Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3654-3667
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3654
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3654
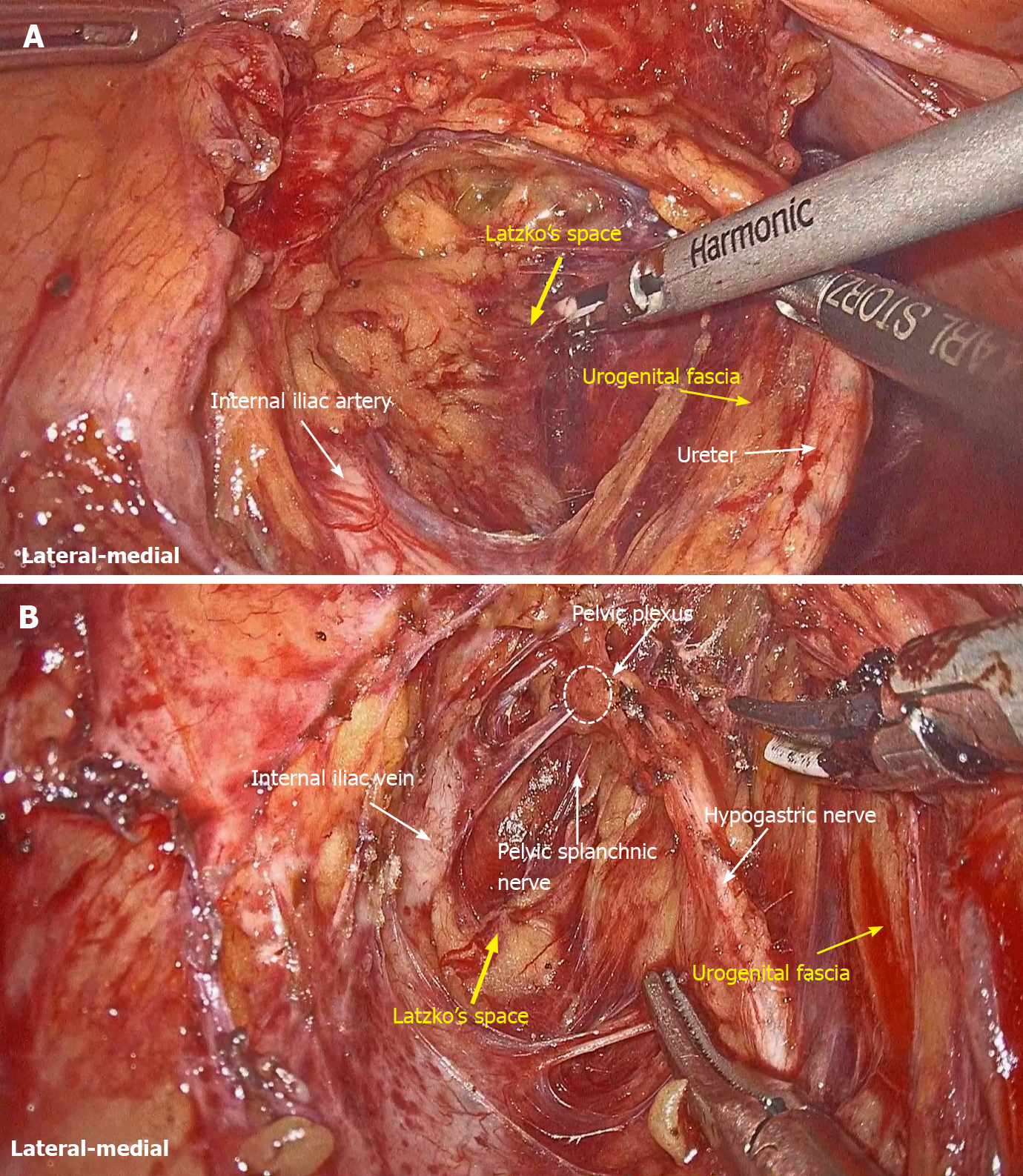
Figure 1 Urogenital fascia is separated to expose the medial boundary of the Latzko's pararectal space, and the dissection continues to the level of the pelvic plexus.
A: Medial boundary of the Latzko's pararectal space; B: Dissection continues to the level of the pelvic plexus.
