Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2021; 27(28): 4667-4686
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4667
Published online Jul 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4667
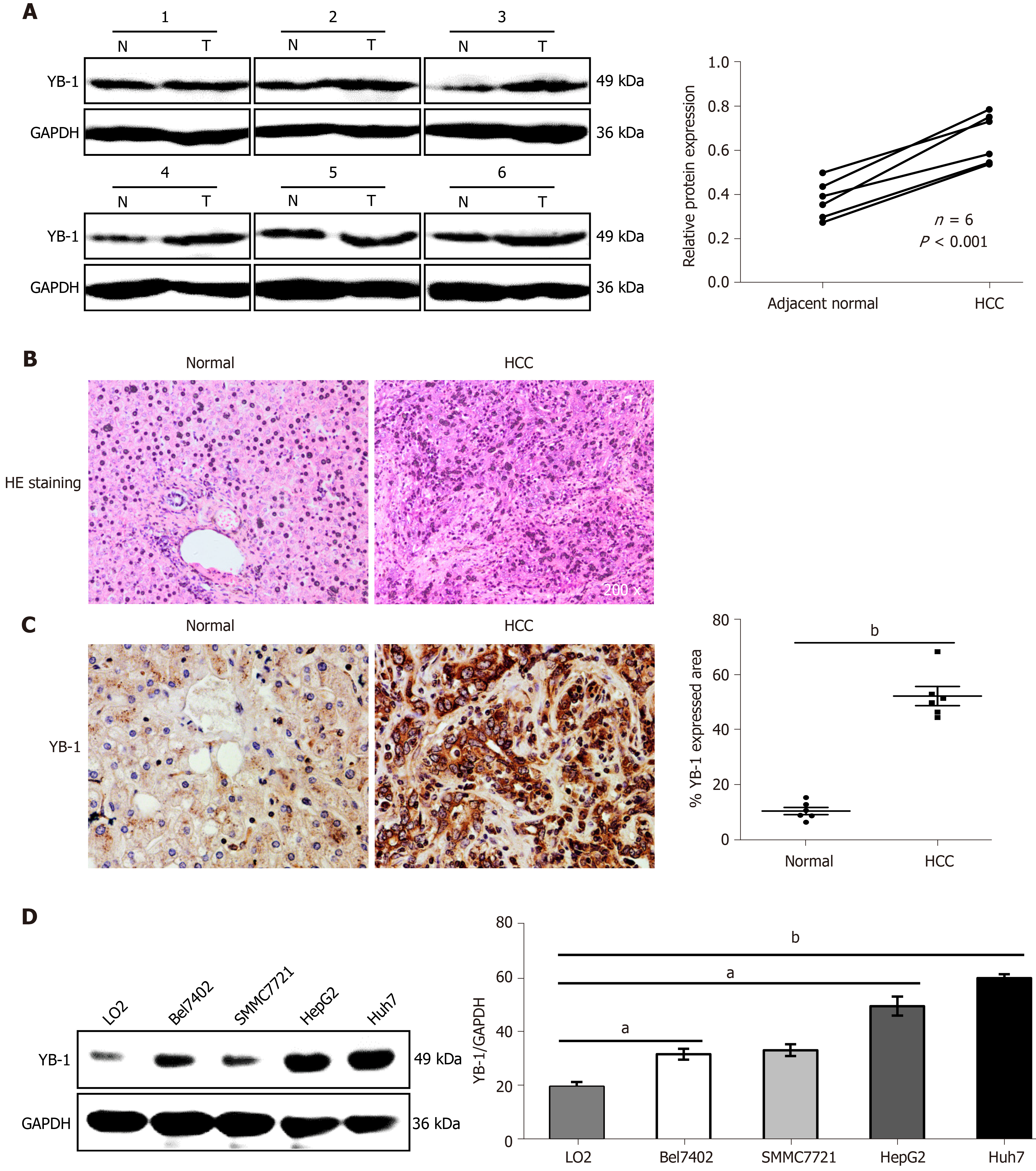
Figure 1 Increased expression of Y-box binding protein 1 in the liver tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and cell lines.
A: The protein expression levels of Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) in 6 pairs of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) liver tissues and their corresponding nontumor tissues were detected by Western blot analysis. Paraffin-embedded sections of liver tissues were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) (B), and immunohistochemistry staining of YB-1 (C) was performed in the 2 groups; D: Western blot analysis showed YB-1 protein expression in one normal (N) liver cell line and four HCC cell lines. YB-1 protein levels (normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)) were measured by scanning densitometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups. T: Tumor.
