Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2020; 26(2): 199-218
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199
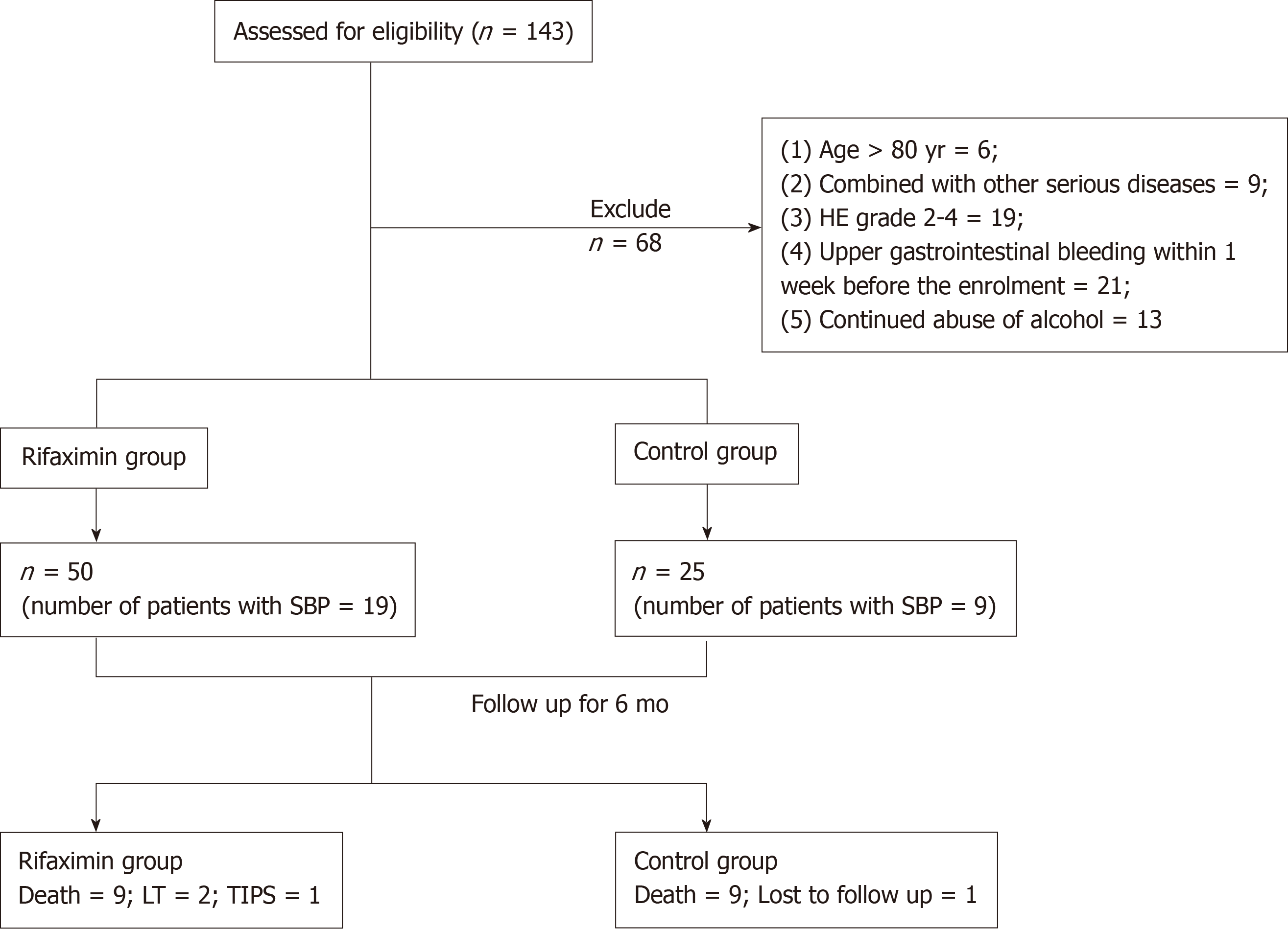
Figure 1 Flow chart for patient selection.
SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; LT: Liver transplantation.
