Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2020; 26(32): 4786-4801
Published online Aug 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4786
Published online Aug 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4786
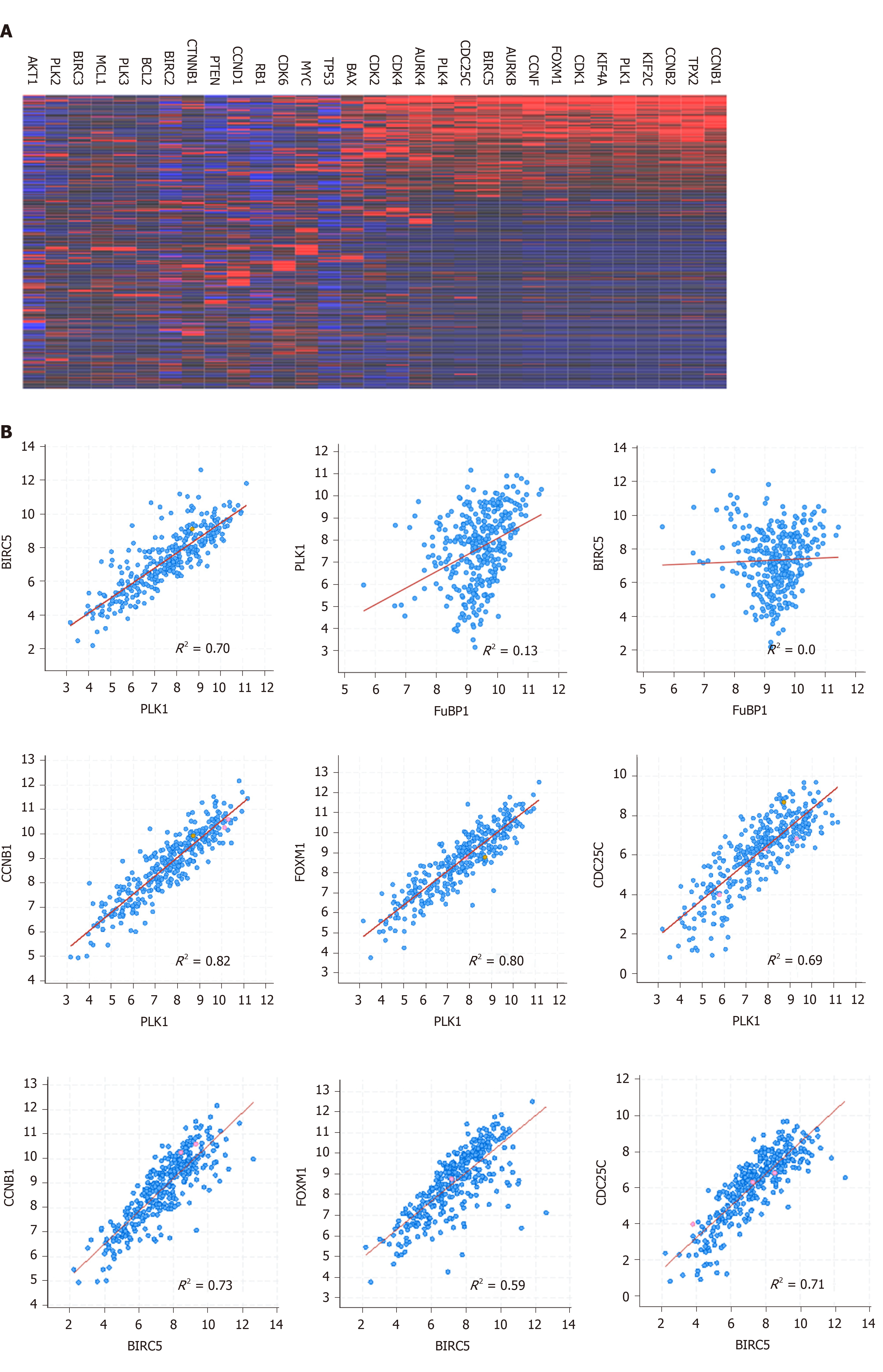
Figure 1 Co-expression of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Heatmap of genes co-expressed with Polo-like kinase 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma; B: Correlations of representative genes that are co-expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. The dataset used in these analysis was Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA, PanCancer Atlas). PLK1: Polo-like kinase 1; BIRC5: Baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5.
