Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2020; 26(4): 404-415
Published online Jan 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i4.404
Published online Jan 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i4.404
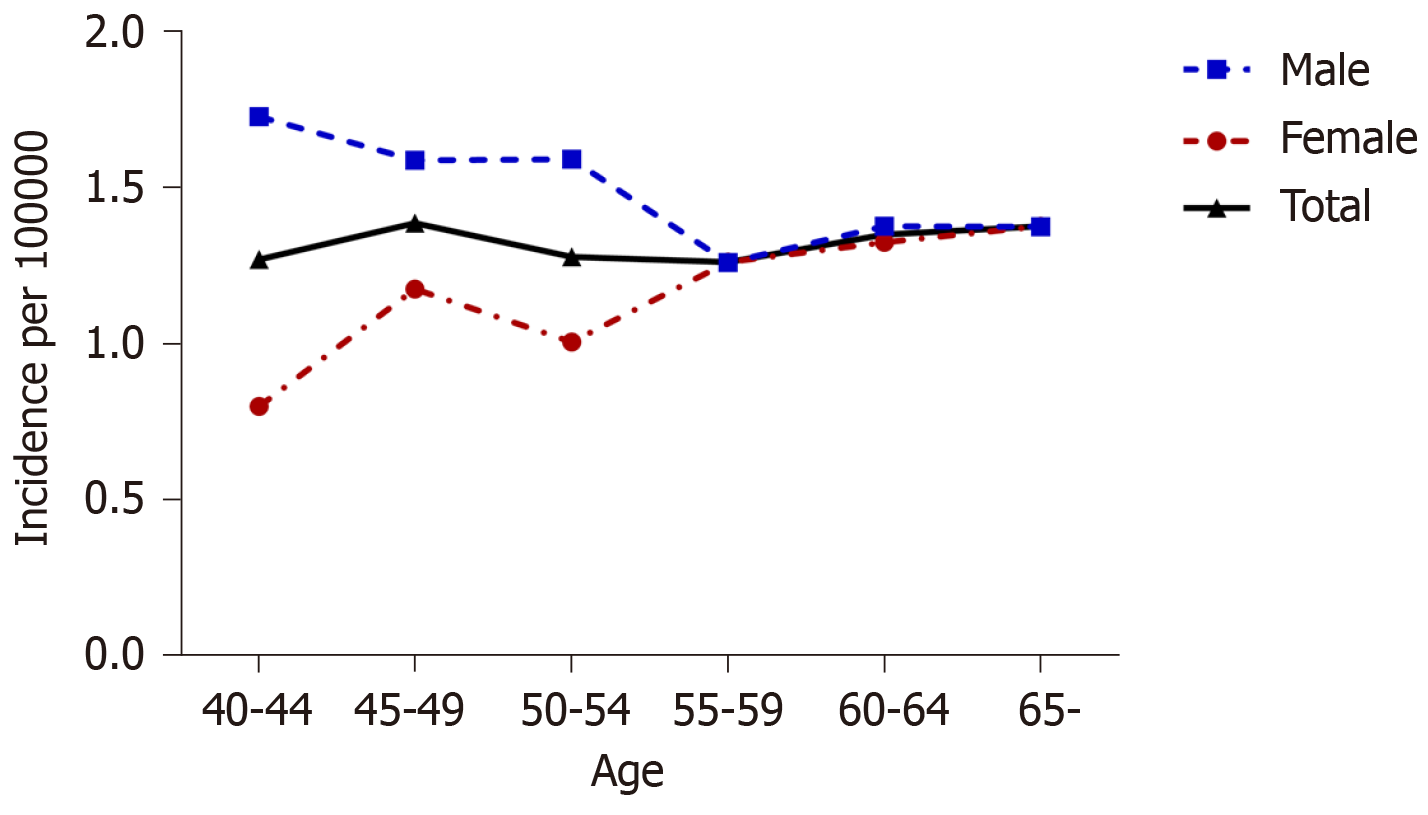
Figure 1 Age-specific incidence rates of Crohn’s disease in the total population and in men and women separately.
