Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2021; 27(36): 6110-6127
Published online Sep 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i36.6110
Published online Sep 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i36.6110
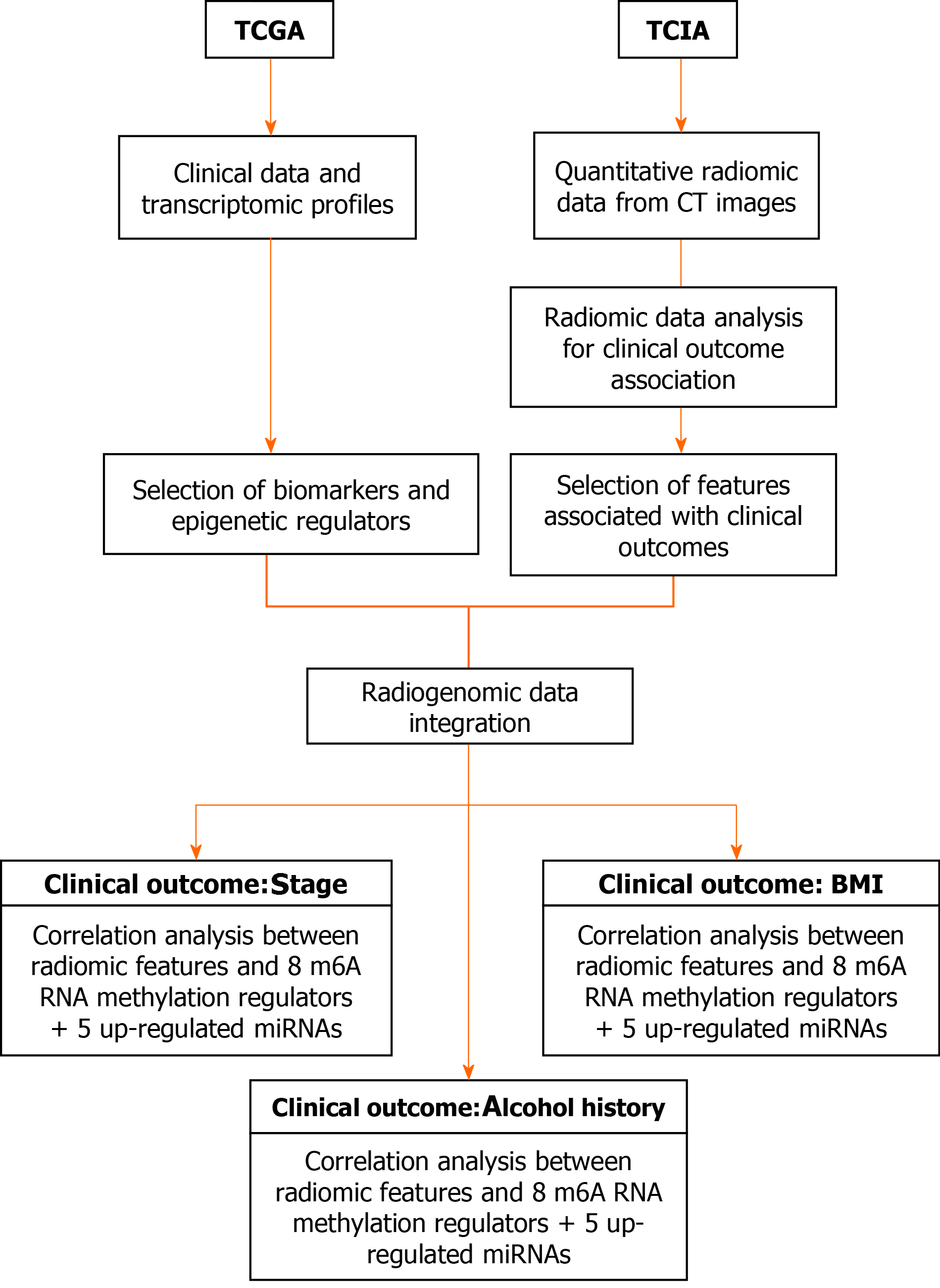
Figure 1 Flowchart reporting the organization of data and analyses in the study.