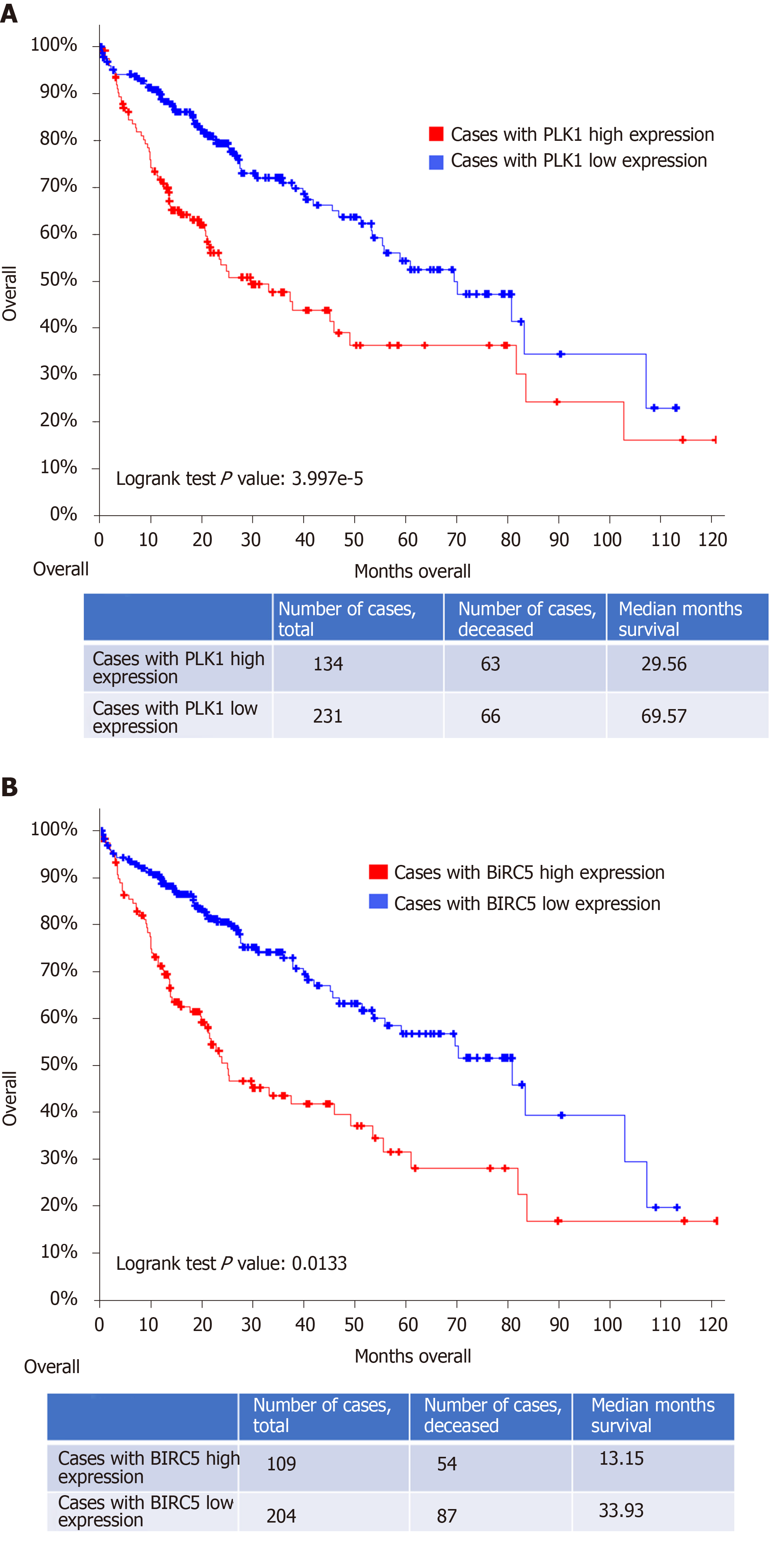
Figure 2 High Polo-like kinase 1 expression correlates with a poor overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Kaplan-Meier estimate of overall clinical survival in patients with high Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) expression (PLK1: Exp > 0.1) and in patients with low PLK1 expression (PLK1: Exp ≤ 0.1). Total cases, deceased cased, and survival months for either group are also indicated in the bottom of the figure; B: Kaplan-Meier estimate of disease/progression-free survival after the initial treatment in patients with high PLK1 expression (PLK1: Exp > 0.1) and in patients with low PLK1 expression (PLK1: Exp ≤ 0.1). The P values generated by log-rank test are also shown. The dataset used in these analyses was Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA, PanCancer Atlas). PLK1: Polo-like kinase 1.