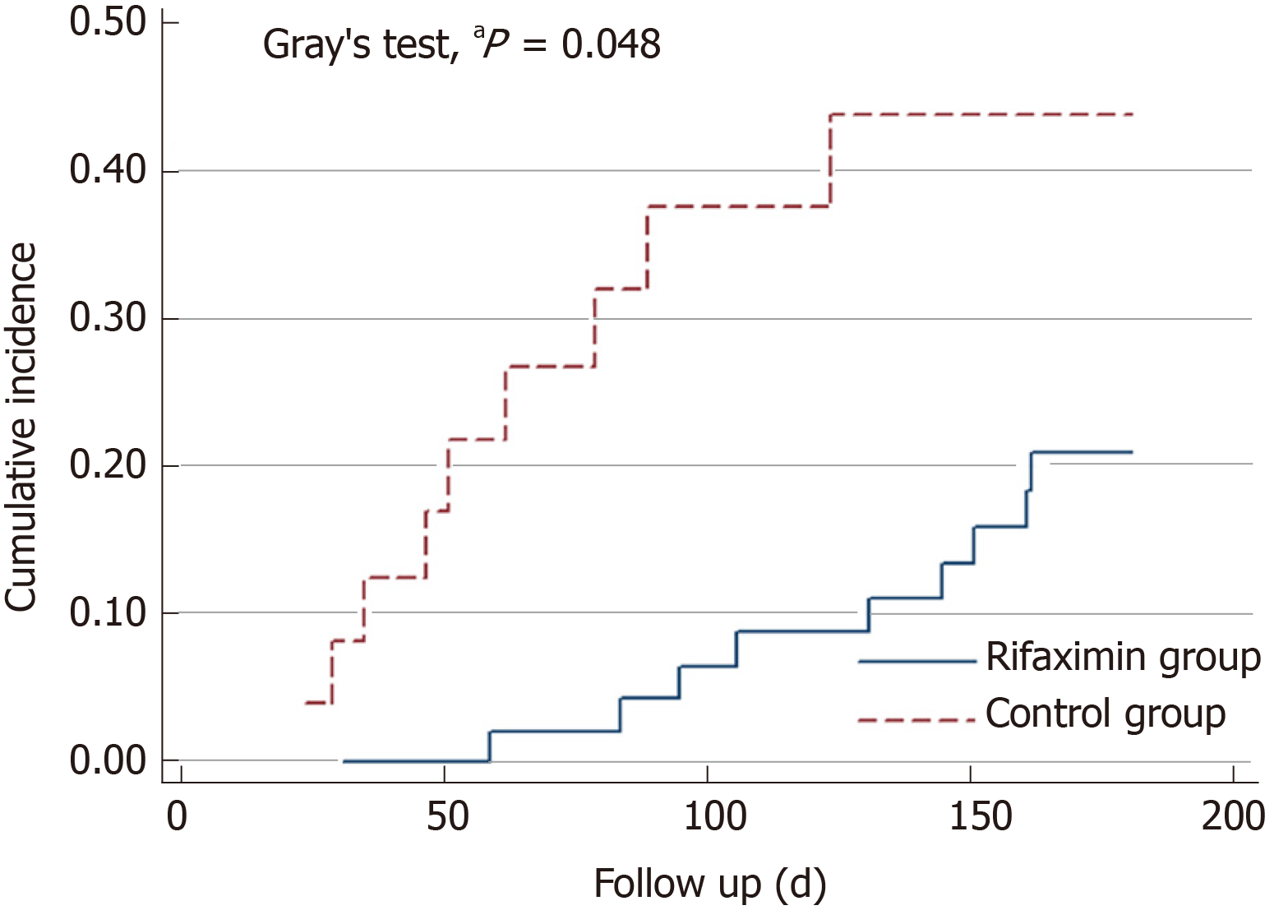
Figure 2 Gray’s test showed that the cumulative survival was significantly higher in the rifaximin group than in the control group.
aP < 0.05 vs control group.
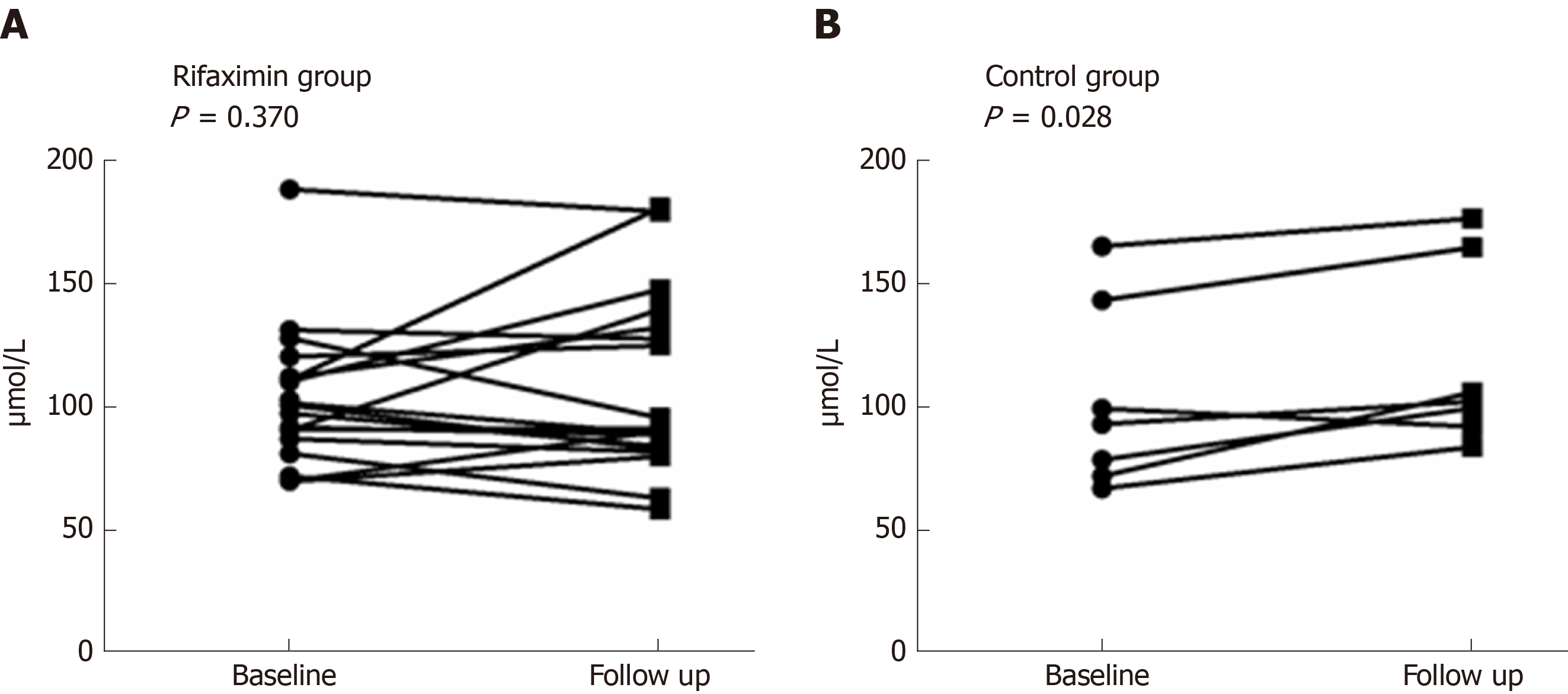