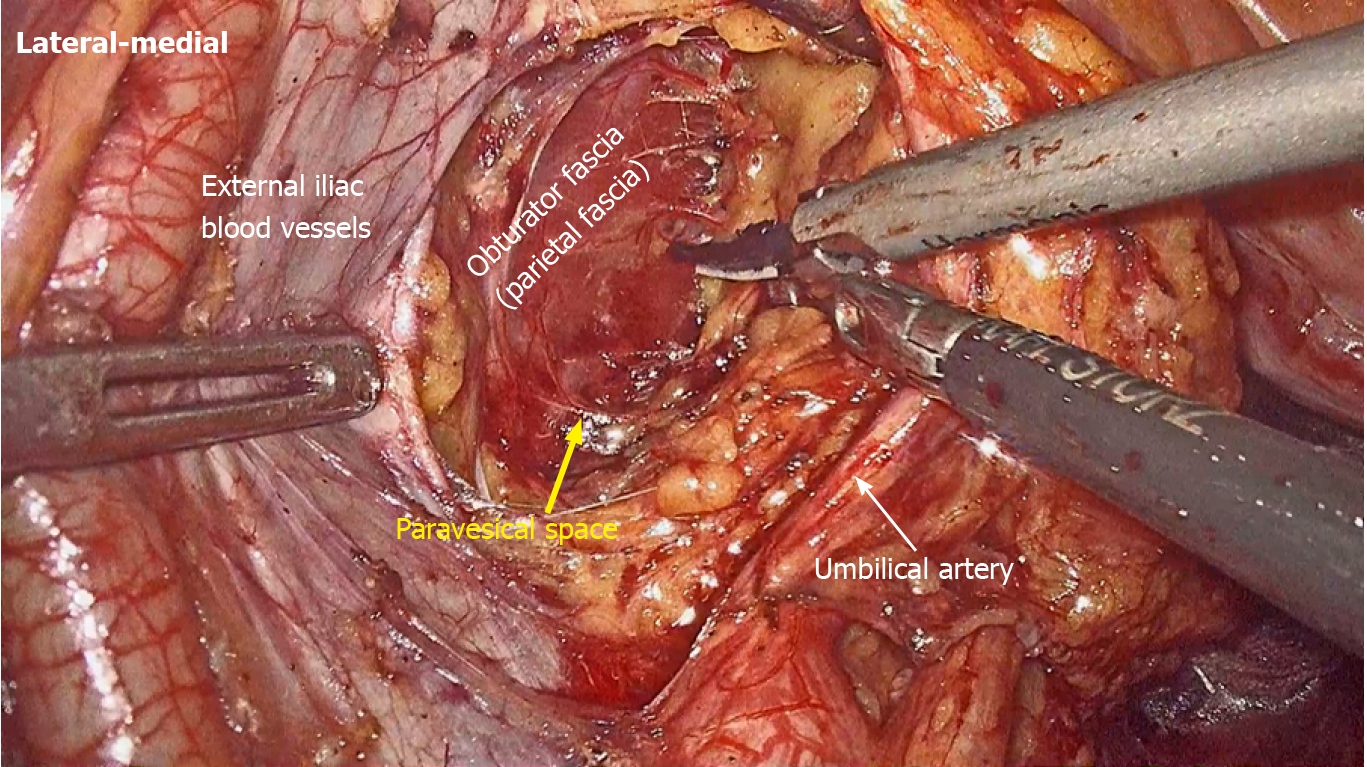
Figure 2
Obturator fascia is separated to expose the lateral boundary of the paravesical space.
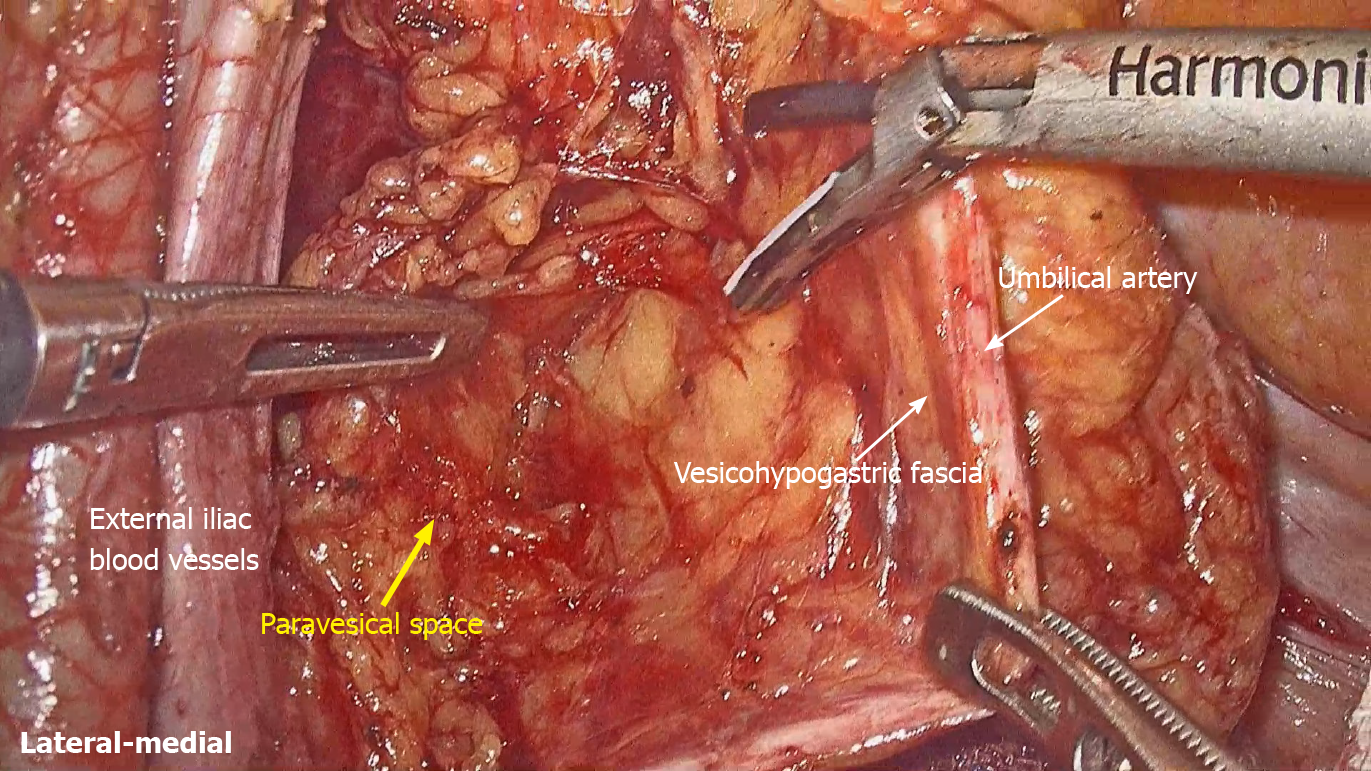
Figure 3
Vesicohypogastric fascia is separated to expose the medial boundary of the paravesical space.