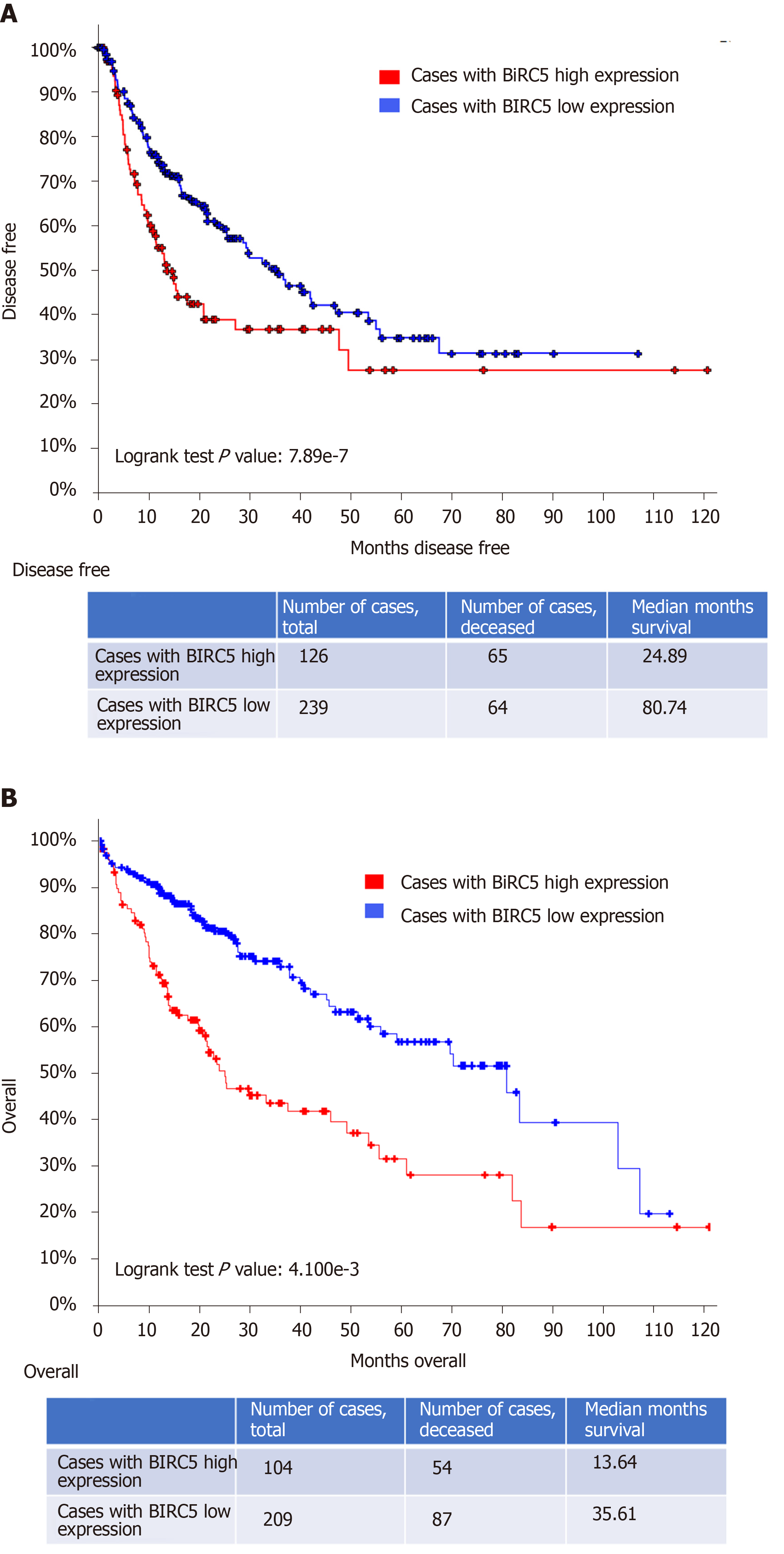
Figure 3 High baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 expression correlates with a poor overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Kaplan-Meier estimate of overall clinical survival in patients with high baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 (BIRC5) expression (BIRC5: Exp > 0.1) and in patients with low BIRC5 expression (BIRC5: Exp ≤ 0.1). Total cases, deceased cased, and survival months for either group are also indicated in the bottom of the figure; B: Kaplan-Meier estimate of disease/progression-free survival after the initial treatment in patients with high BIRC5 expression (BIRC5: Exp > 0.1) and in patients with low BIRC5 expression (BIRC5: Exp ≤ 0.1). The P values generated by log-rank test are also shown. The dataset used in this analysis was Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA, PanCancer Atlas). BIRC5: Baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5.