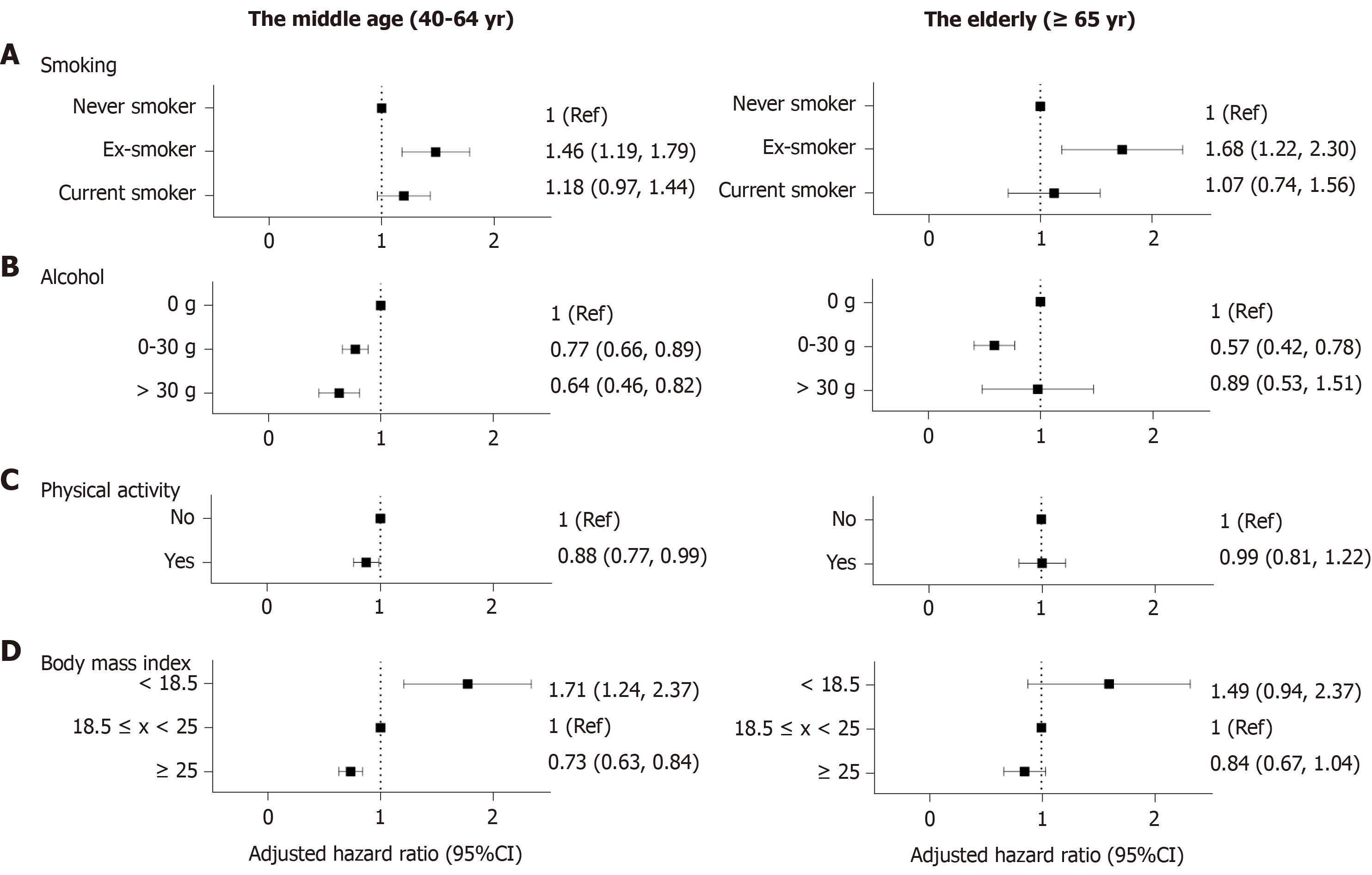
Figure 2 Forrest plots showing lifestyle parameters as environmental risk factors of Crohn’s disease.
Adjusted for age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, alcohol consumption, regular exercise, body mass index, anemia, chronic kidney disease and dyslipidemia. A: Setting non-smoker as the reference, ex-smokers demonstrated an increased risk of CD in both age groups after adjusting for age and sex; B: In the middle-aged group, those who consumed more alcohol showed a decreased risk for CD compared with non-drinkers, however, In the elderly, mild drinkers (≤ 30 g/d) showed a decreased risk for CD but the status of heavy drinkers (> 30 g) did not show statistical significance; C: Regular exercise demonstrated a protective effect against CD in the middle-aged group; D: A BMI of > 25 kg/m2 was a protective factor against CD in the population older than 40 years. BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 posed a relatively higher risk of CD development than BMI > 25 kg/m2. Ref: Reference; CI: Confidence interval.