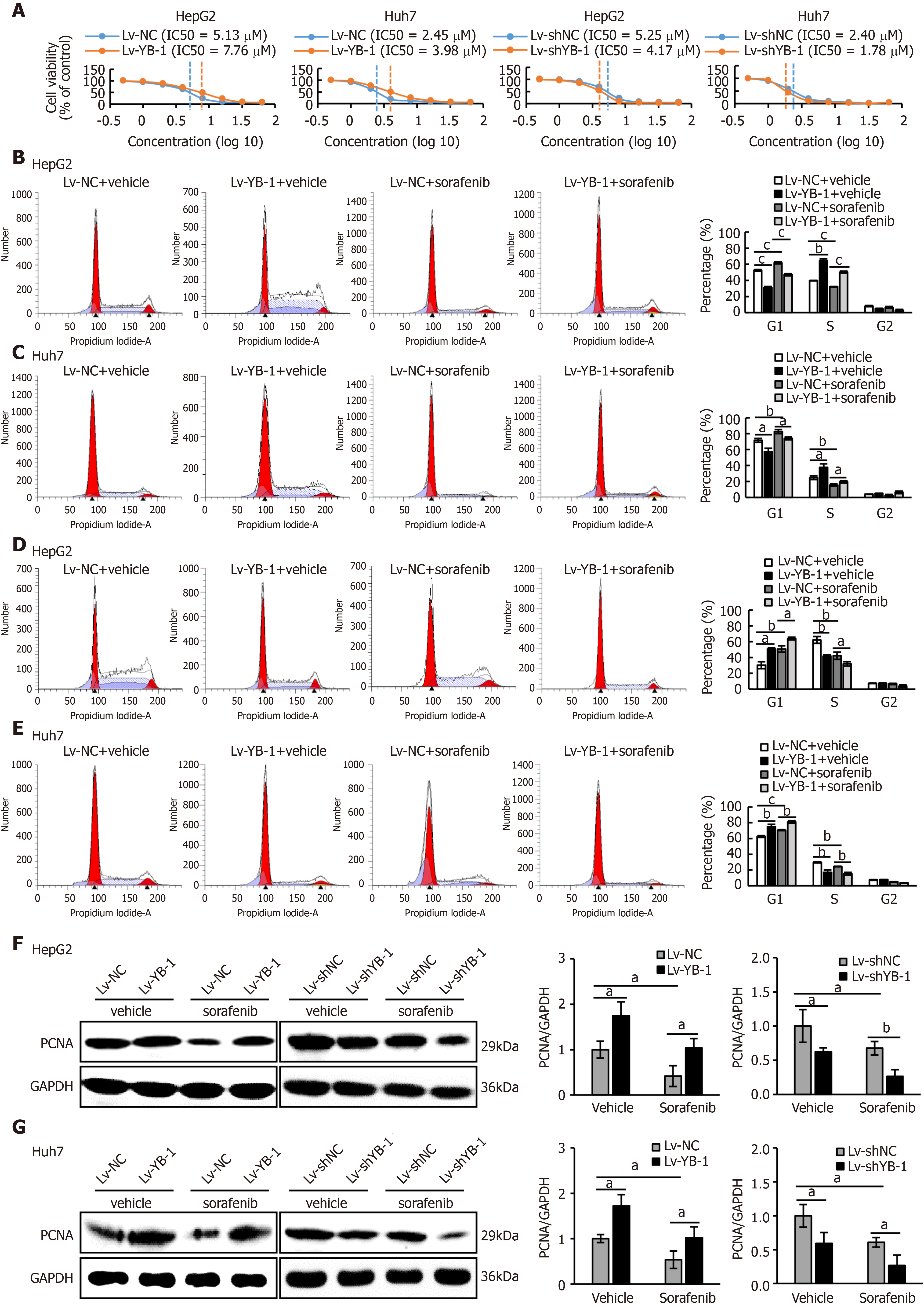
Figure 2 Y-box binding protein 1 offsets the effect of sorafenib on proliferation in hepatoma cell lines.
A: The IC50 values of sorafenib in HepG2 and Huh7 cells infected with lentivirus encoding the Y-box binding protein 1 (lv-YB-1) or lentivirus encoding short hairpin RNA targeting YB-1 (Lv-shYB-1) were detected by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay; B-E: Flow cytometry was conducted to perform cell cycle distribution analysis of the cells infected with the empty lentivirus vector as a negative control (Lv-NC) ± sorafenib vs Lv-YB-1 ± sorafenib groups (B, C) and lentivirus containing non-specific short hairpin RNA as a negative control (Lv-shNC) ± sorafenib vs Lv-shYB-1 ± sorafenib groups (D, E); F, G: Western blot analysis showed proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) protein expression in the Lv-NC ± sorafenib vs Lv-YB-1 ± sorafenib groups and Lv-shNC ± sorafenib vs Lv-shYB-1 ± sorafenib groups of HepG2 (F) and Huh7 (G) cells. PCNA protein levels (normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)) were measured by scanning densitometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups.