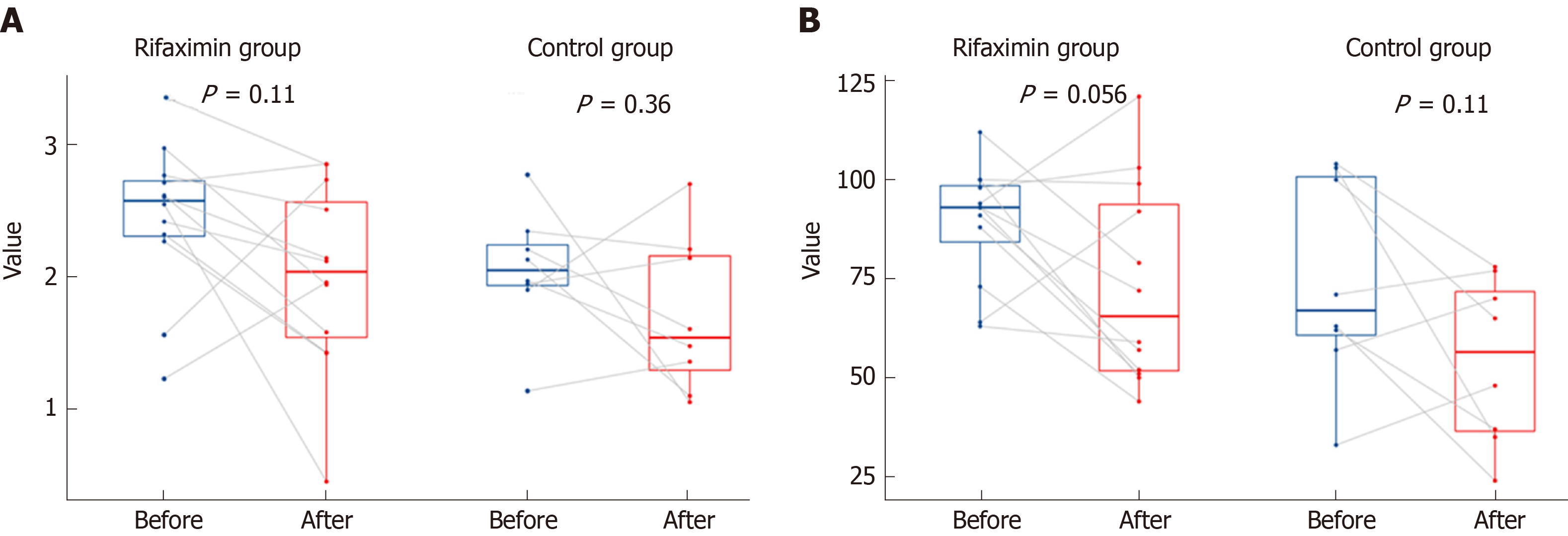
Figure 3 Changes in the concentration of Scr after treatment in patients with renal dysfunction.
A: A downtrend in the rifaximin group; B: An uptrend in the control group.