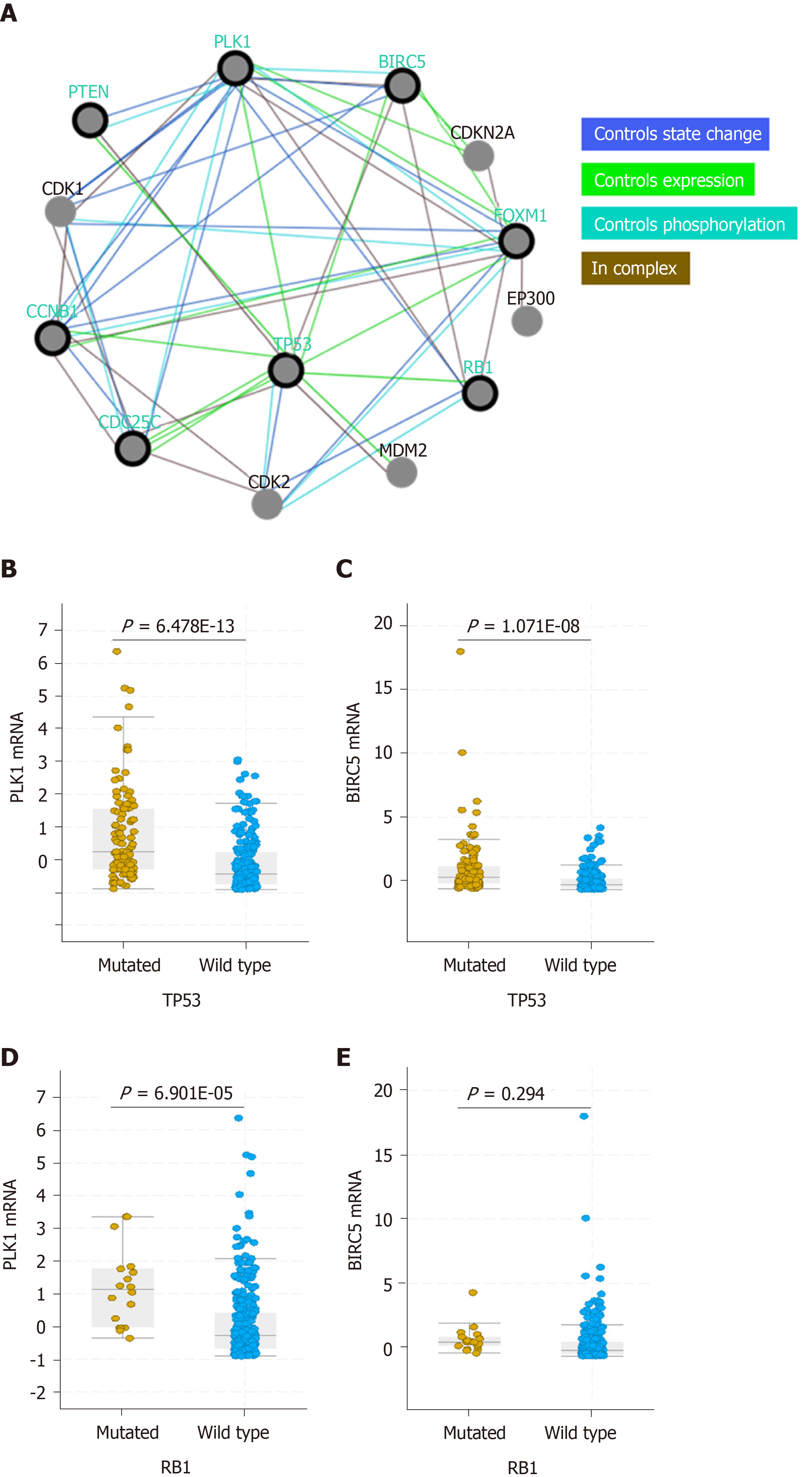
Figure 4 High expression of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 in TP53-mutated hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A: PLK1- and BIRC5-associated pathway networks; B and C: Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) (B) or baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 (BIRC5) (C) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with wild-type and mutated TP53; D and E: PLK1 (D) or BIRC5 (E) expression in HCC patients with wild-type and mutated RB1. The dataset used in these analysis was Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA, PanCancer Atlas). PLK1: Polo-like kinase 1; BIRC5: Baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5.