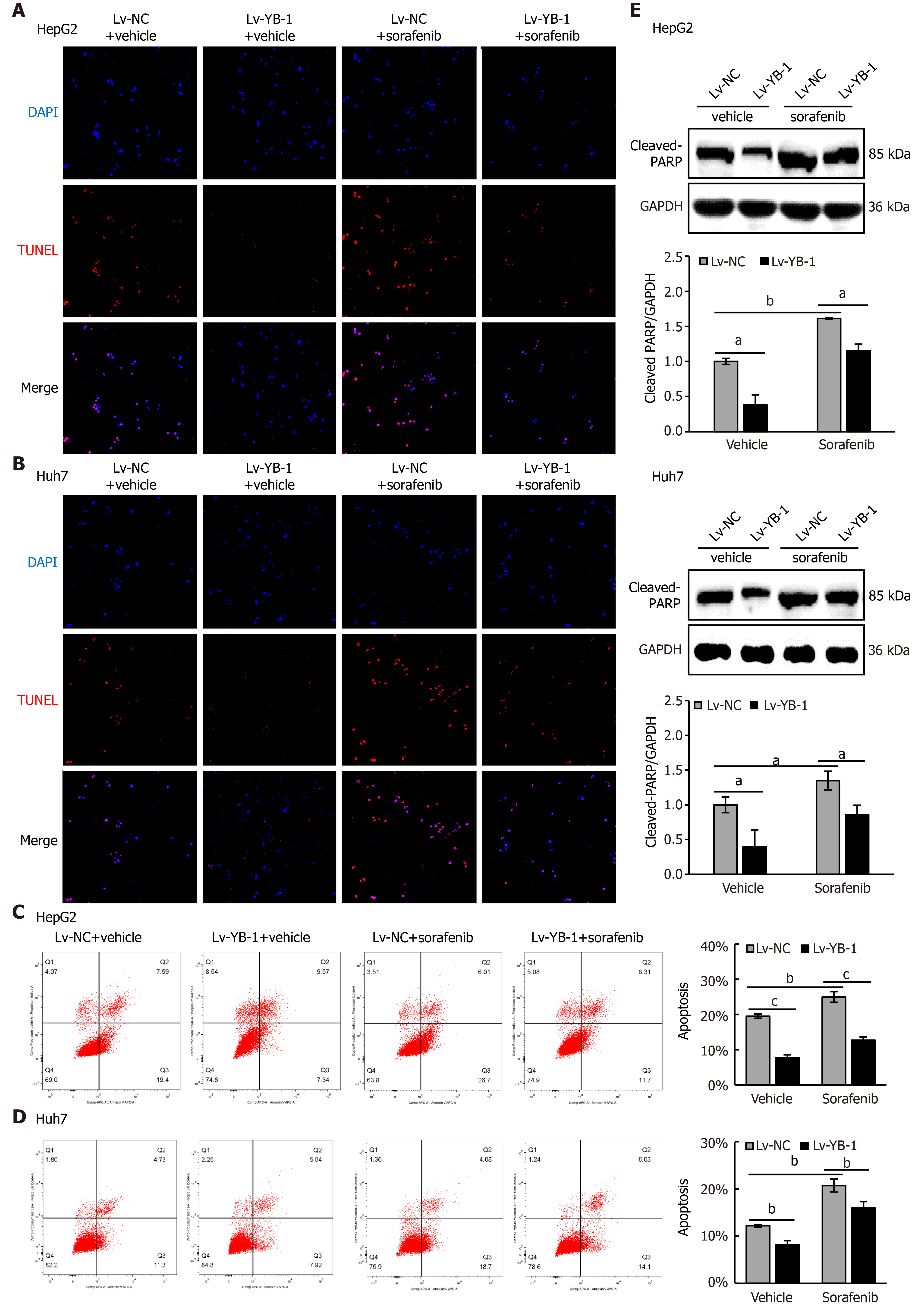
Figure 3 Y-box binding protein 1 suppresses apoptosis induced by sorafenib treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
A-D: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and flow cytometry were employed to analyze apoptosis in the cells infected with empty lentivirus vector as a negative control (Lv-NC) ± sorafenib vs lentivirus with Y-box binding protein 1 (Lv-YB-1) ± sorafenib groups; E, F: Western blot analysis showed cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) protein expression in the Lv-NC ± sorafenib/Lv-YB-1 ± sorafenib groups. Cleaved PARP protein levels (normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)) were measured by scanning densitometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups. DAPI: 4’6’-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride.
