Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2020; 26(34): 5130-5145
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5130
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5130
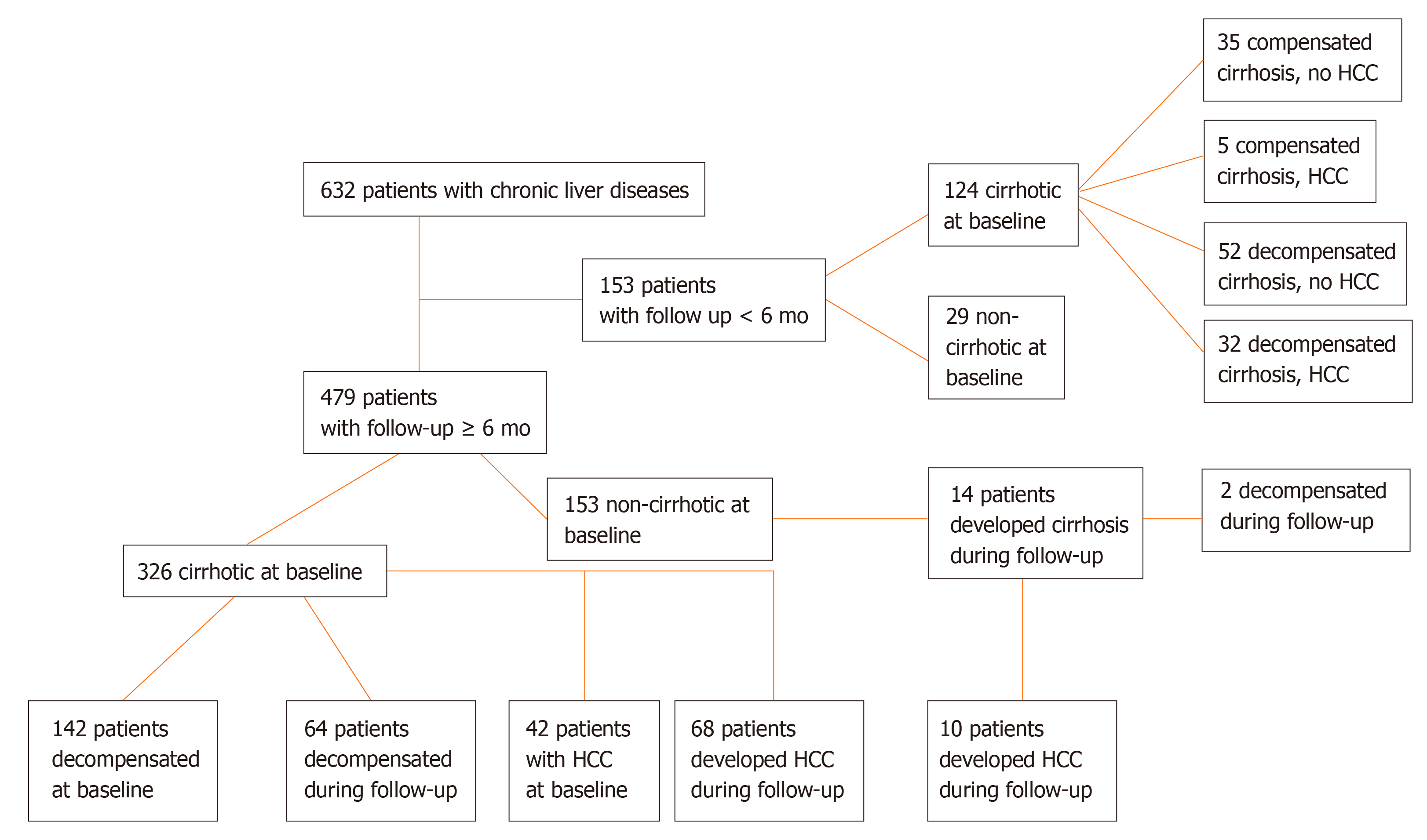
Figure 1 Flow-sheet of the 632 patients participated in the study and liver-related events (development of cirrhosis, liver decompensation, hepatocellular carcinoma development) observed during follow up.