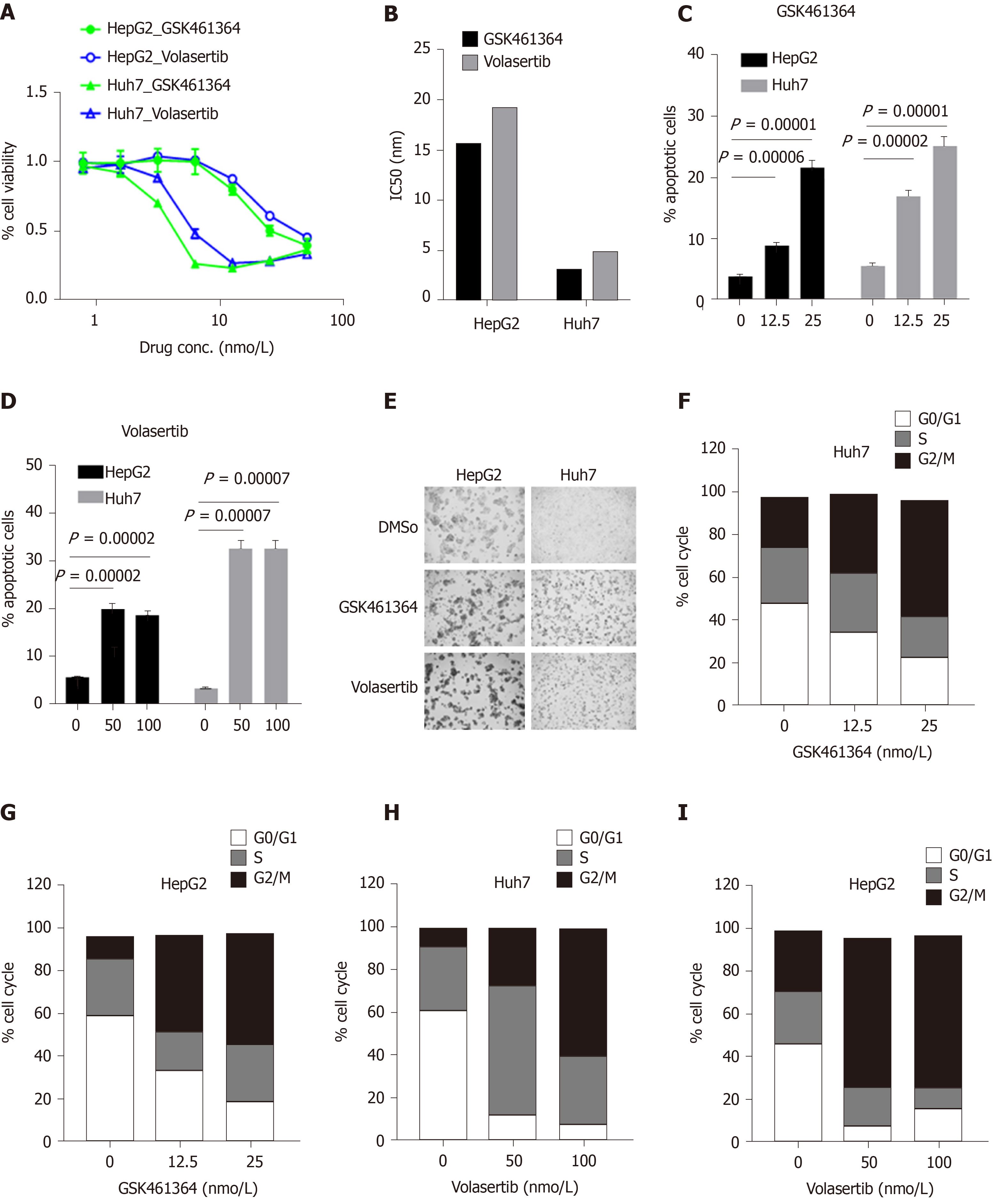
Figure 5 Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors GSK461364 and volasertib selectively target Huh7 cells with mutated p53 over HepG2 cells with wild-type p53.