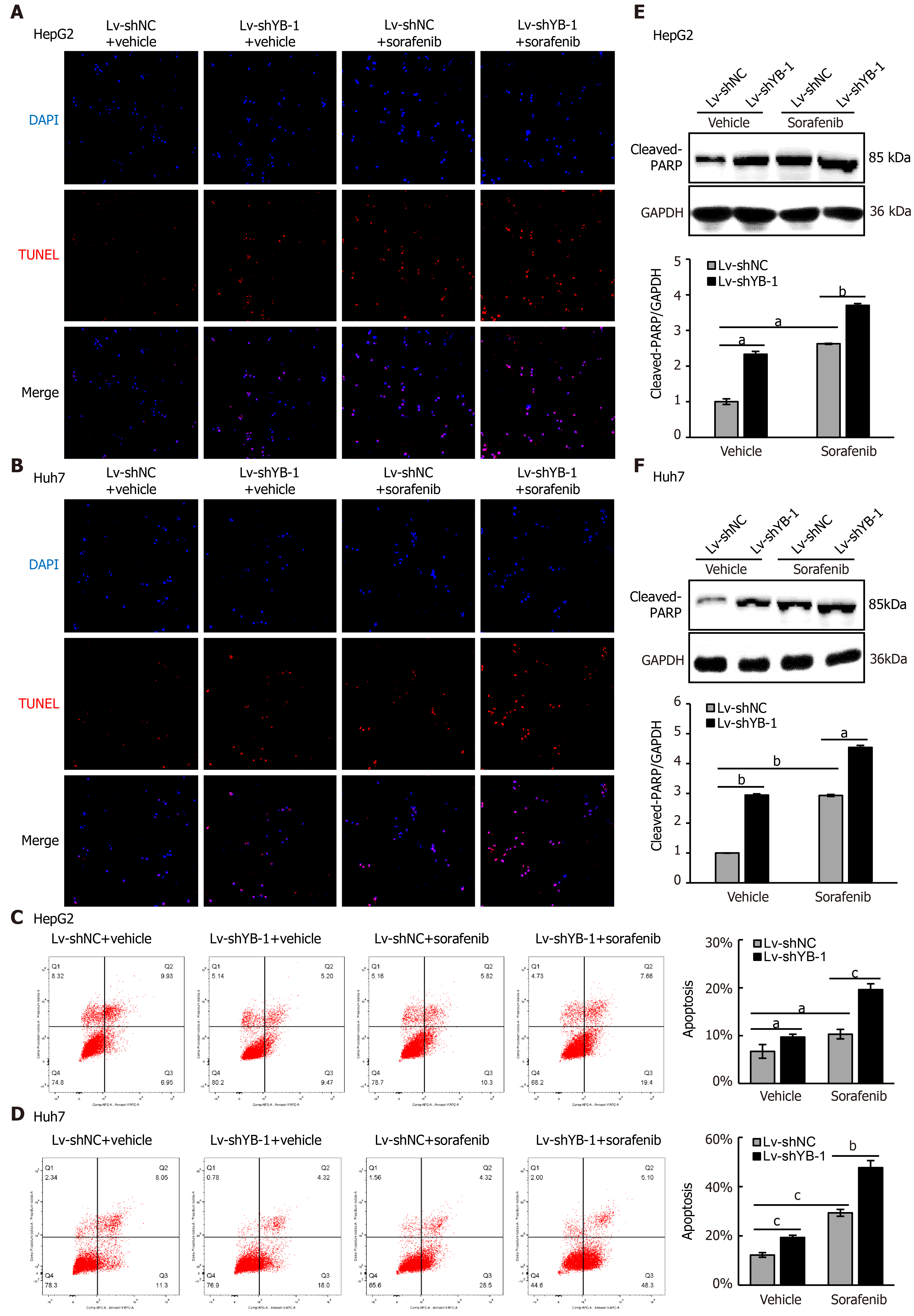
Figure 4 Y-box binding protein 1 suppresses apoptosis induced by sorafenib treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
A-D: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and flow cytometry were employed to analyze apoptosis in the cells infected with lentivirus encoding non-specific short hairpin RNA as a negative control (Lv-shNC) ± sorafenib vs lentivirus with short hairpin RNA targeting the Y box binding protein 1 (Lv-shYB-1) ± sorafenib groups; E, F: Western blot analysis showed cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) protein expression in the Lv-shNC ± sorafenib/Lv-shYB-1±sorafenib groups. Cleaved PARP protein levels (normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)) were measured by scanning densitometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups.
