994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2994