A and B: In vitro efficacy of the Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors GSK461364 and volasertib in HepG2 and Huh7 cells after 72 h of treatment as assessed through cell viability assays (A) and IC50 values for the inhibitors were also calculated and plotted (B); C and D: Percentage of apoptotic HepG2 and Huh7 cells treated with GSK461364 (C) or volasertib (D) for 24 h at the indicated dosage; E: Representative bright-field images of HepG2 and Huh7 cells treated with GSK461364 or volasertib for 24 h; F-I: Cell cycle status of Huh7 (F and H) and HepG2 (G and I) cells treated with GSK461364 (F and G) or volasertib (H and I) for 24 h at the indicated dosage.
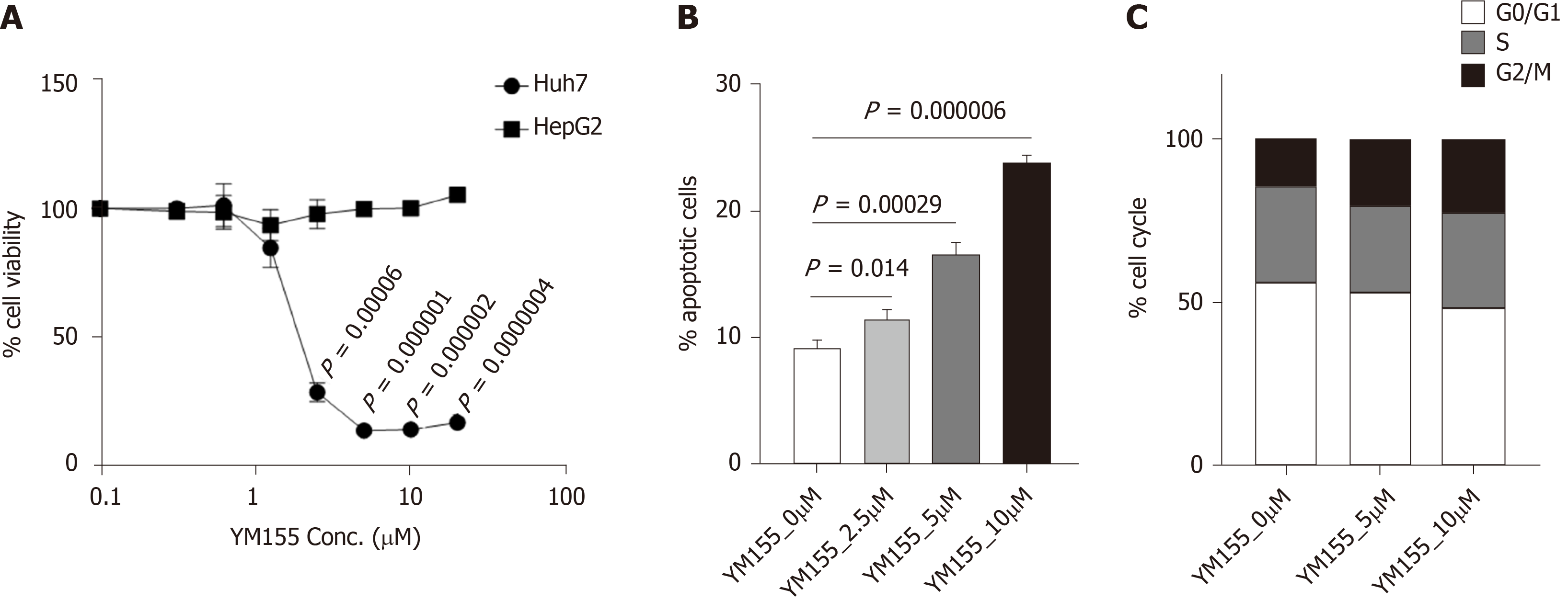
Figure 6 Baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 inhibitor YM155 selectively target Huh7 cells with mutated p53 over HepG2 cells with wild-type p53.
A: In vitro efficacy of the baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 inhibitor YM155 in HepG2 and Huh7 cells after 72 h of treatment as assessed through cell viability assays; B: Percentage of apoptotic Huh7 cells treated with YM155 for 24 h at the indicated dosage; C: Cell cycle status of Huh7 cells treated with YM155 for 24 h at the indicated dosage.