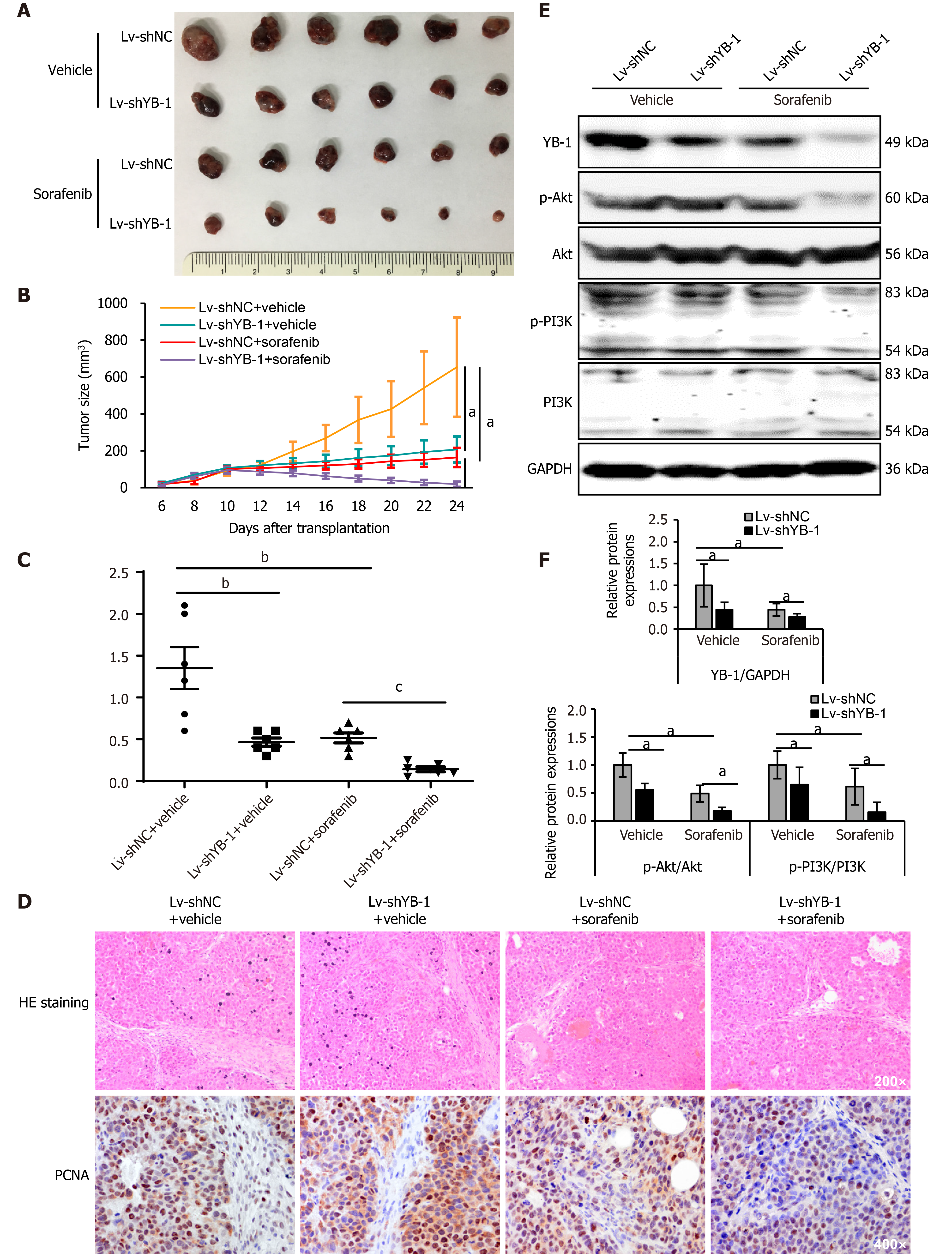
Figure 5 Sorafenib efficiency improves after Y-box binding protein 1 knockdown in vivo.