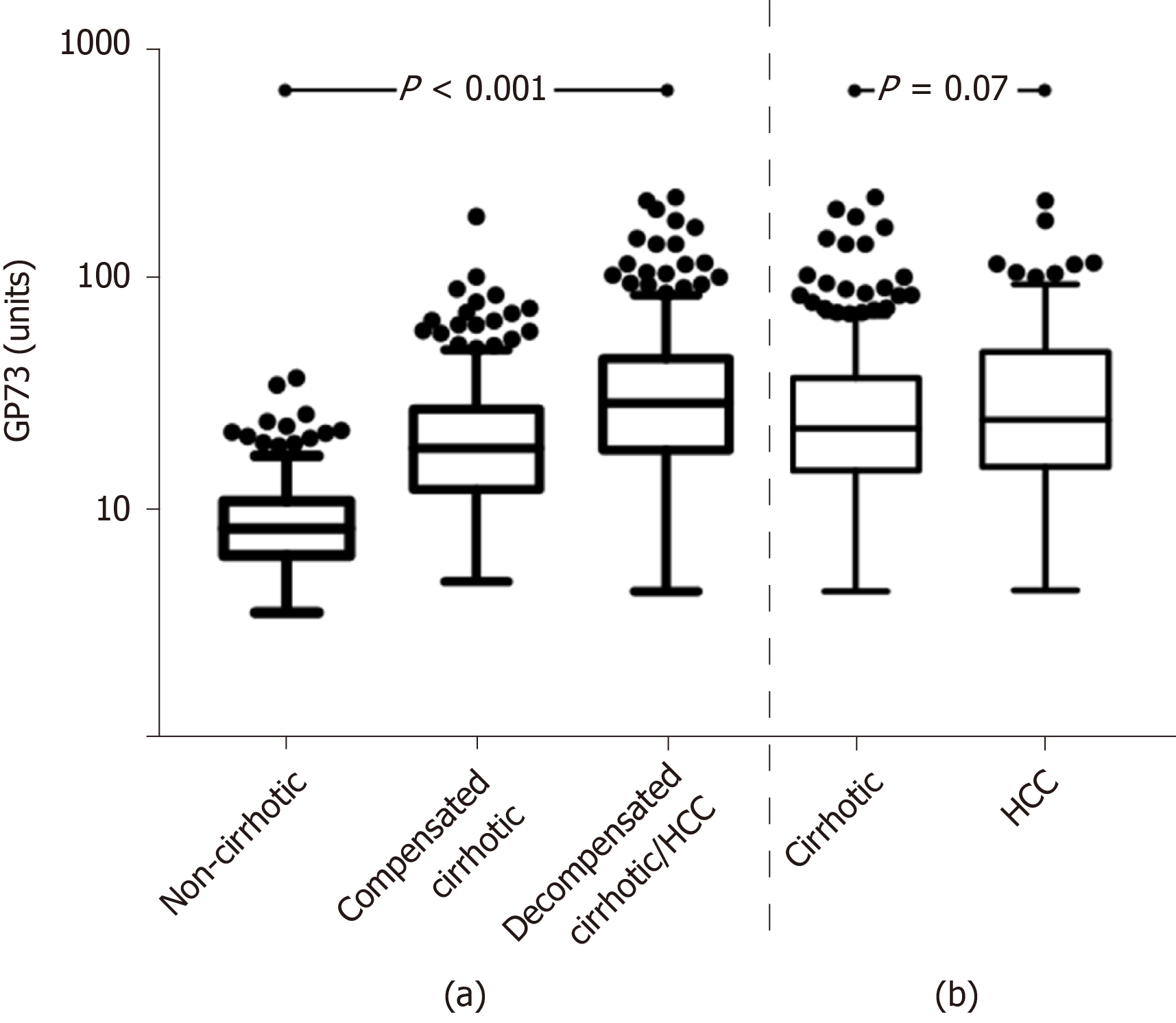
Figure 2 Golgi protein 73 values distribution in different stages of chronic liver diseases.