BMI: Body mass index; CT: Computed tomography; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; TCIA: The Cancer Imaging Archive.
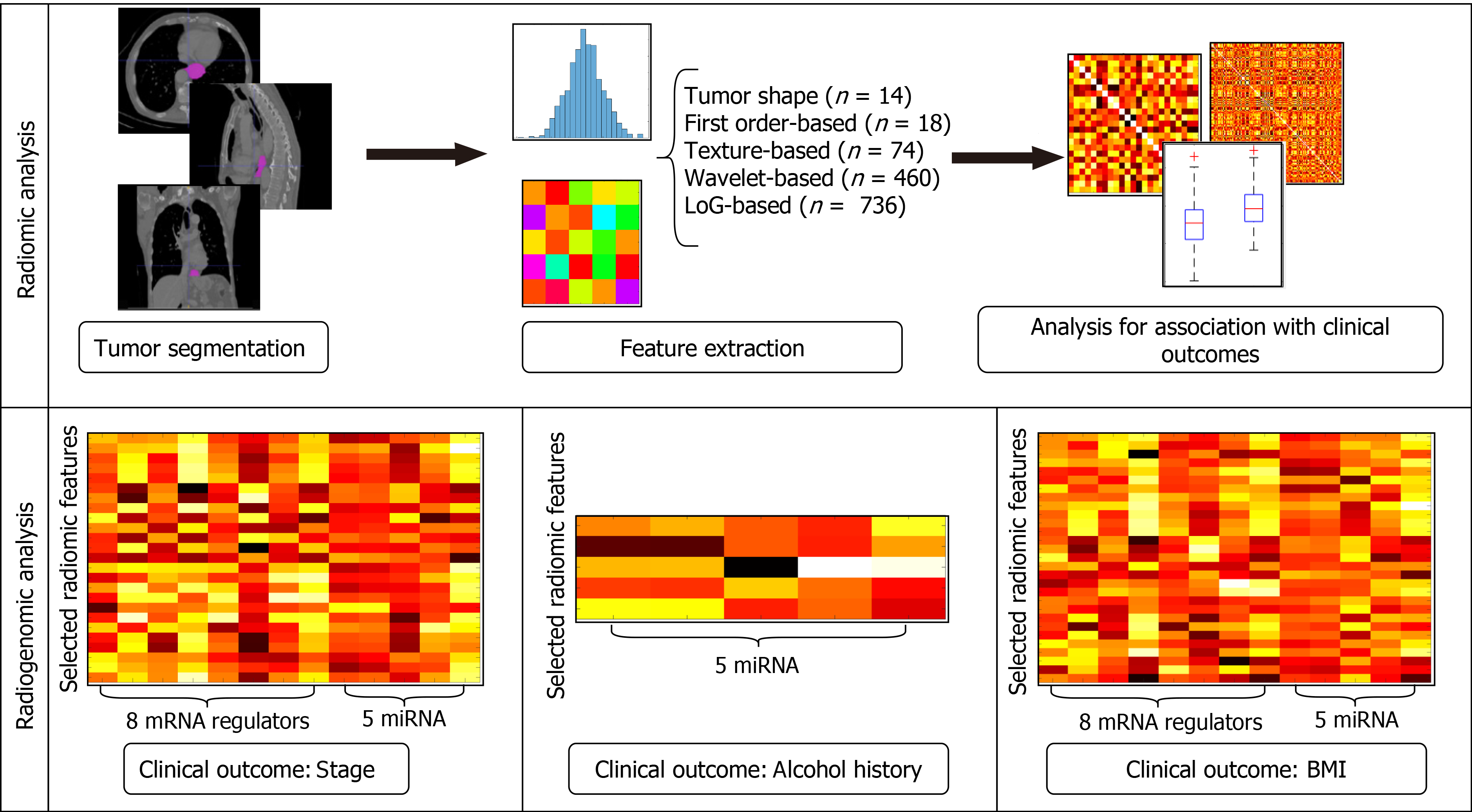
Figure 2 Workflow of radiogenomic analysis implemented in the study.