Figure 4
Obturator lymph nodes are dissected in the paravesical space.
Figure 5
Internal iliac lymph nodes are dissected in the Latzko's pararectal space.
Figure 6
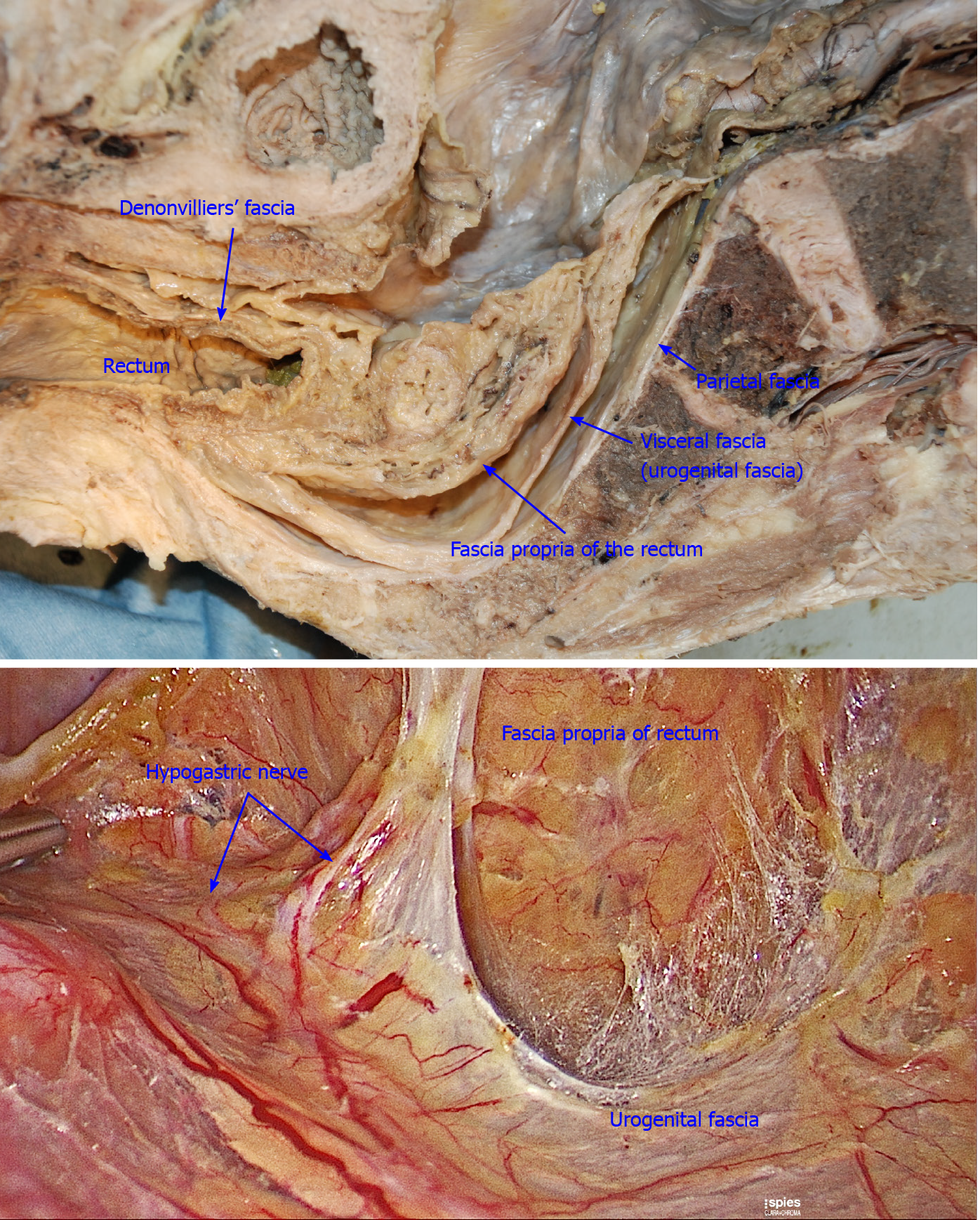
Fascia propria is the innermost fascia around the rectum, and appears as a thin and transparent fascia.