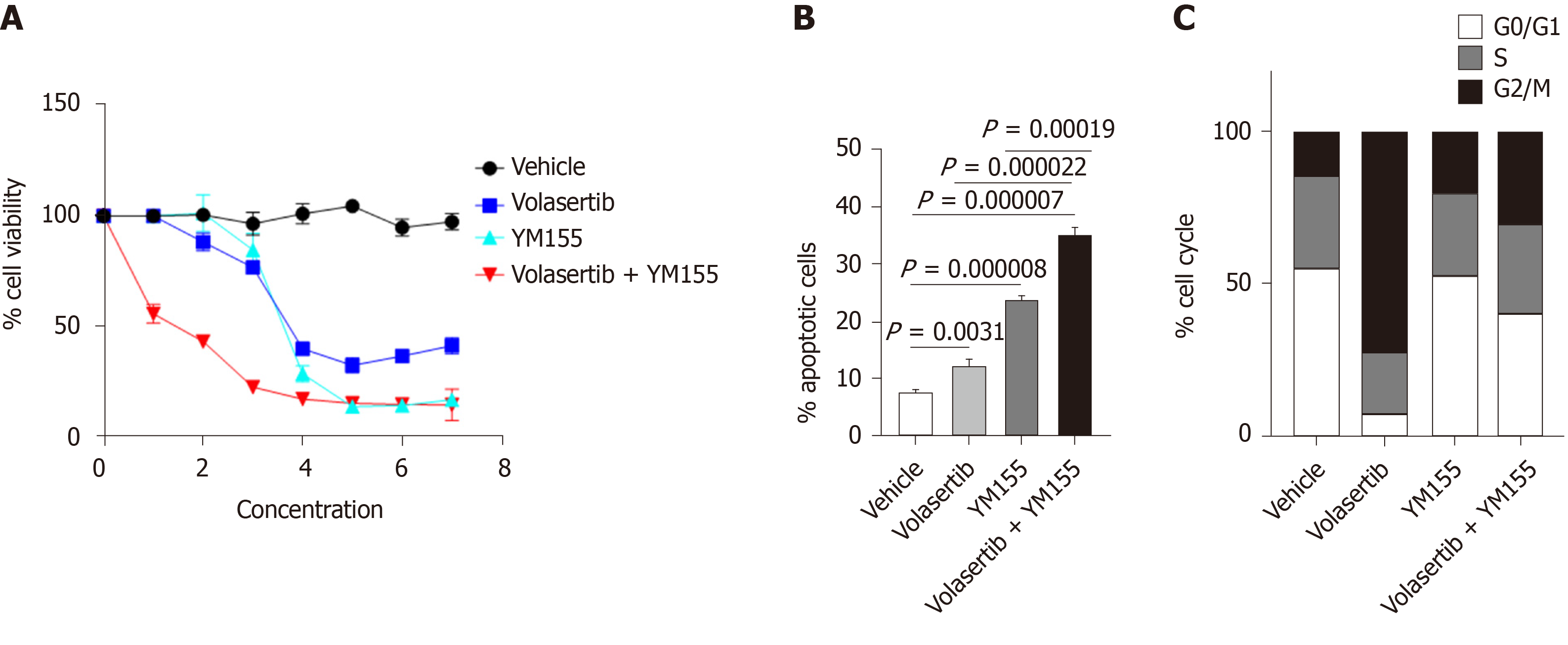
Figure 7 Dual targeting of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 shows synergistic anti-tumor effects in p53 mutated Huh7 cells.
A: In vitro efficacy of the combination treatment of the baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 inhibitor YM155 (0-20 μmol/L) and the Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor volasertib (0-50 nmol/L) against Huh7 cells after 72 h of treatment as assessed through cell viability assays; B: Percentage of apoptotic Huh7 cells treated with YM155 and volasertib for 24 h; C: Cell cycle status of Huh7 cells treated with YM155 and volasertib for 24 h.