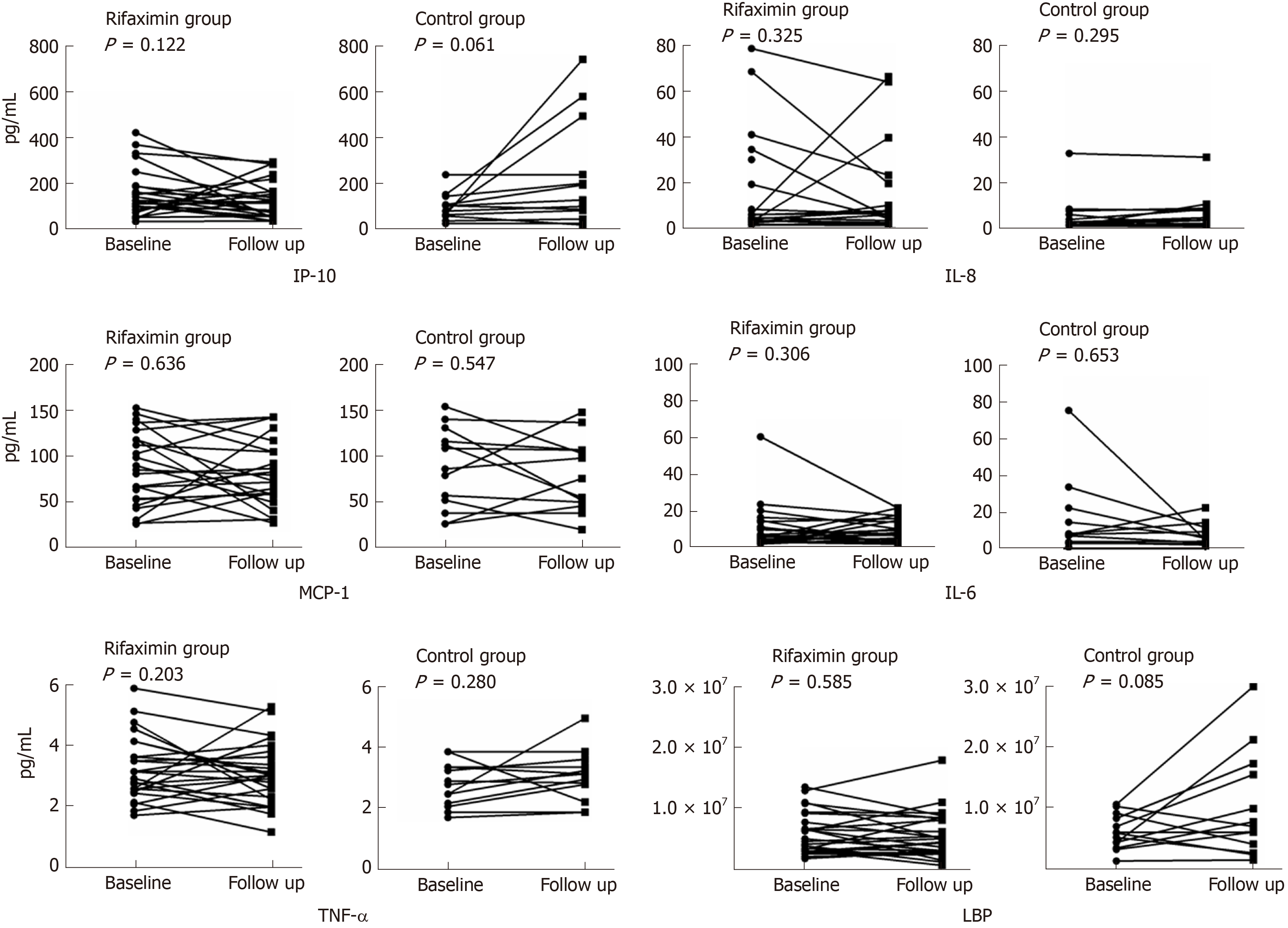
Figure 4 Changes in inflammatory factors and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein after treatment in the two groups.
The concentrations of interferon-inducible protein 10, tumour necrosis factor alpha, and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein showed a downtrend in the rifaximin group but uptrend in the control group, and interferon-inducible protein 10 decreased significantly in the rifaximin compared with the control group (Table 3). IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; LBP: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; IP-10: Interferon-inducible protein 10.