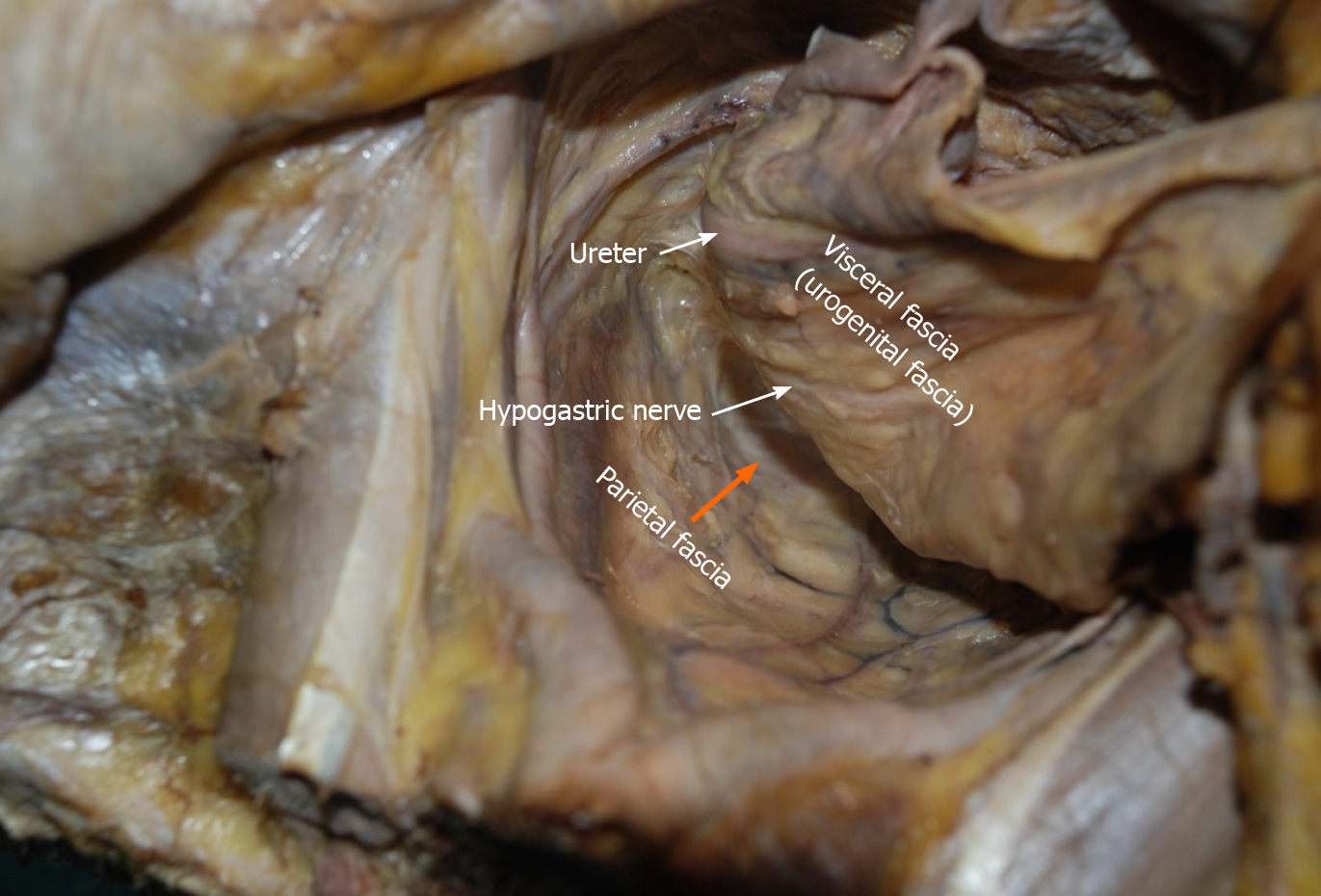
Figure 7 Urogenital fascia extends posterolaterally to the rectum, with the hypogastric nerve and ureter running in it.
The “Holy plane” for total mesorectal excision is between the urogenital fascia (visceral fascia) and the parietal fascia (orange arrowhead).
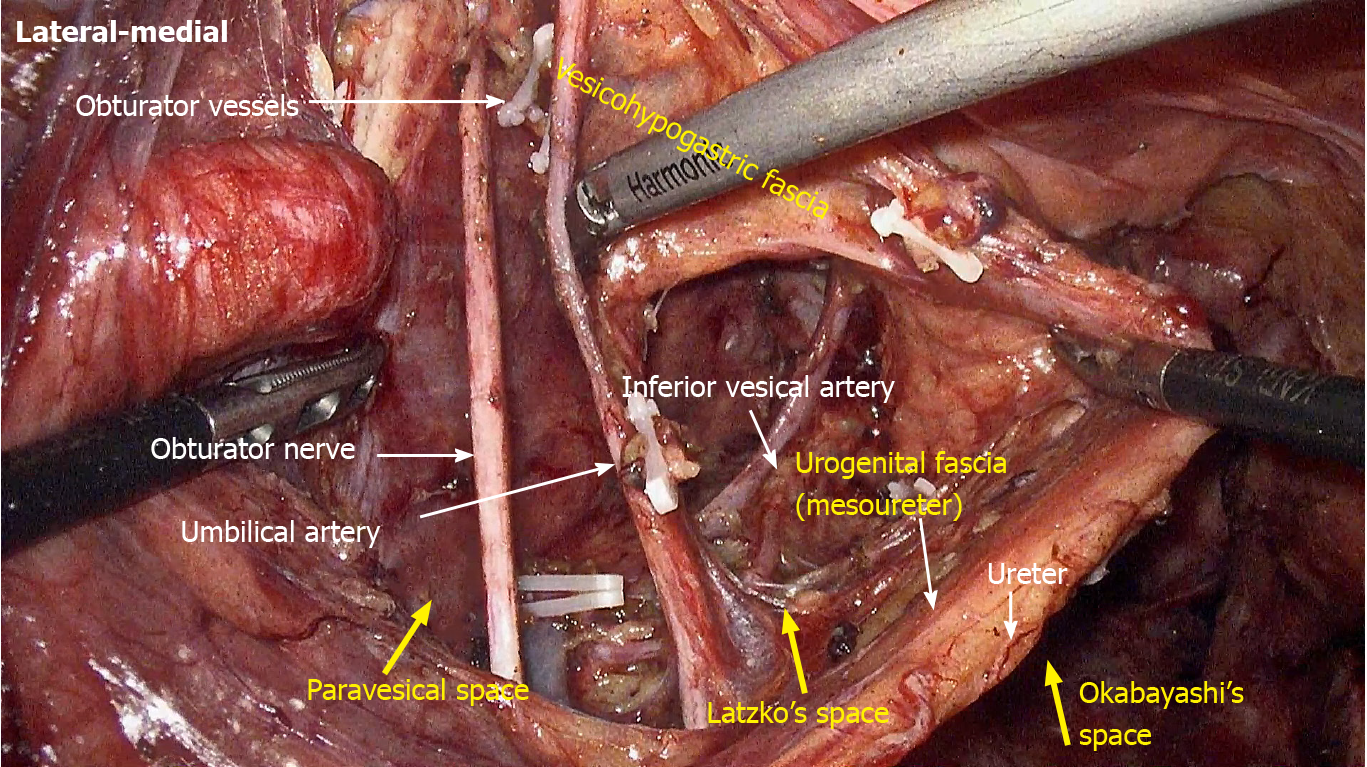
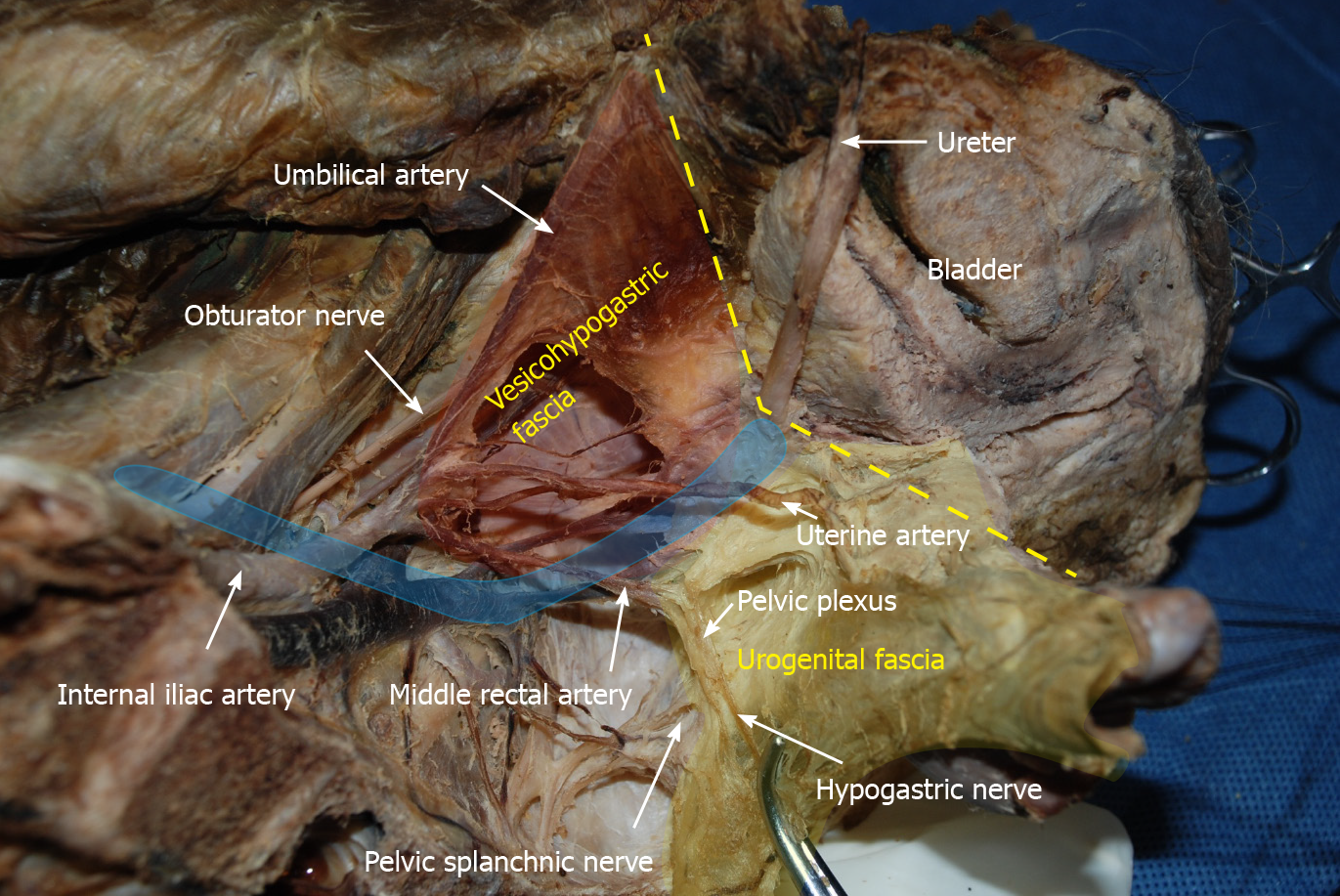
Figure 8 Vesicohypogastric fascia and urogenital fascia.
Vesicohypogastric fascia is a triangular fascia composed of umbilical artery, tendinous arch of pelvic fascia and bladder (red shadow). The urogenital fascia (yellow shadow) and the vesicohypogastric fascia blend with each other and appear as a V-shape (yellow dotted line). The ureter is pulled up and the actual position is shown in blue shadow.