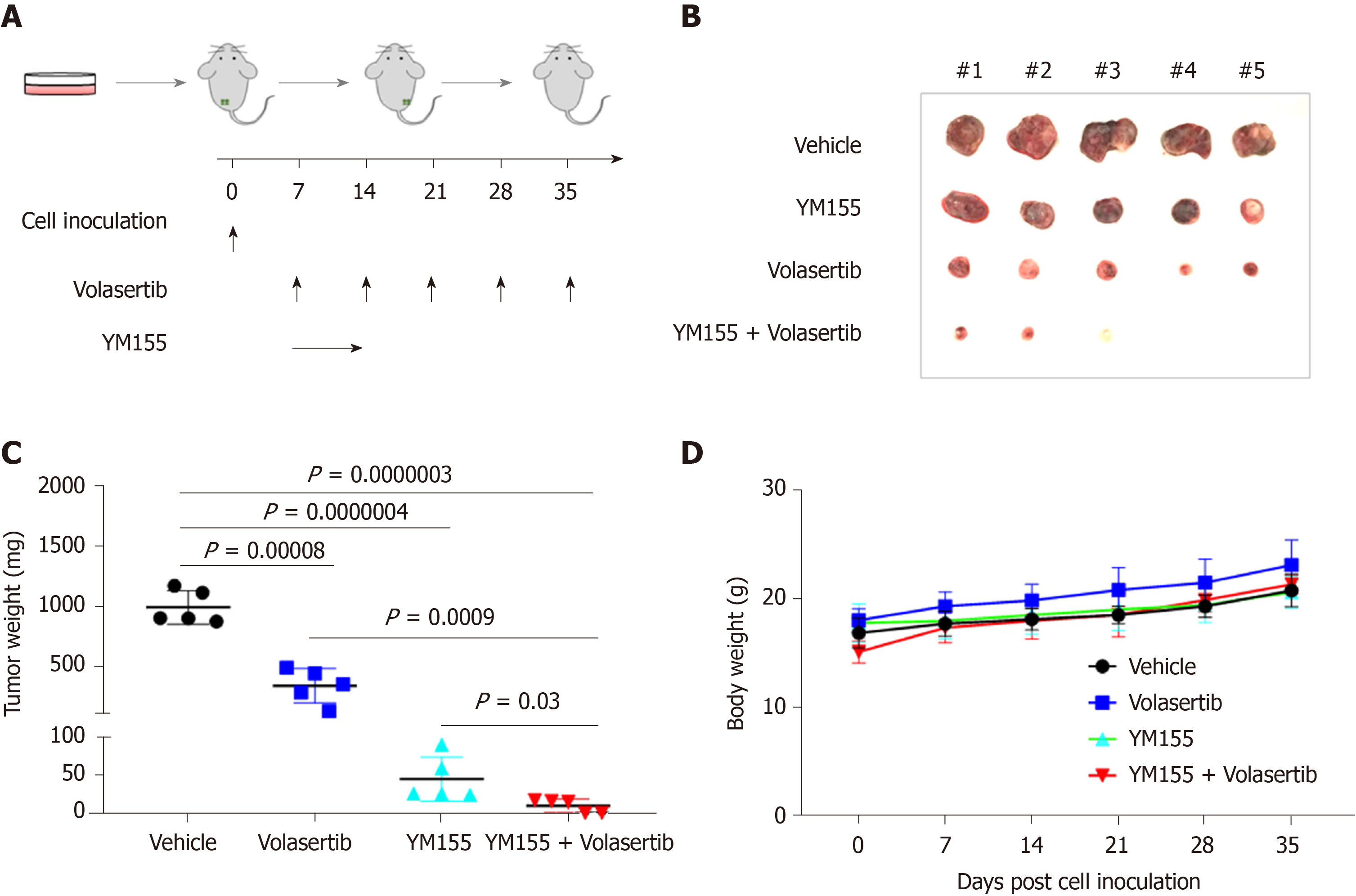
Figure 8 Dual targeting of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 potently inhibits p53-mutated Huh7 cell-derived xenografts.
A: Schematic of the experimental set up for the in vivo xenograft model. Huh7 cells were injected into NSG mice (n = 5 per group). The mice were treated with vehicle or volasertib (10 mg/kg, ip, weekly) for 4 wk, or continuously infused with YM155 (3 mg/kg) for 7 d and off for the next 3 wk; B and C: The mice were euthanized and dissected at the end of experiments. The xenografts were imaged (B) and weighed (C); D: The body weight of mice were measured once a week.
- Citation: Li Y, Zhao ZG, Luo Y, Cui H, Wang HY, Jia YF, Gao YT. Dual targeting of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 in TP53-mutated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(32): 4786-4801
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i32/4786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4786