(a) non-cirrhotic patients, 8.4 (4.6) units vs compensated cirrhotic patients, 18.7 (15.3) units vs decompensated cirrhotic or patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), 29.5 (27.6) units; P < 0.001; and (b) cirrhotic (compensated and decompensated), 22.8 (22.9) units vs HCC patients, 25 (33.7) units; P = 0.07 (Tukey box-and-whisker plots; y-axis is presented in log scale). GP73: Golgi protein 73; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
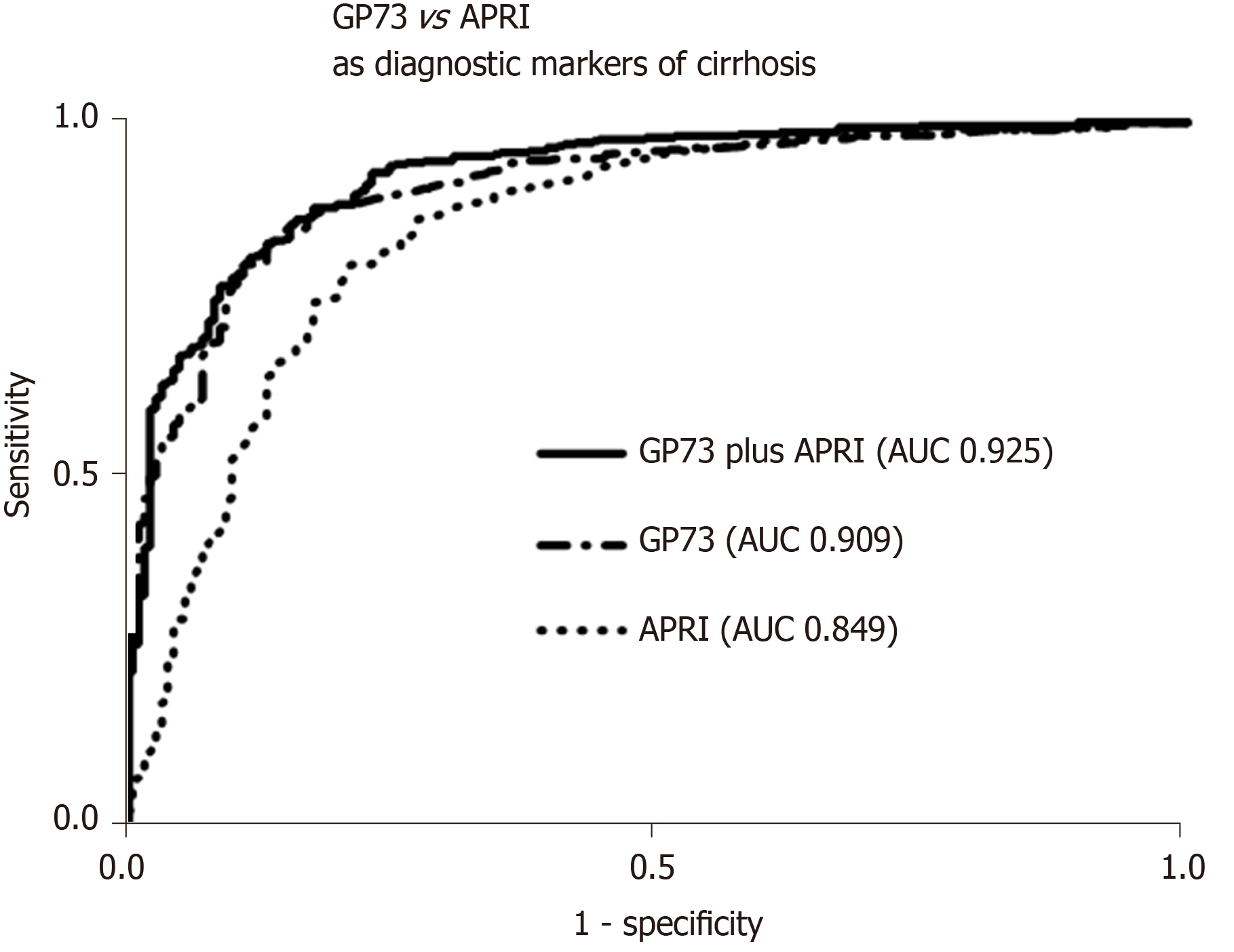
Figure 3 Golgi protein 73 vs aspartate aminotransferase to platelets index as diagnostic markers of cirrhosis.