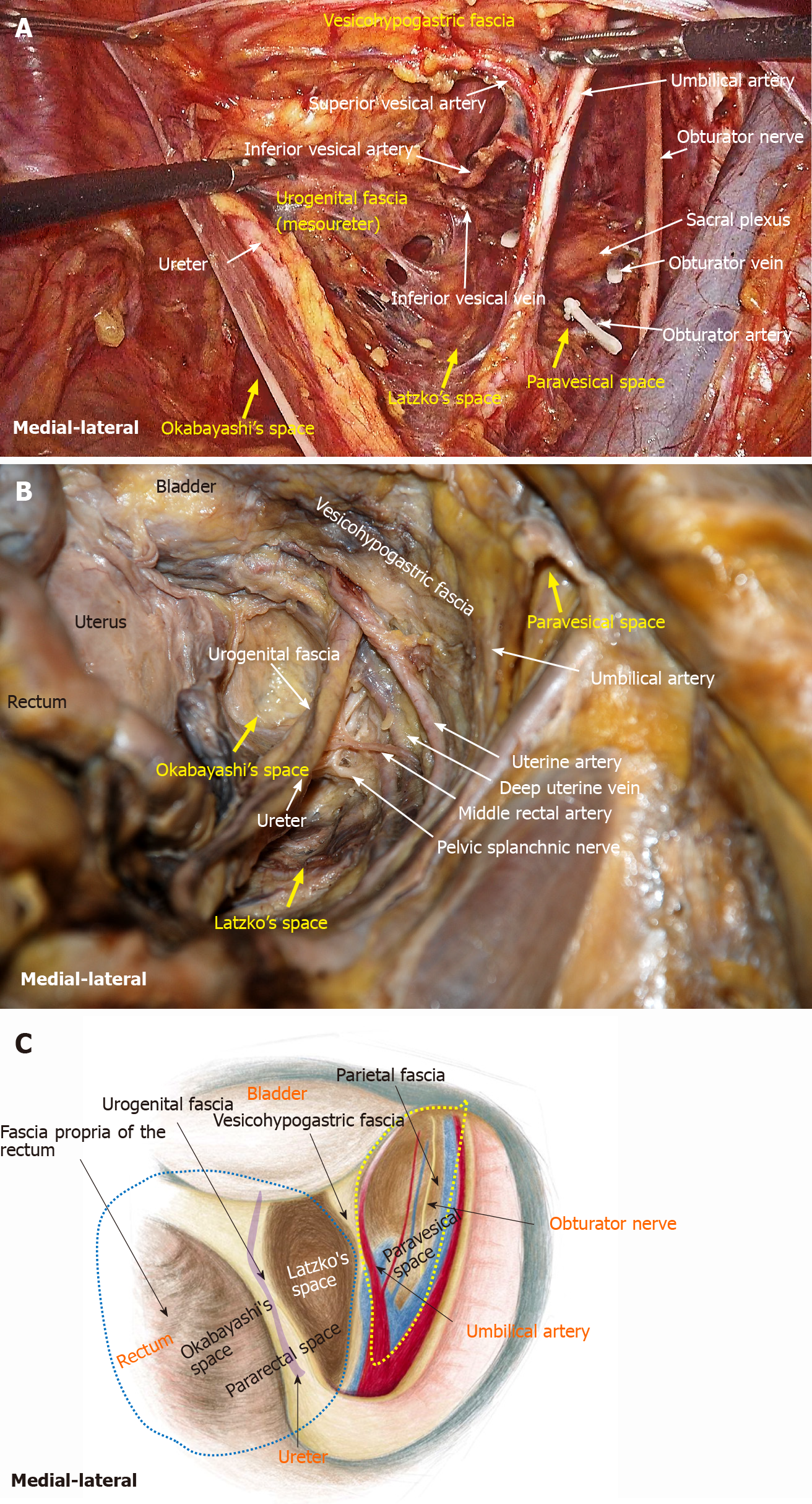
Figure 9 Fascial spaces related to rectal cancer surgery are showed in photograph of operation, photograph of cadaver dissection and diagram.
A: Photograph of operation; B: Photograph of cadaver dissection; C: Photograph of diagram. The pararectal space (blue dotted line) can be divided into Okabayashi's space and Latzko's space. Fascia propria of the rectum, urogenital fascia, vesicohypogastric fascia and parietal fascia form Okabayashi's, Latzko's space and paravesical space (yellow dotted line). The last two spaces are the surgical area for lateral lymph node dissection.