A: The morphologies of collected tumors in subcutaneous Huh7 xenografts in nude mice; B: Tumor growth curves; C: Tumor weights were measured after collection; D: Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and immunohistochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen; E, F: Western blot analysis showed Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1), phosphorylated protein kinase B (p-Akt), protein kinase B (Akt), phosphorylated phosphoinositide-3-kinase (p-PI3K), and phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) expression in cells infected with lentivirus encoding non-specific short hairpin RNA as a negative control (Lv-shNC) ± sorafenib vs lentivirus containing short hairpin RNA targeting YB-1 (Lv-shYB-1) ± sorafenib groups. p-Akt (normalized to Akt) and p-PI3K (normalized to PI3K) protein levels were measured by scanning densitometry. Protein samples derived from the same experiment and gels were processed in parallel. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
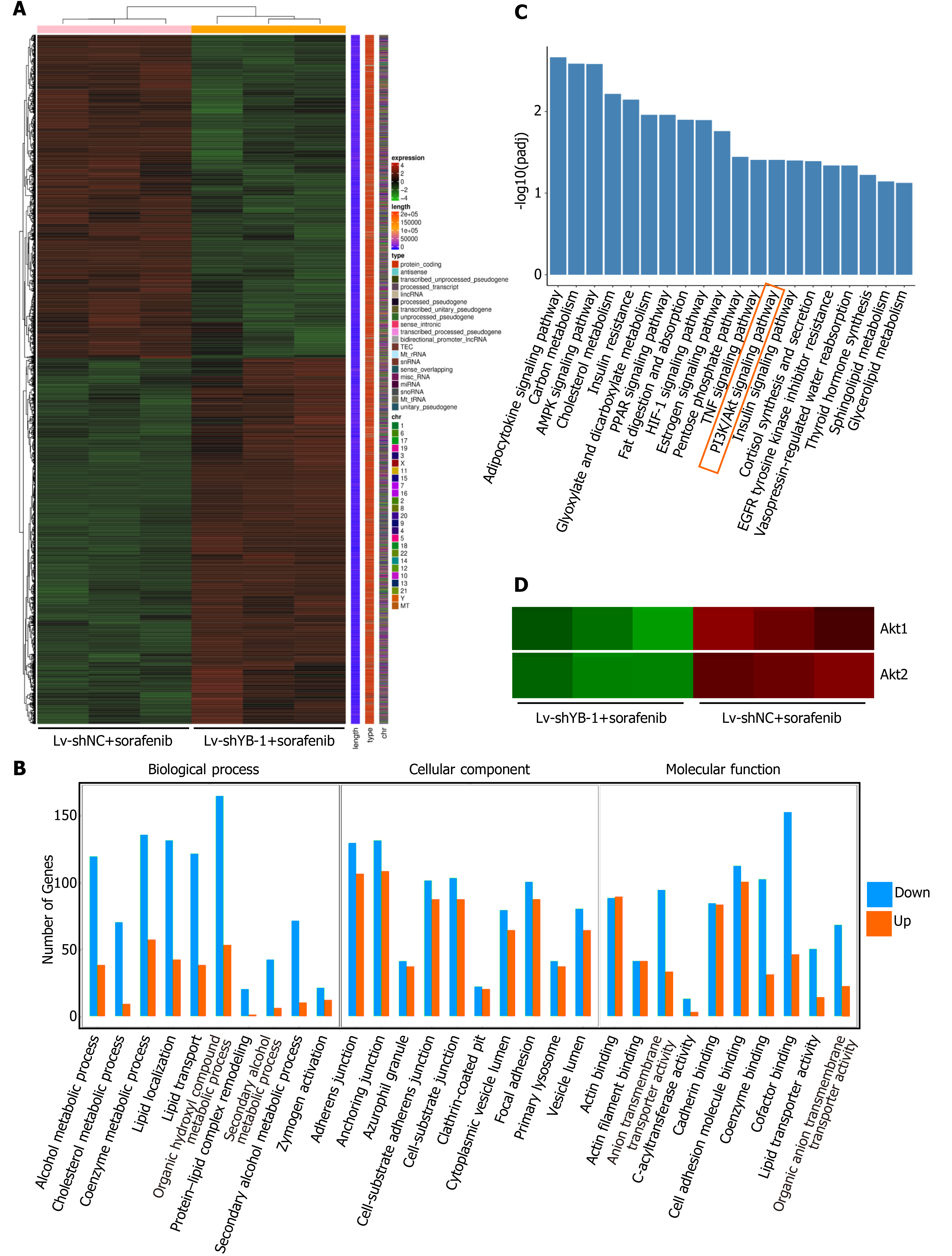
Figure 6 Digital gene expression profiling-seq analysis in HepG2 cells.
A: Heat map of the results from the cluster analysis of the digital gene expression profiling (DGE)-seq data (cells infected with: lentivirus encoding non-specific short hairpin RNA as a negative control (Lv-shNC) + sorafenib vs lentivirus encoding short hairpin RNA against Y box protein 1 (Lv-shYB-1) + sorafenib). Each column denotes the DEGs identified in our study. Each row indicates a sample. For each gene, red represents a high level of expression relative to the mean, while green expresses a low level. The scale bar is the number of standard deviations from the mean; B: Histogram of GO functional analysis for the DEGs obtained from DGE sequencing. GO terms with padj < 0.05 were thought to be notably enriched by DEGs. The y axis represents the number of genes in a GO classification category. Red represents increased expression in the Lv-shYB-1 + sorafenib group, whereas green indicates decreased expression in that group; C: Pathway enrichment analysis showed the top 20 signaling pathways in KEGG (padj < 0.05); D: mRNA expression levels of protein kinase B1 (Akt1) and protein kinase B2 (Akt2) from the DGE-seq data (Lv-shNC + sorafenib, Lv-shYB-1 + sorafenib).