Receiver operating characteristic curves for the prediction of cirrhosis according to Golgi protein 73 (GP73) levels and aspartate aminotransferase to platelets index (APRI) score. Combination of GP73 and APRI had a higher diagnostic accuracy for cirrhosis), compared to GP73 (P = 0.005) or APRI score alone (P < 0.001). GP73: Golgi protein 73; APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase to platelets index; AUC: Area under the curve.
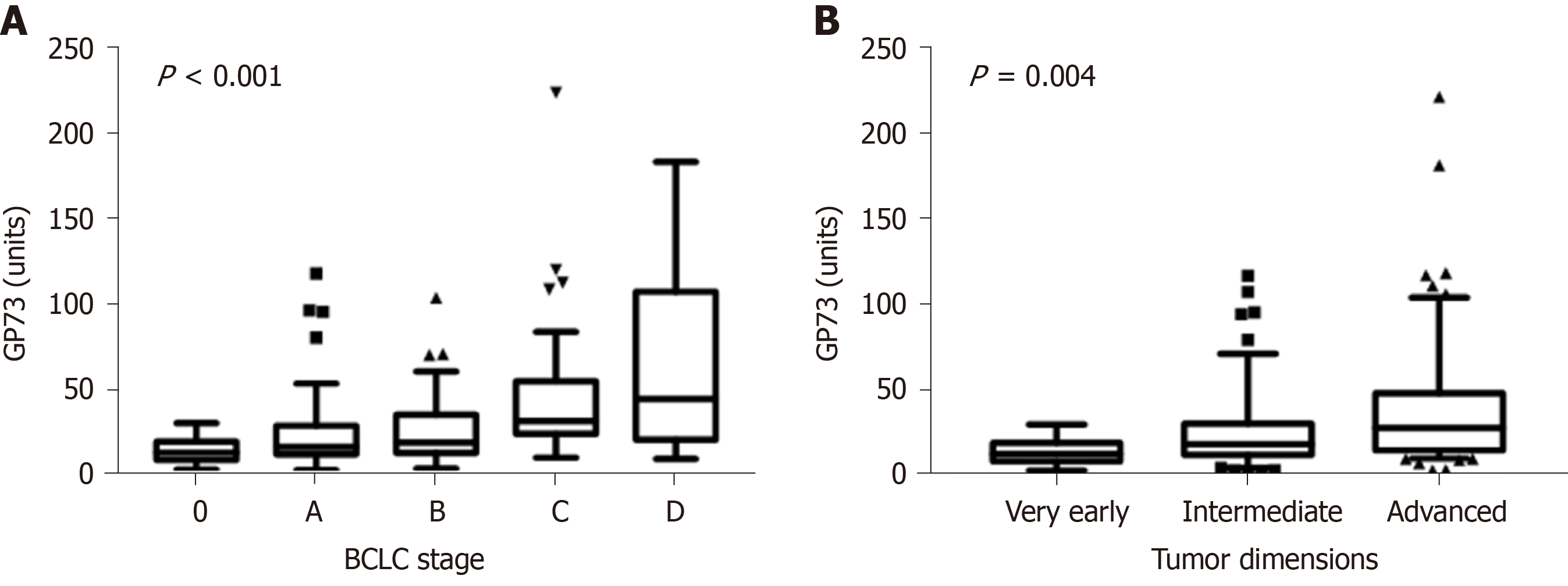
Figure 4 Golgi protein values distribution among hepatocellular carcinoma stages according to.
A: BCLC staging system [stage 0, 13.9 (10.8) units; stage A, 17.1 (16.8) units; stage B, 19.6 (22.3) units; stage C, 32.2 (30.8) units; stage D, 45.3 (86.6) units; P < 0.001]. B: Tumor dimensions [very early, 13.9 (10.8) units; intermediate, 19.6 (18.4) units; advanced, 29.1 (33.6) units; P = 0.004] (Tukey box-and-whisker plots). GP73: Golgi protein 73; BCLC: Barcelona clinic liver cancer.
