Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2021; 27(27): 4413-4428
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4413
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4413
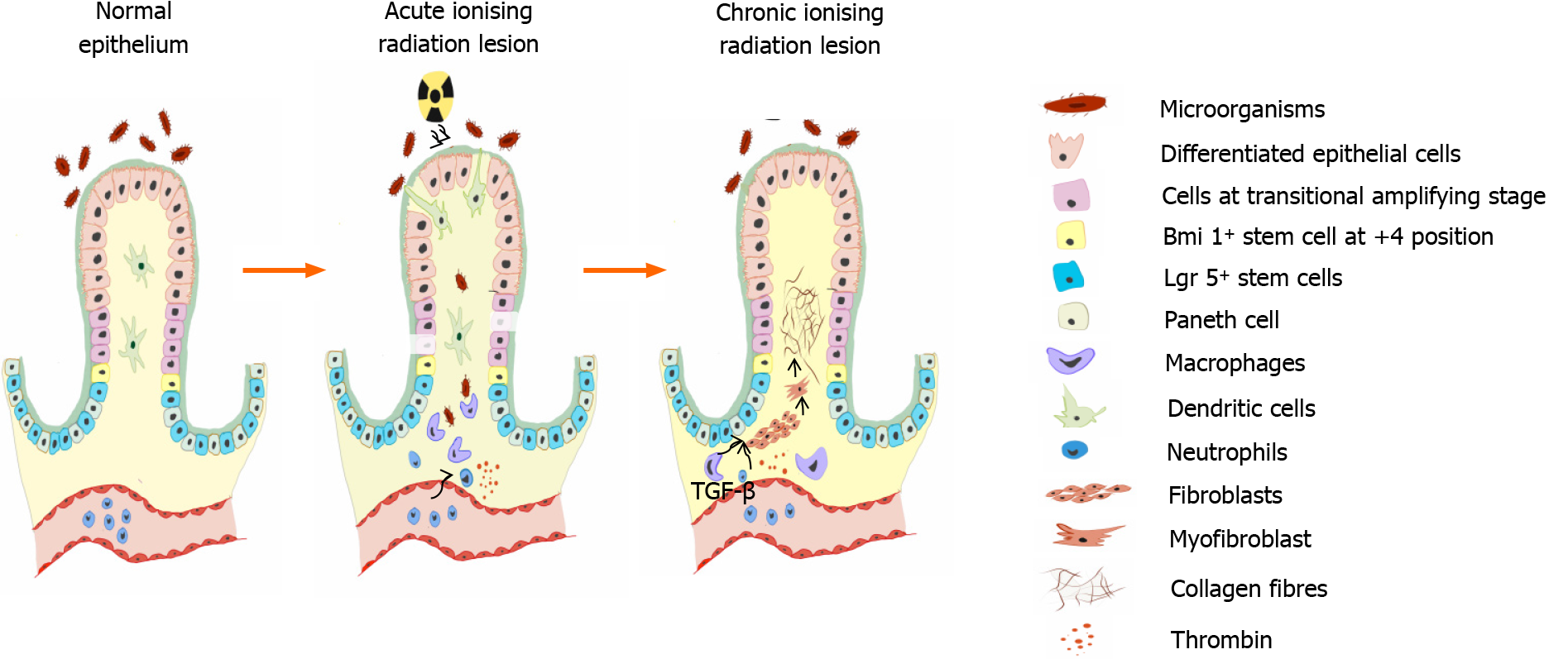
Figure 1 Representative scheme of intestinal injury induced by ionising radiation.
In a healthy gut, crypts are with intact mucosa. Lgr5+ stem cells proliferate and cells migrate upwards to provide differentiated epithelial cells of the villi. Acute lesions occur predominantly through different pathological processes: Depletion of epithelial cells due to cytotoxicity in progenitor cells and consequent apoptosis; inflammation and infiltration of the lamina propria with polymorphonuclear leukocytes and plasma cells; eosinophilic abscesses of intestinal crypts; endothelial lesions of intestinal microvascularisation with the release of thrombin and eventual oedema of the submucosa; influx of antigenic material, including gut microbiota into the lamina propria. If the submucosa modifications are not impactful, the epithelial cells regenerate, and the process resolves spontaneously. The constitutive and chronic phase comprises obliterating endarteritis with progressive reduction of parietal irrigation and consequent local ischaemia; formation and diffuse progression of mucosal and submucosal fibrosis through a local proinflammatory cytokine cascade (high levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, and transforming growth factor-β), which is promoted by macrophages, neutrophils and by the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Citation: Adapted from Costa et al[21] and Kumagai et al[23].