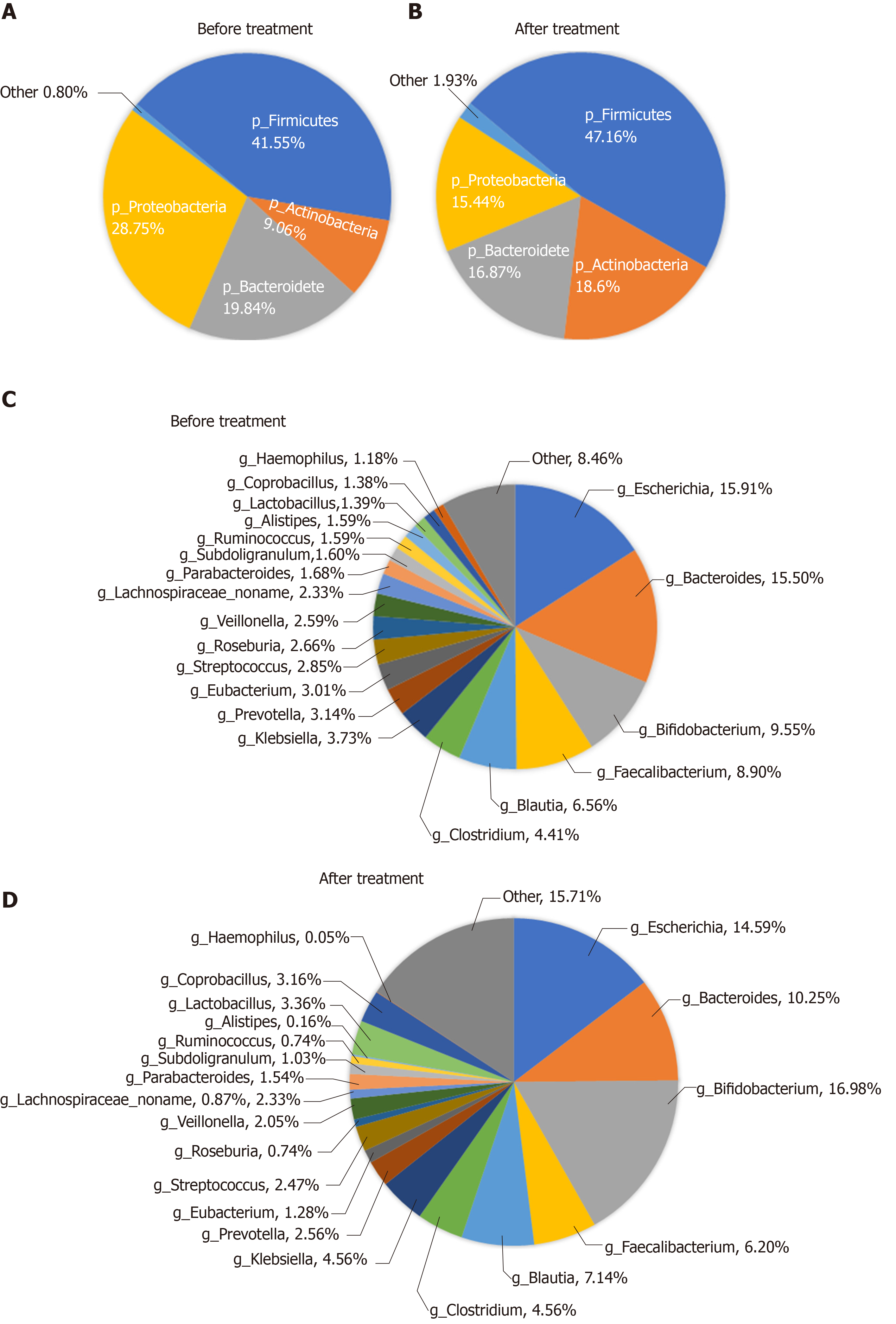
Figure 5 Abundance of the microbiota before and after treatment at the phylum and genus levels.
A and B: Phylum level; C and D: Genus level.
Figure 6 Changes in the Shannon index and Richness in patients of the two groups before and after treatment.
A: Changes in the Shannon index in patients of the two groups before and after treatment (no significant decrease); B: Changes in the