On the first row the radiomic analysis steps. On the second row the radiogenomic analysis for each clinical outcome. BMI: Body mass index; miRNA: MicroRNA; mRNA: Messenger RNA.
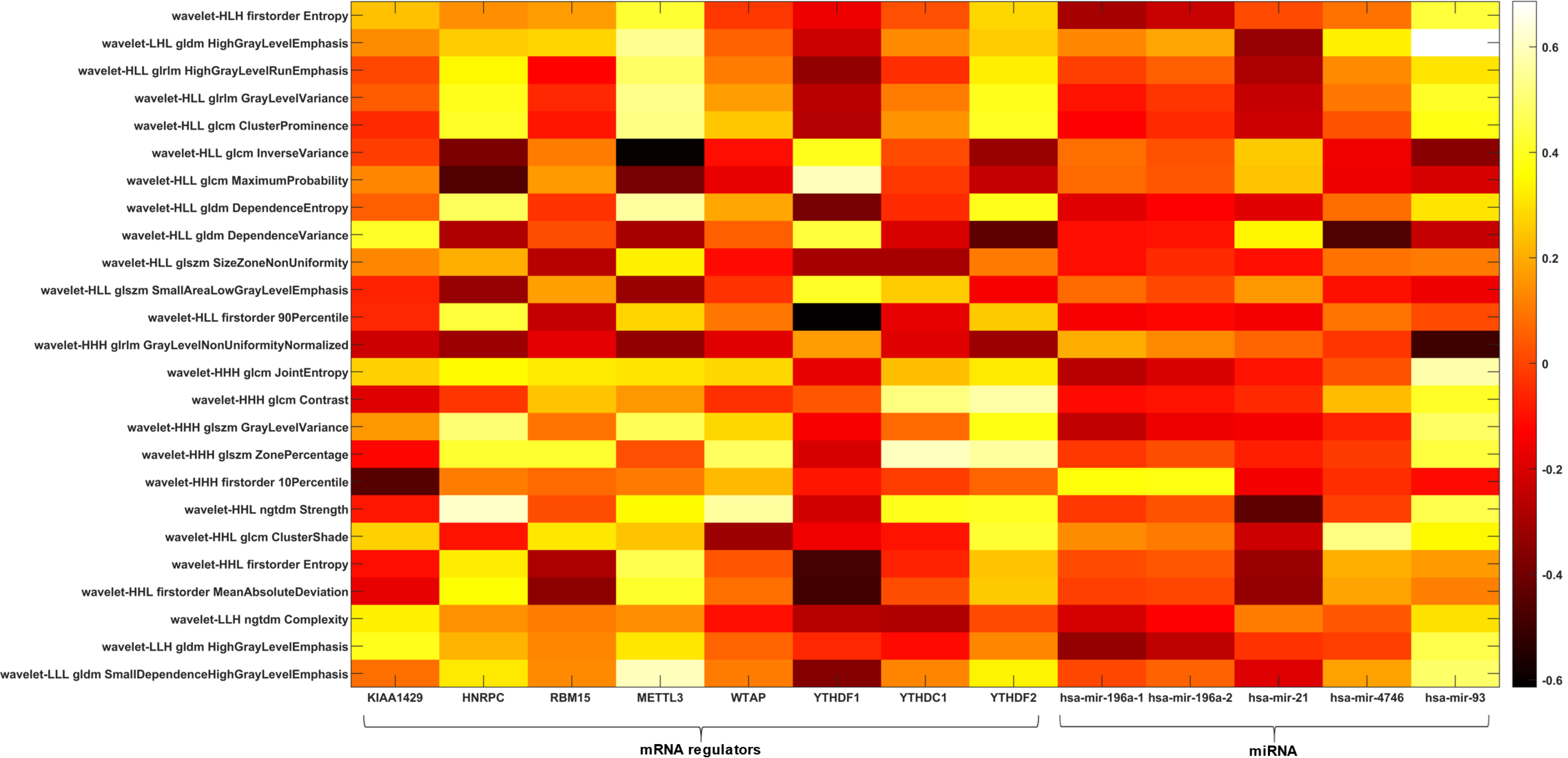
Figure 3 Radiogenomic analysis using stage as clinical outcome.