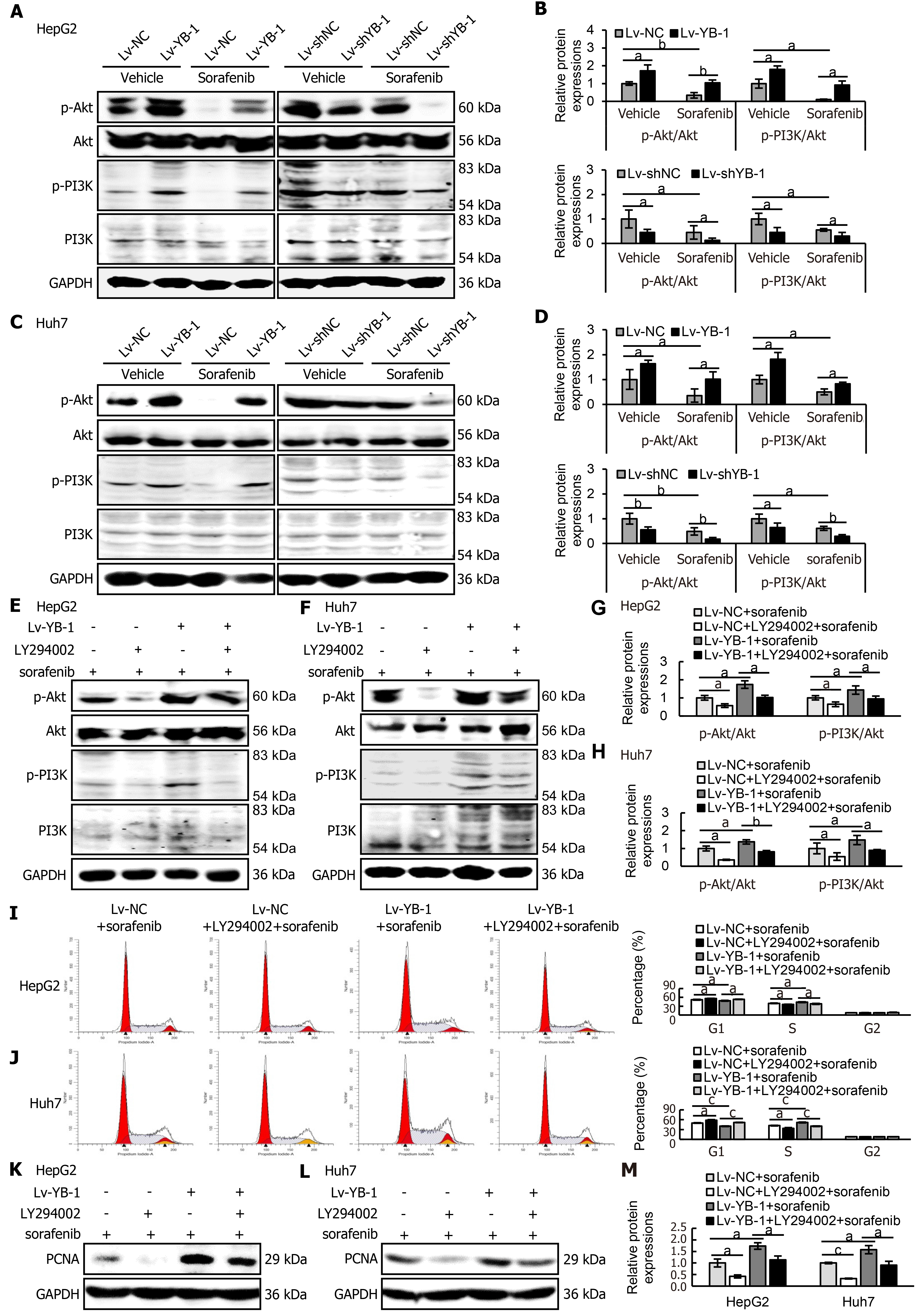
Figure 7 Y-box binding protein 1 suppresses the function of sorafenib in the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and blockade of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibits the promoting effect of YB-1 on proliferation.
A-D: The protein expression levels of phosphorylated protein kinase B (p-Akt), protein kinase B (Akt), phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), and phosphorylated PI3K (p-PI3K) were detected by Western blot analysis in cells infected with lentivirus vector as a negative control (Lv-NC)±sorafenib vs cells infected with lentivirus encoding Y-box protein 1 (Lv-YB-1) ± sorafenib groups and lentivirus encoding non-specific short hairpin RNA as a negative control (Lv-shNC)±sorafenib vs cells infected with lentivirus encoding short hairpin RNA targeting Y-box binding protein 1 (Lv-shYB-1) ± sorafenib groups of HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 (C, D) cells; E-H: Western blot analysis was also applied to evaluate the expression of p-Akt, Akt, p-PI3K and PI3K in the Lv-NC + sorafenib, Lv-NC + LY294002 + sorafenib, Lv-YB-1 + sorafenib, Lv-YB-1 + LY294002 + sorafenib groups of HepG2 (E, G) and Huh7 (F, H) cells. Protein samples derived from the same experiment and gels were processed in parallel; I, J: Flow cytometry was conducted to analyze the cell cycle distribution; K-M: Western blot analysis showed proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) protein expression, and its protein levels were measured by scanning densitometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the indicated groups.