Richness in patients of the two groups before and after treatment: (no significant decrease).
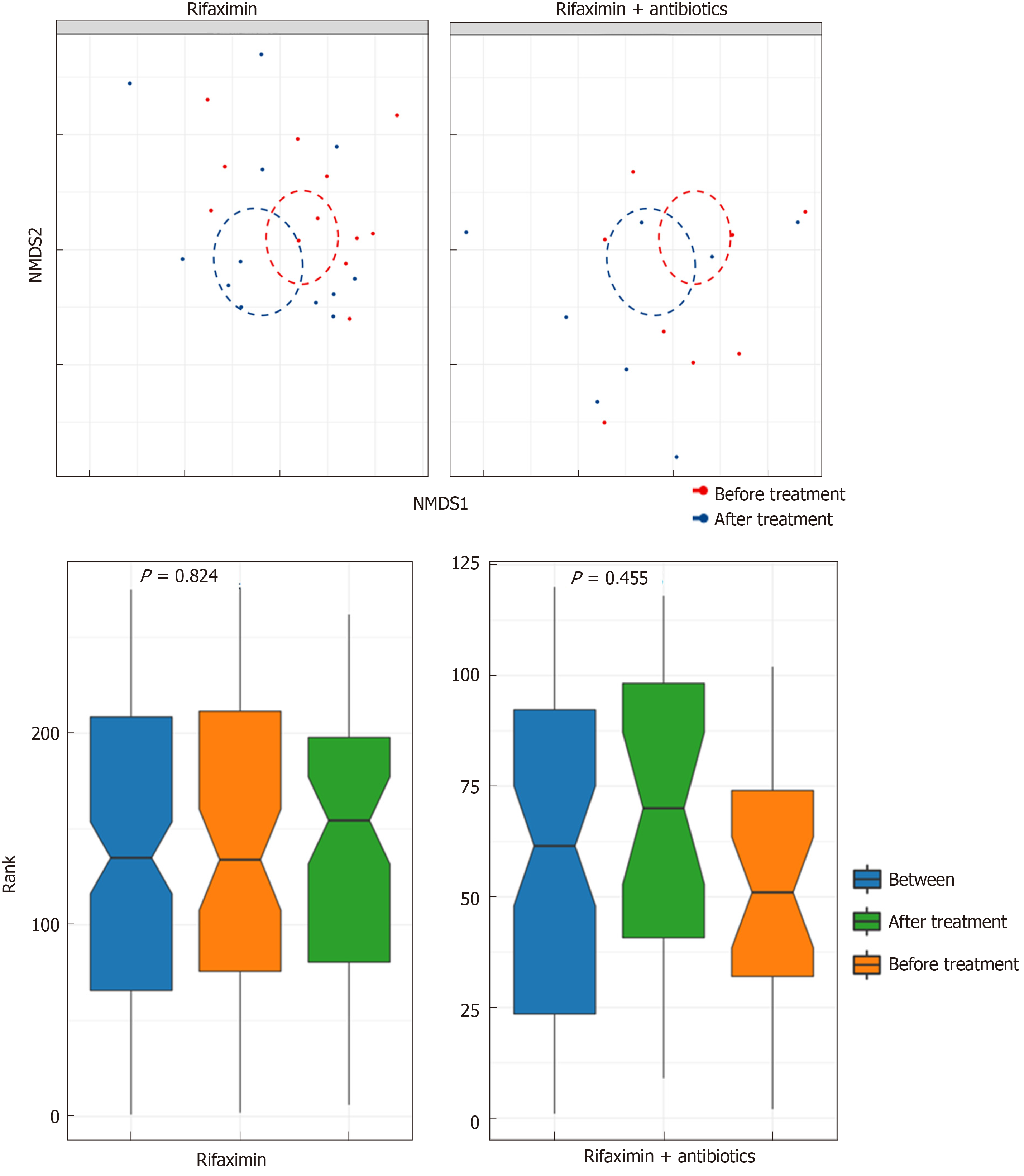
Figure 7 Change in the beta diversity of patients in the two groups before and after treatment.
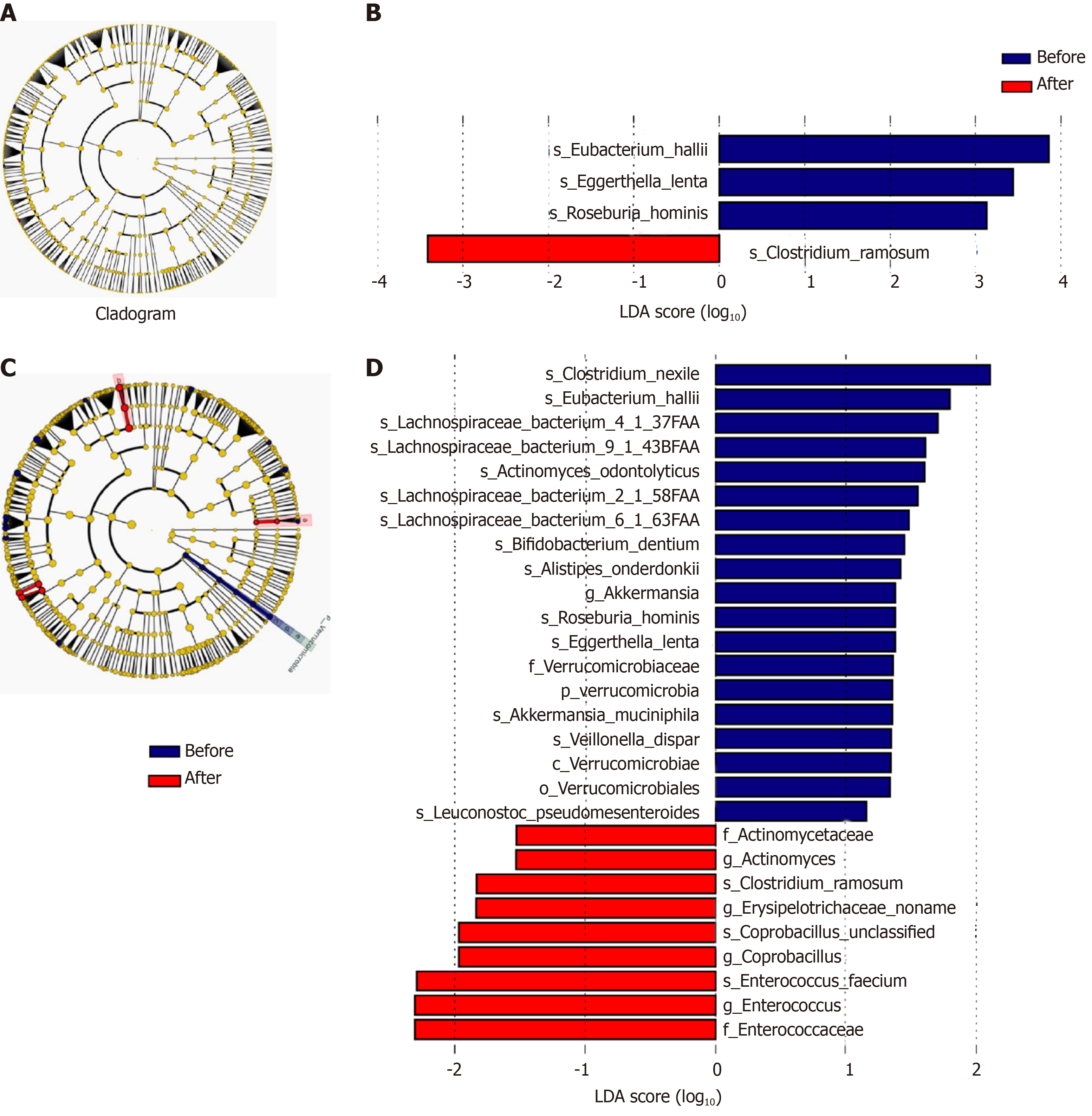
Figure 8 Cladogram and Linear discriminant analysis score of Lefse analysis of patients in the subgroup of rifaximin and rifaximin plus intravenous antibiotics.