Heatmap depicting the correlation matrix between transcriptomic features and radiomic features significantly associated with stage. GLCM: Gray level co-occurrence matrix; GLDM: Gray level dependence matrix; GLRLM: Gray level run length matrix; GLSZM: Gray level size zone matrix; H: High-pass filter; L: Low-pass filter; NGTDM: Neighboring gray tone difference matrix.
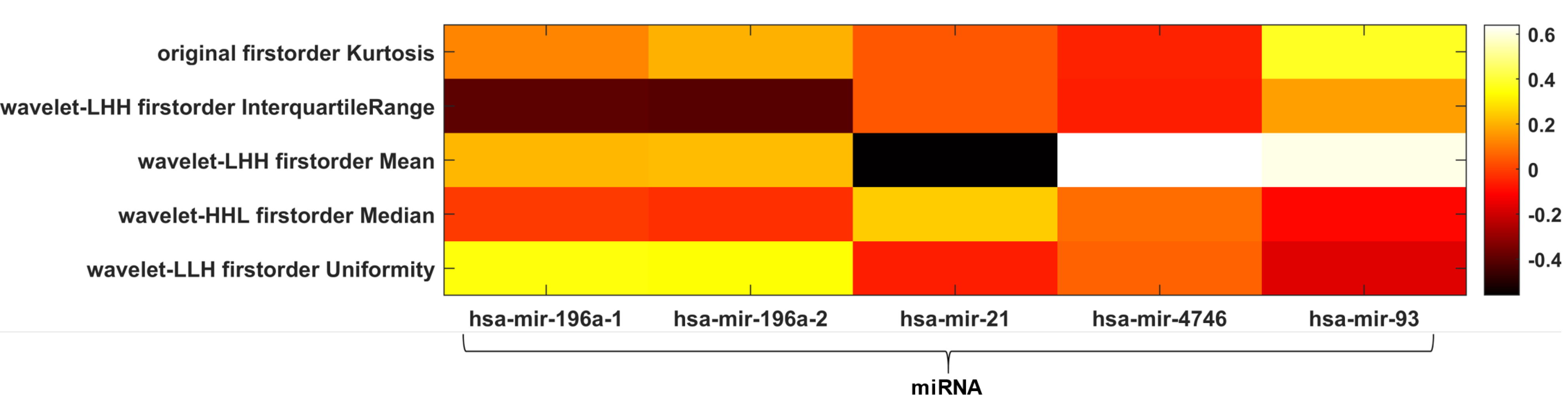
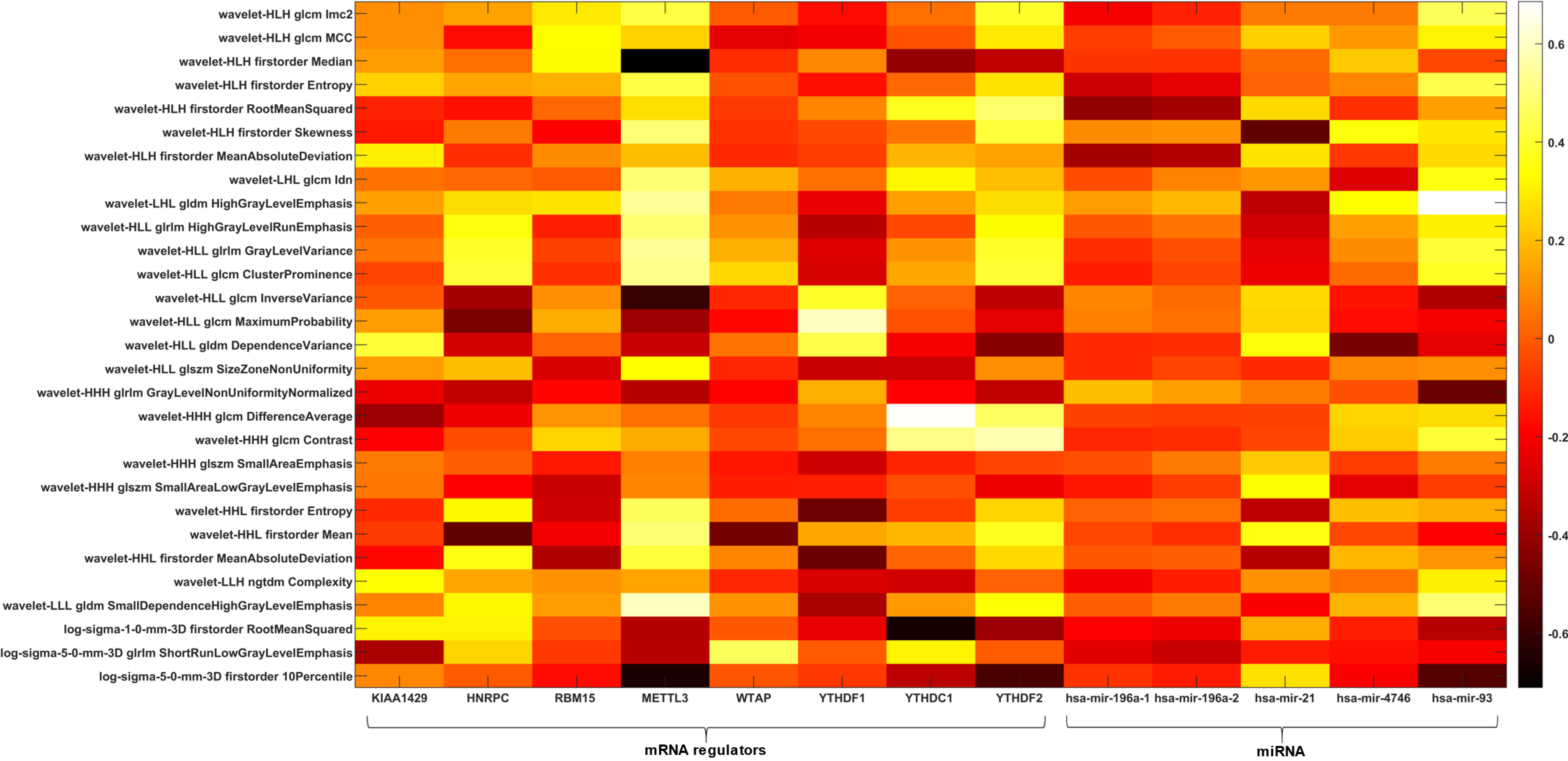
Figure 4 Radiogenomic analysis using alcohol history as clinical outcome.
Heatmap depicting the correlation matrix between transcriptomic features and radiomic features significantly associated with alcohol history. H: High-pass filter; L: Low-pass filter; miRNA: MicroRNA.
Figure 5 Radiogenomic analysis using body mass index as clinical outcome.
Heatmap depicting the correlation matrix between transcriptomic features and radiomic features significantly associated with body mass index. GLCM: Gray level co-occurrence matrix; GLDM: Gray level dependence matrix; GLRLM: Gray level run length matrix; GLSZM: Gray level size zone matrix; H: High-pass filter; L: Low-pass filter; miRNA: MicroRNA; mRNA: Messenger RNA; NGTDM: Neighboring gray tone difference matrix.
- Citation: Brancato V, Garbino N, Mannelli L, Aiello M, Salvatore M, Franzese M, Cavaliere C. Impact of radiogenomics in esophageal cancer on clinical outcomes: A pilot study. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(36): 6110-6127
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i36/6110.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i36.6110