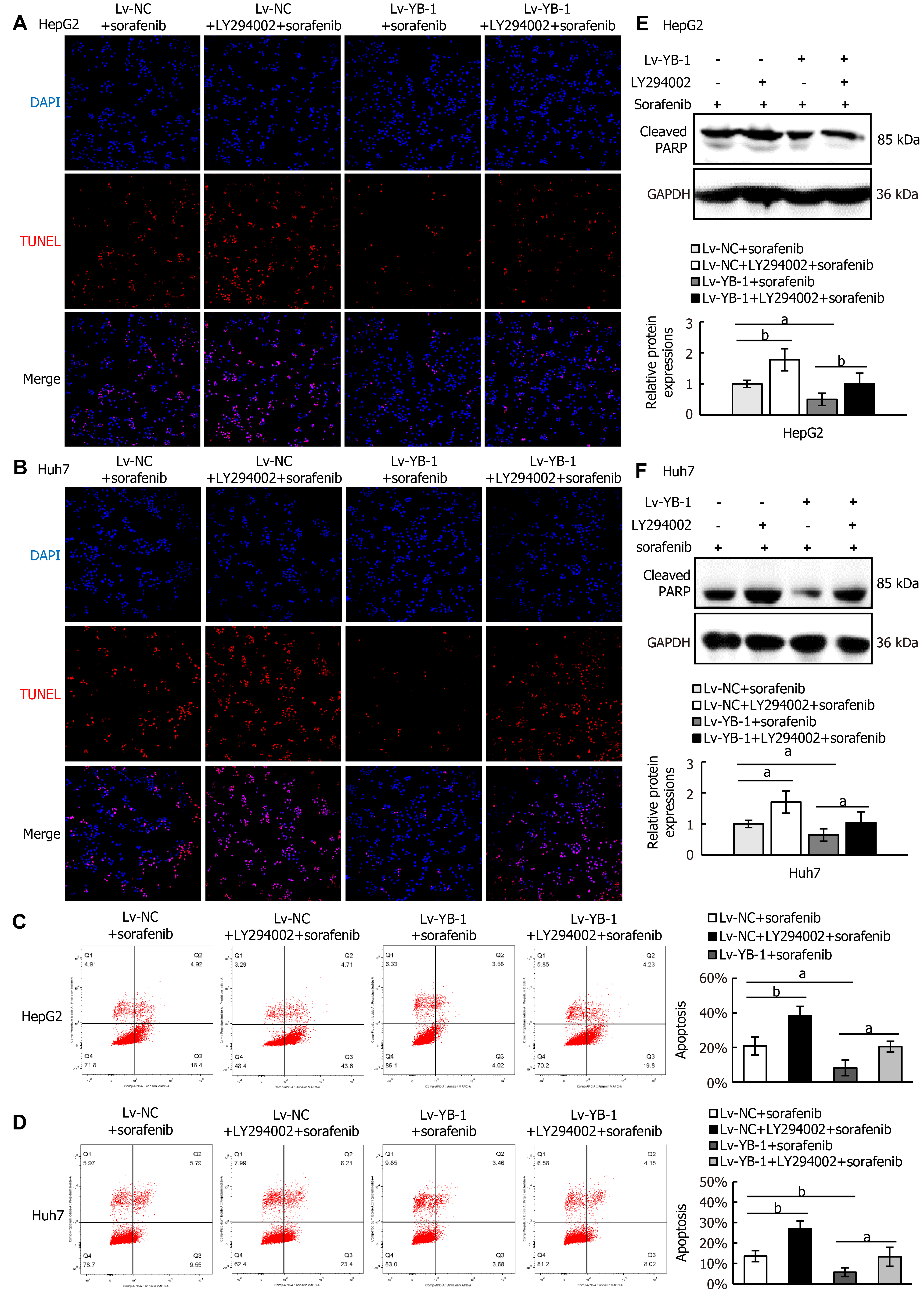
Figure 8 Blocking the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway suppresses the effect of Y-box binding protein 1 on apoptosis.
A-D: Apoptosis analysis was conducted by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining (A, B) and flow cytometry with Annexin V-APC and PI staining (C, D); E, F: Western blot analysis showed cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) protein expression. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the indicated groups. Lv: Lentivirus; NC: Negative control; YB-1: Y-box binding protein 1; DAPI: 4’6’-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Liu T, Xie XL, Zhou X, Chen SX, Wang YJ, Shi LP, Chen SJ, Wang YJ, Wang SL, Zhang JN, Dou SY, Jiang XY, Cui RL, Jiang HQ. Y-box binding protein 1 augments sorafenib resistance via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(28): 4667-4686
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i28/4667.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4667