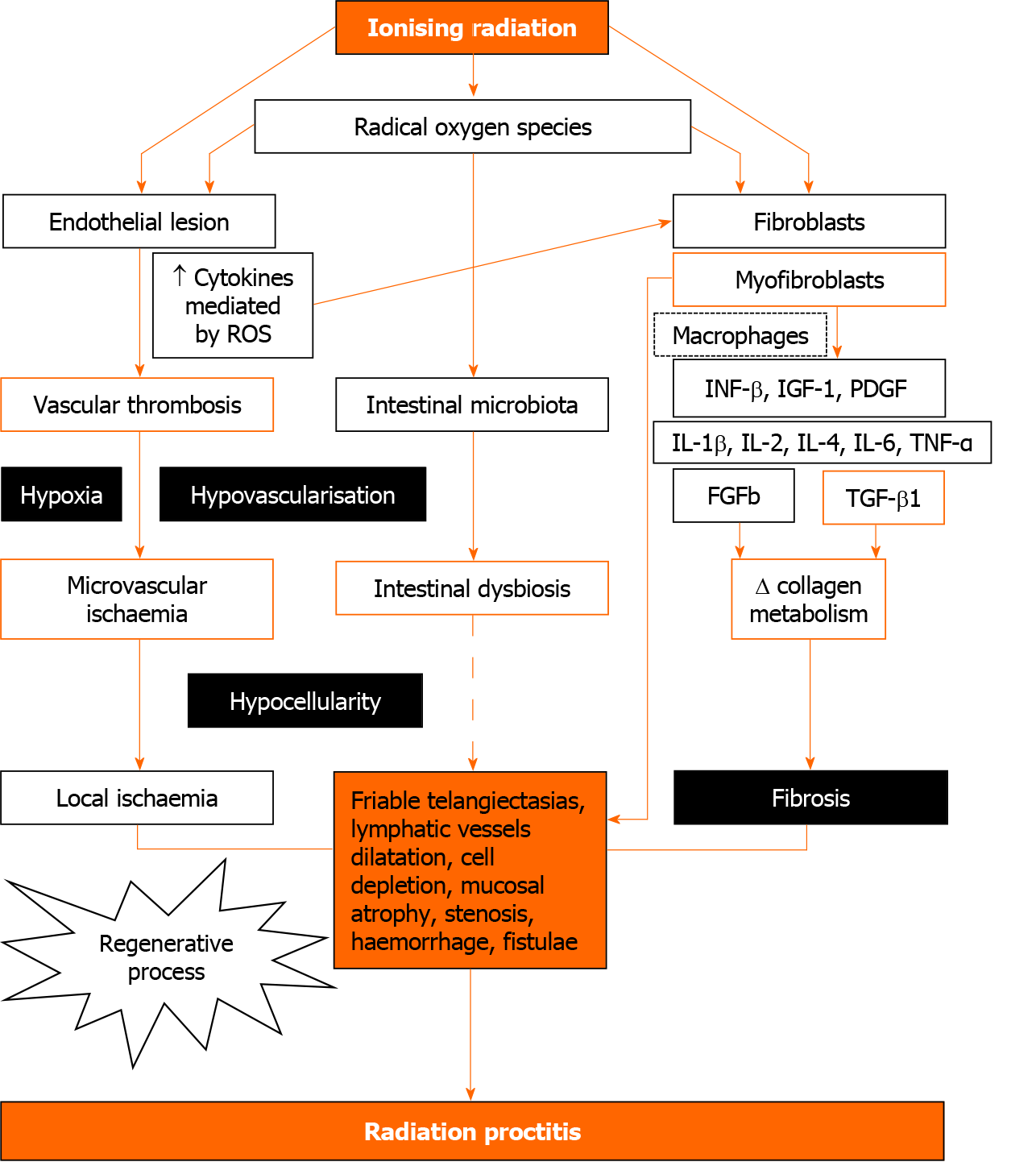
Figure 2 Representative scheme of the several pathophysiological mechanisms involved in radiation proctitis: The hypoxia/hypocel
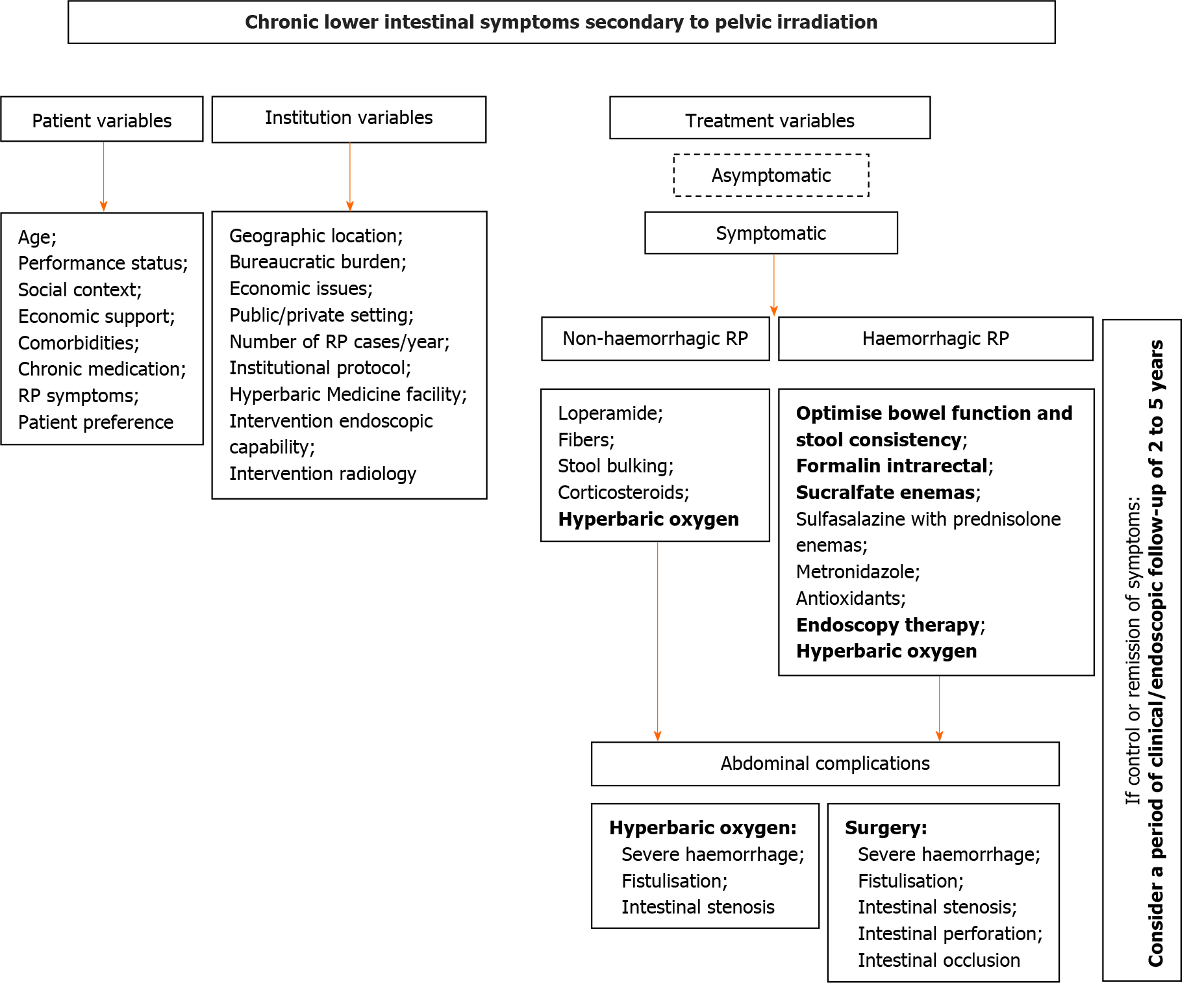
Figure 3 Suggested treatment algorithm for radiation proctitis based on variables related to the patient, institution, and the severity of the clinical context.
RP: Radiation proctitis; RT: Radiotherapy.
- Citation: Alpuim Costa D, Amaro CE, Nunes A, Cardoso JS, Daniel PM, Rosa I, Branco JV. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a complementary treatment for radiation proctitis: Useless or useful? – A literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(27): 4413-4428
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i27/4413.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4413