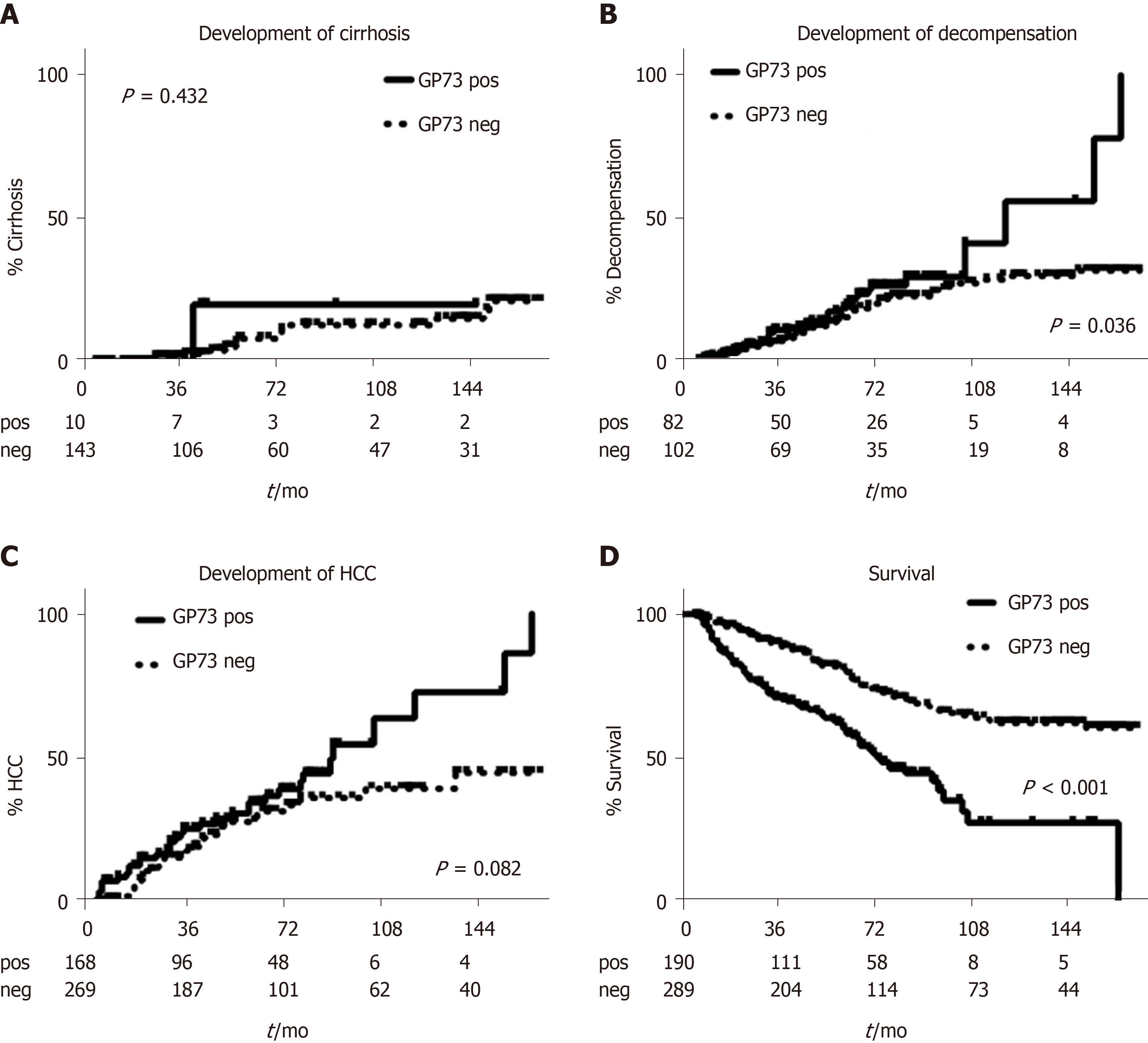
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier analysis of patients according to Golgi protein 73 detection.
Only 14 patients (one GP73 positive and 13 GP73 negative) developed cirrhosis during follow-up A. GP73 positive patients were characterized by higher decompensation B, HCC development C and liver-related mortality rates D. GP73: Golgi protein 73 detection; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Gatselis NK, Tornai T, Shums Z, Zachou K, Saitis A, Gabeta S, Albesa R, Norman GL, Papp M, Dalekos GN. Golgi protein-73: A biomarker for assessing cirrhosis and prognosis of liver disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(34): 5130-5145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i34/5130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5130