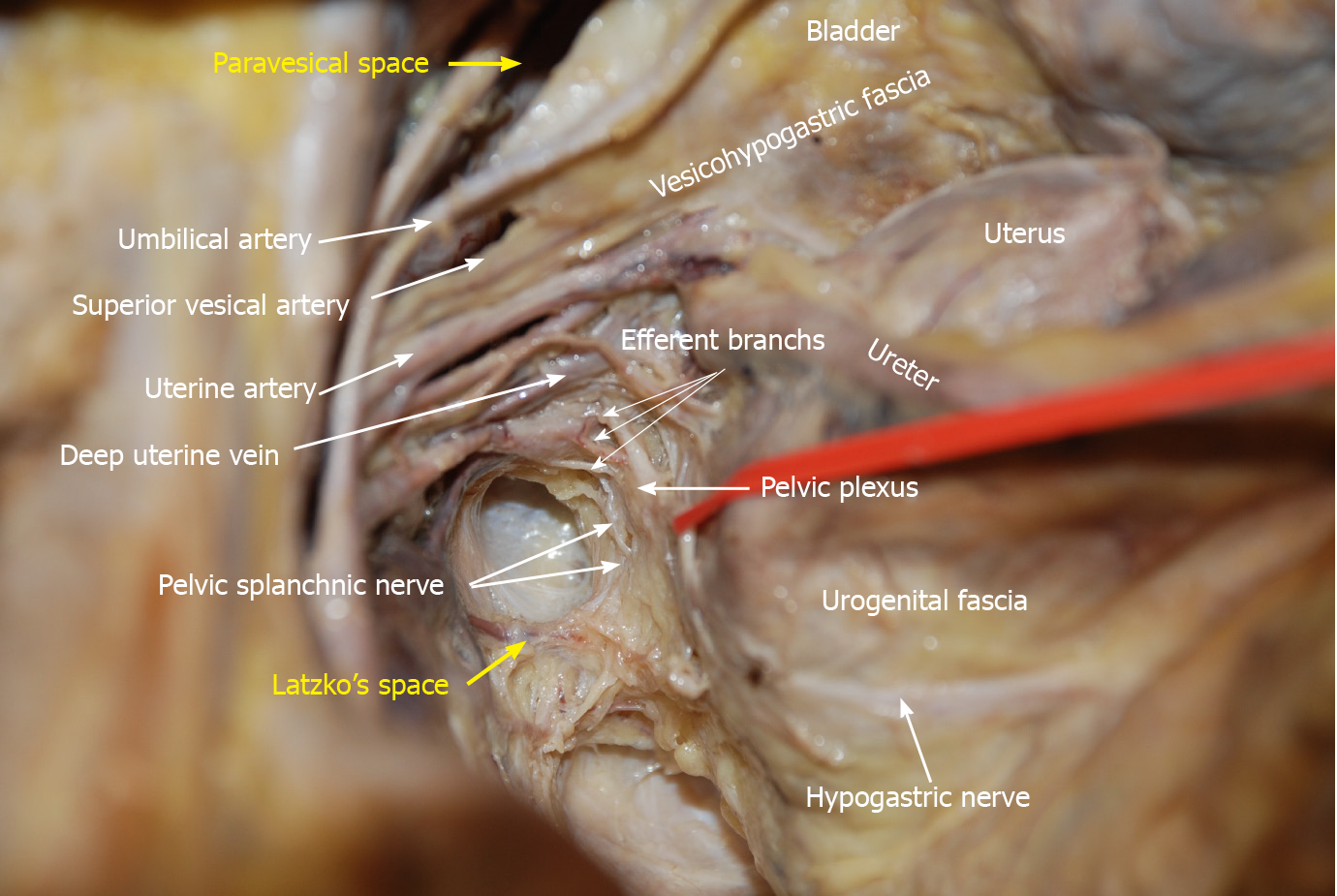
Figure 10 Anatomy of the branches of the internal iliac blood vessel and nerves related to lateral lymph node dissection.
The hypogastric nerve, pelvic splanchnic nerves and pelvic plexus are located in the same connective tissue plane and presents as a T-shape “pelvic nerve plate”.
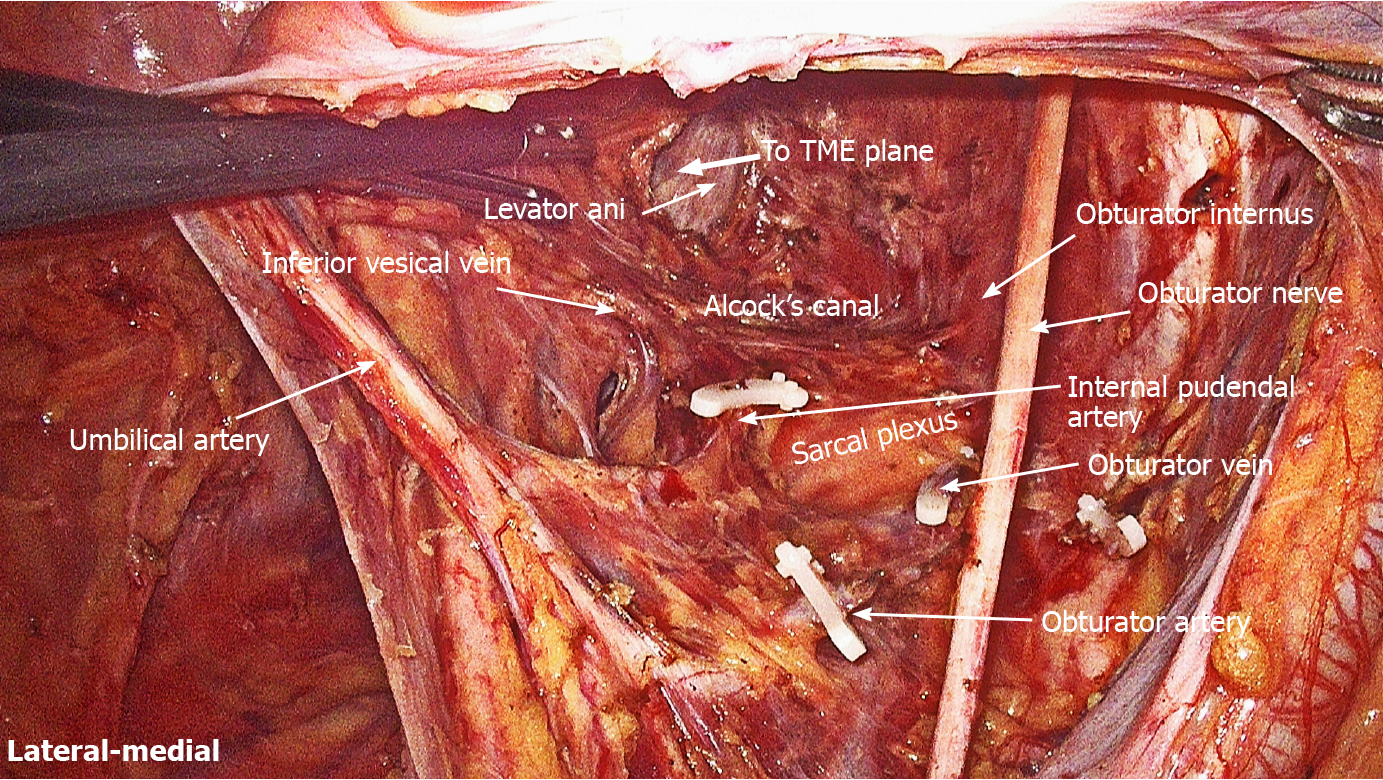
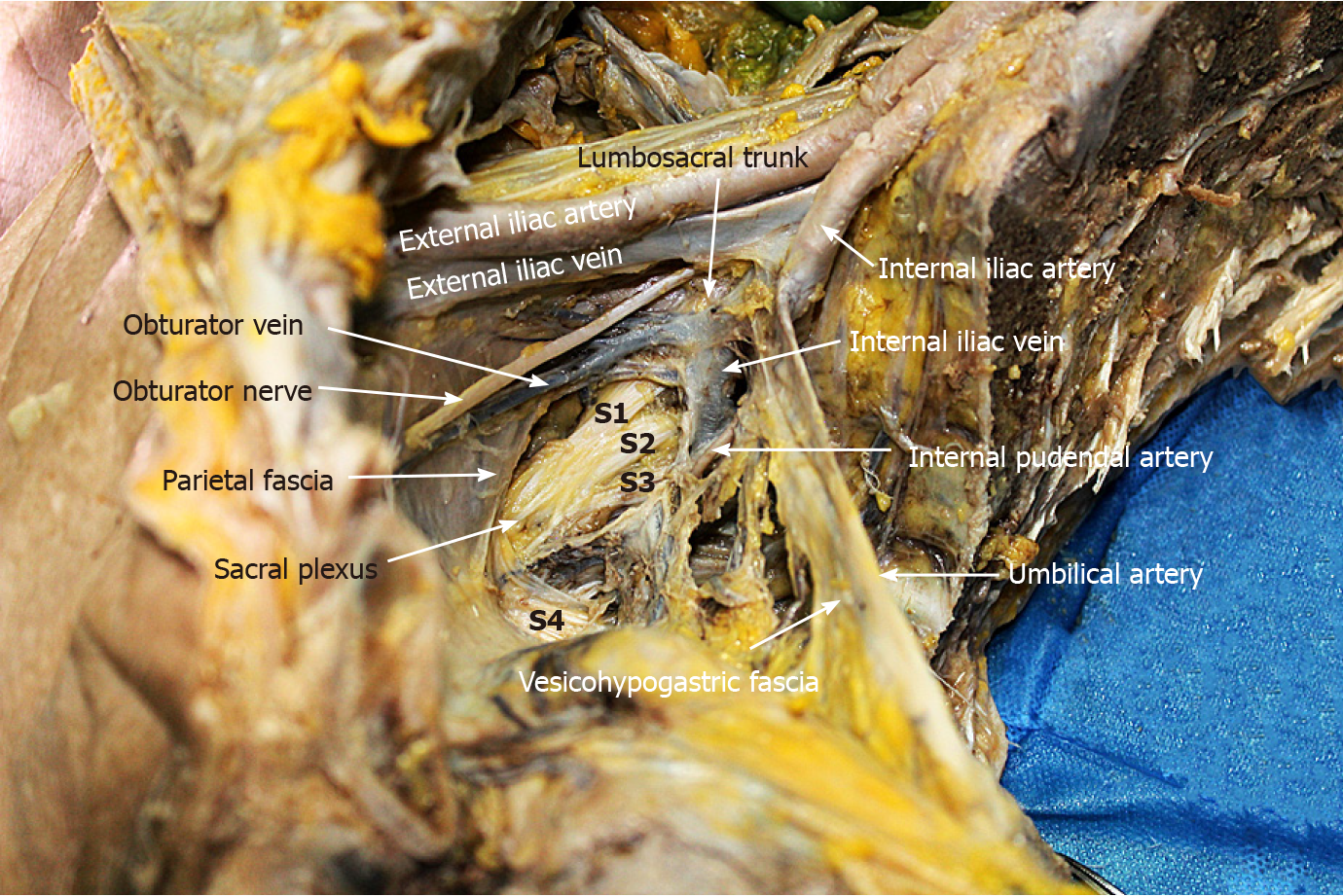
Figure 11
Lumbosacral trunk is located at the bifurcation of internal and external iliac vessels, while sacral plexus is located between obturator vein and internal pudendal artery.
Sacral plexus was covered by parietal fascia.
- Citation: Jiang HH, Liu HL, Li AJ, Wang WC, Lv L, Peng J, Pan ZH, Chang Y, Lin MB. Laparoscopic lateral lymph node dissection in two fascial spaces for locally advanced lower rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3654-3667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3654