A and B: Subgroup of rifaximin; C and D: Rifaximin plus intravenous antibiotics. The taxonomic levels are shown in the cladograms, represented by rings with kingdoms at the innermost ring and genera at the outermost ring, the small circles at each classification level represent different classifications at that level, and the diameters represent the relative abundance. Yellow represents no significant difference while blue and red represent significantly different microbiota before and after treatment, respectively. The Linear discriminant analysis score shows significant differences at > 2.0; red and blue represent before and after treatment, respectively, and the length represents the Linear discriminant analysis score, which is the degree of significant difference. LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
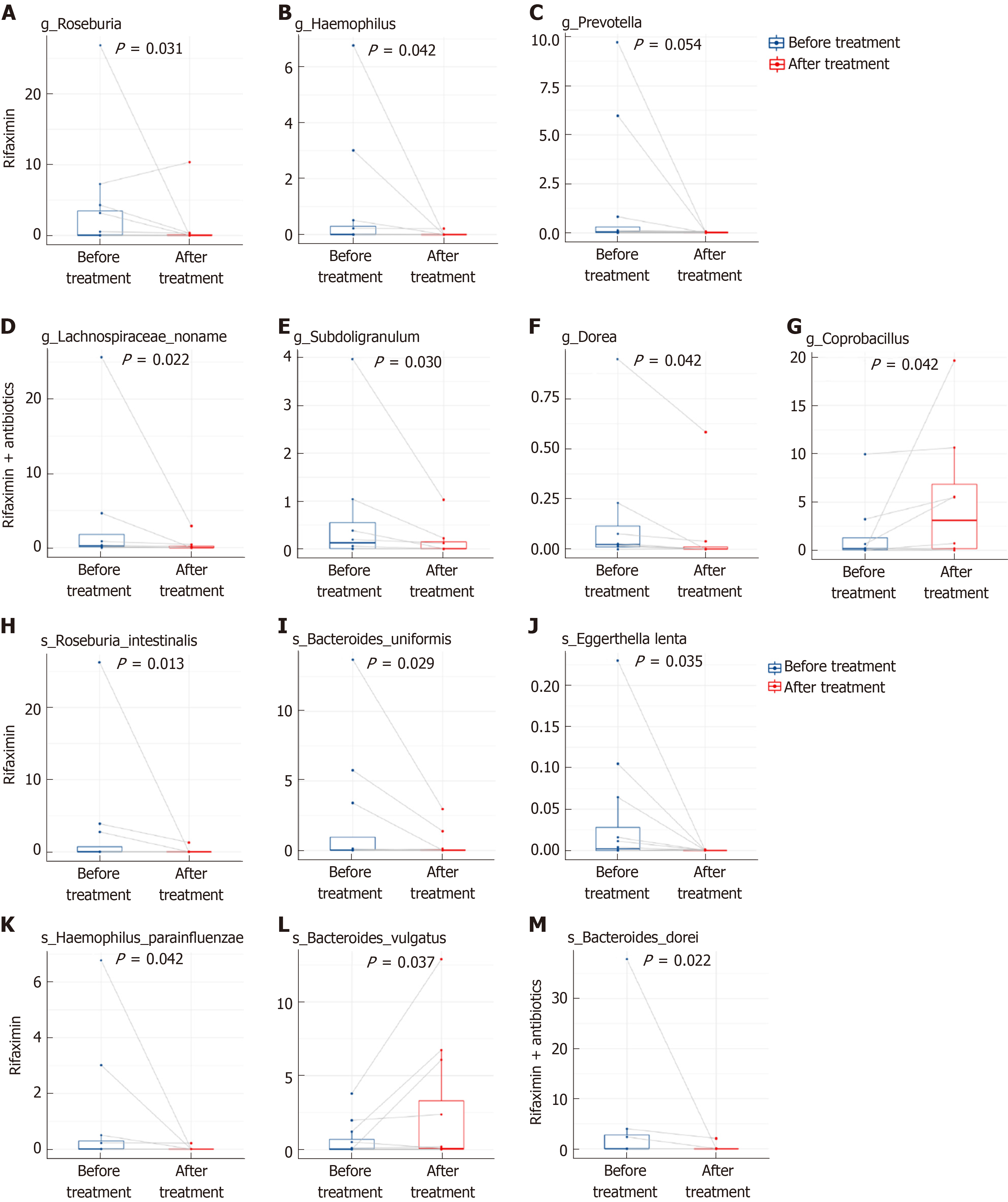
Figure 9 Abundance of microbiota with significant changes at the genus and species levels.