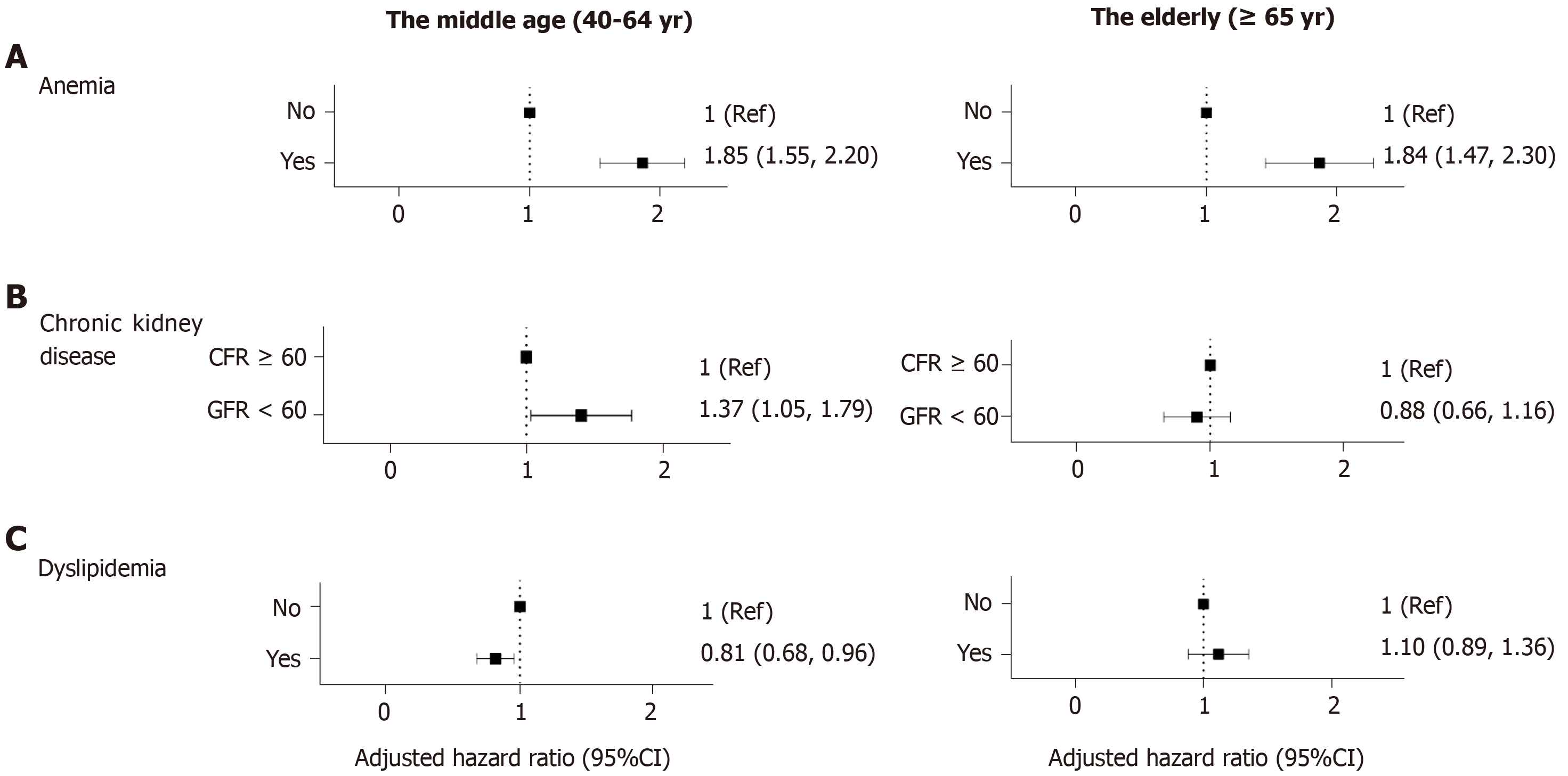
Figure 3 Forrest plots showing comorbidities as risk factors of Crohn’s disease.
Adjusted for age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, alcohol consumption, regular exercise, body mass index, anemia, chronic kidney disease and dyslipidemia. A: Compared with the other factors analyzed in this study, anemia proved to have the largest effect on the risk of Crohn’s disease (CD); B: Patients with chronic kidney disease in the middle-aged group were more likely to be diagnosed with CD; however, in the elderly population, chronic kidney disease did not prove to have statistical meaning; C: Patients diagnosed with dyslipidemia were less likely to develop CD than the control population, among those aged between 40 and 65 years. Ref: Reference, CI: Confidence interval, GFR: Glomerular filtration rate.
- Citation: Moon JM, Kang EA, Han K, Hong SW, Soh H, Park S, Lee J, Lee HJ, Im JP, Kim JS. Trends and risk factors of elderly-onset Crohn’s disease: A nationwide cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(4): 404-415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i4/404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i4.404