A-G: Abundance of microbiota with significant changes at the genus level; H-M: Abundance of microbiota with significant changes at the species level.
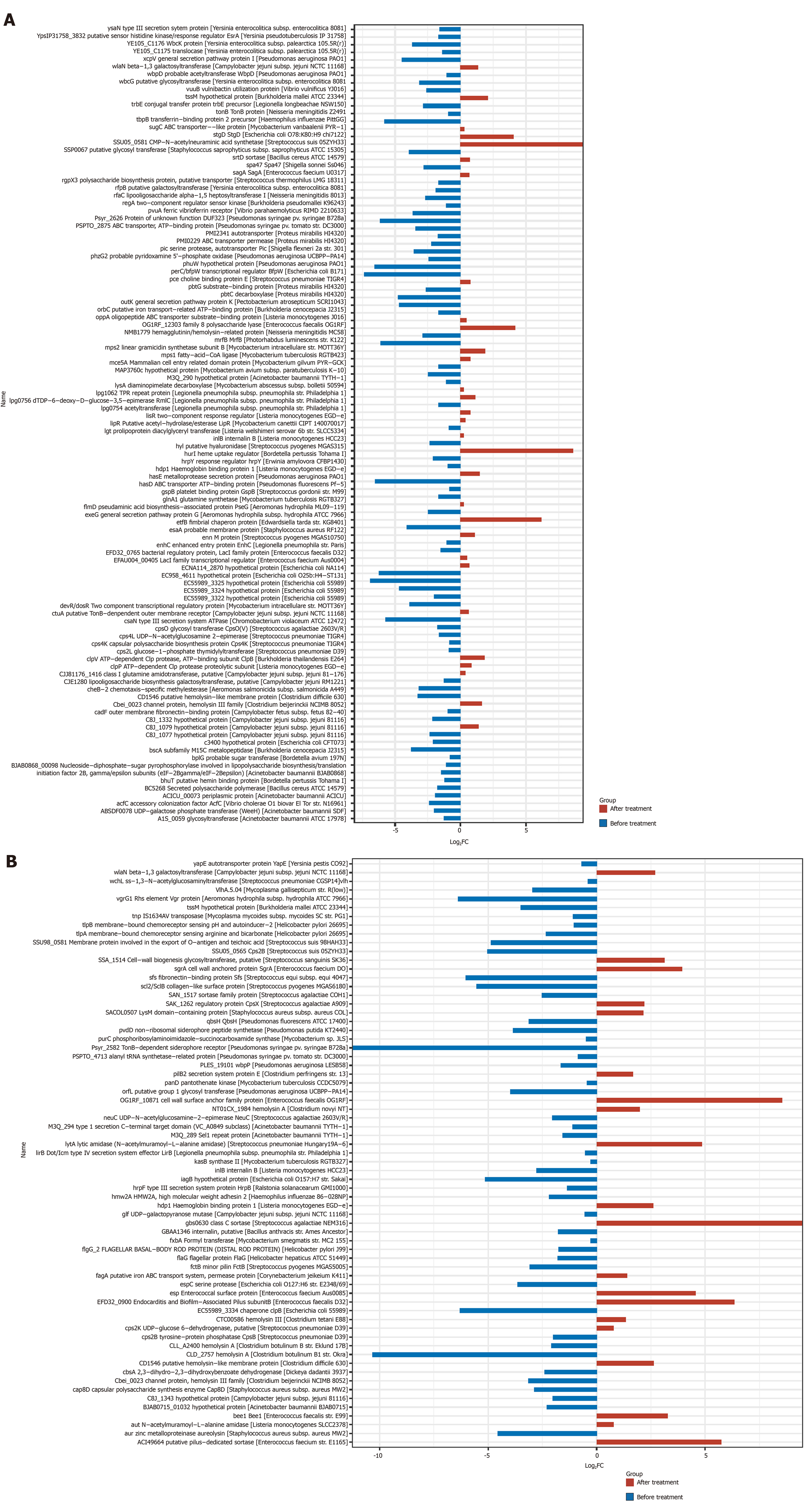
Figure 10 Expression of virulence factor genes before and after treatment with rifaximin and rifaximin plus intravenous antibiotics.
A: Treatment with rifaximin; B: Treatment with rifaximin plus intravenous antibiotics.
- Citation: Lv XY, Ding HG, Zheng JF, Fan CL, Li L. Rifaximin improves survival in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: A real-world study. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(2): 199-218
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i2/199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199