Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2019; 25(39): 5918-5925
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5918
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5918
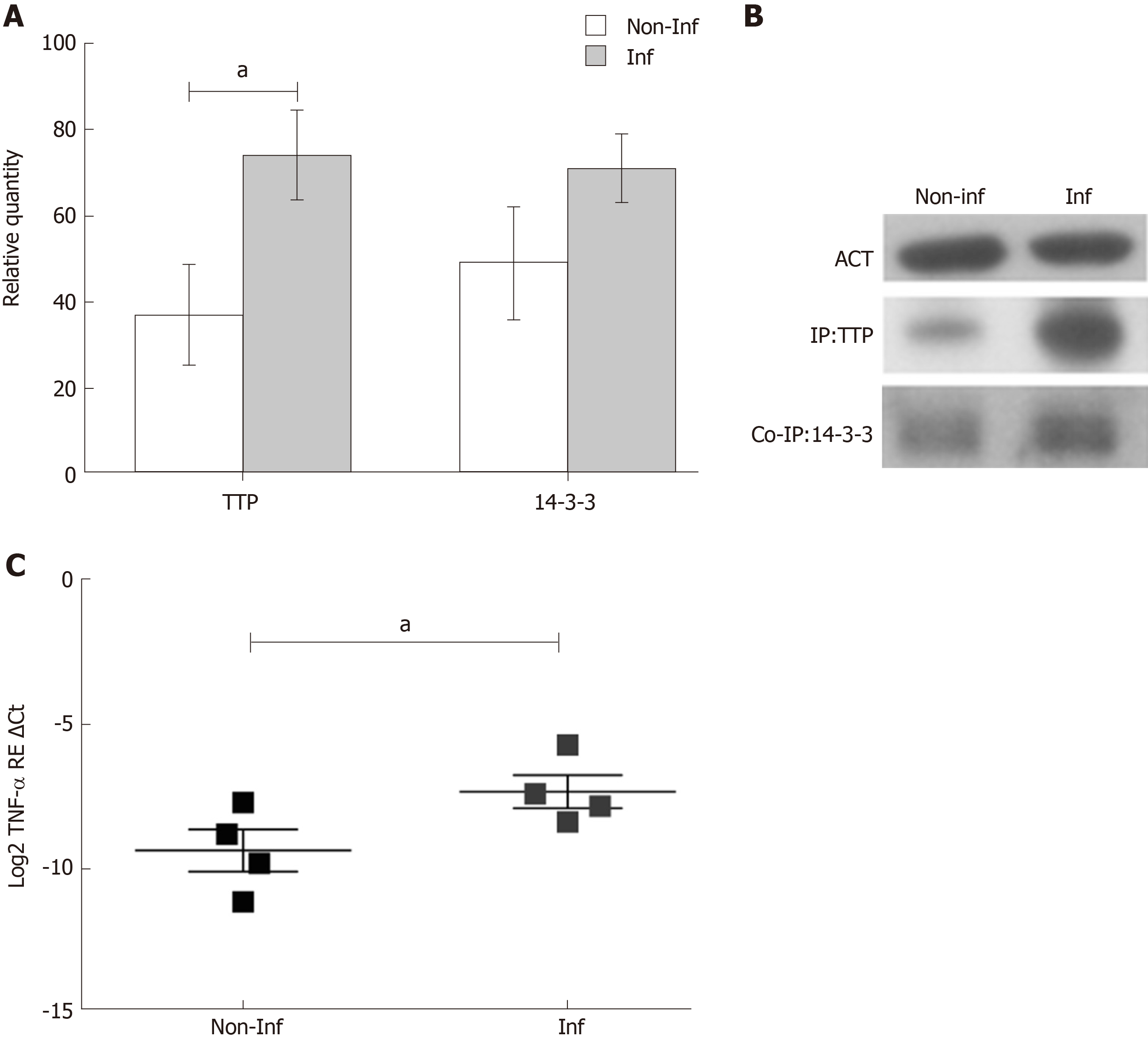
Figure 1 Tristetraprolin, 14-3-3 protein and tumor necrosis factor-α expression in colonic mucosa of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients.
A: Tristetraprolin (TTP) immunoprecipitated, 14-3-3 co-immunoprecipitated expressions in inflamed and non-inflamed frozen colonic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) tissues were calculated with respect to actin as loading control. Parametric t-test, TTP aP < 0.05; B: Representative image of immunoblot experiments; C: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) gene expression in inflamed and non-inflamed frozen colonic IBD tissues was calculated with respect to ribosomal protein lateral stalk subunit P0 (RPLP0) and expressed as Log2 of relative expression (RE) of ΔCt. Parametric t-test, TNF-α aP < 0.05. IP: Immunoprecipitated; Co-IP: Co-immunoprecipitated; Inf: Inflamed; Non-Inf: Non-inflamed; TTP: Tristetraprolin; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; ACT: Actin.
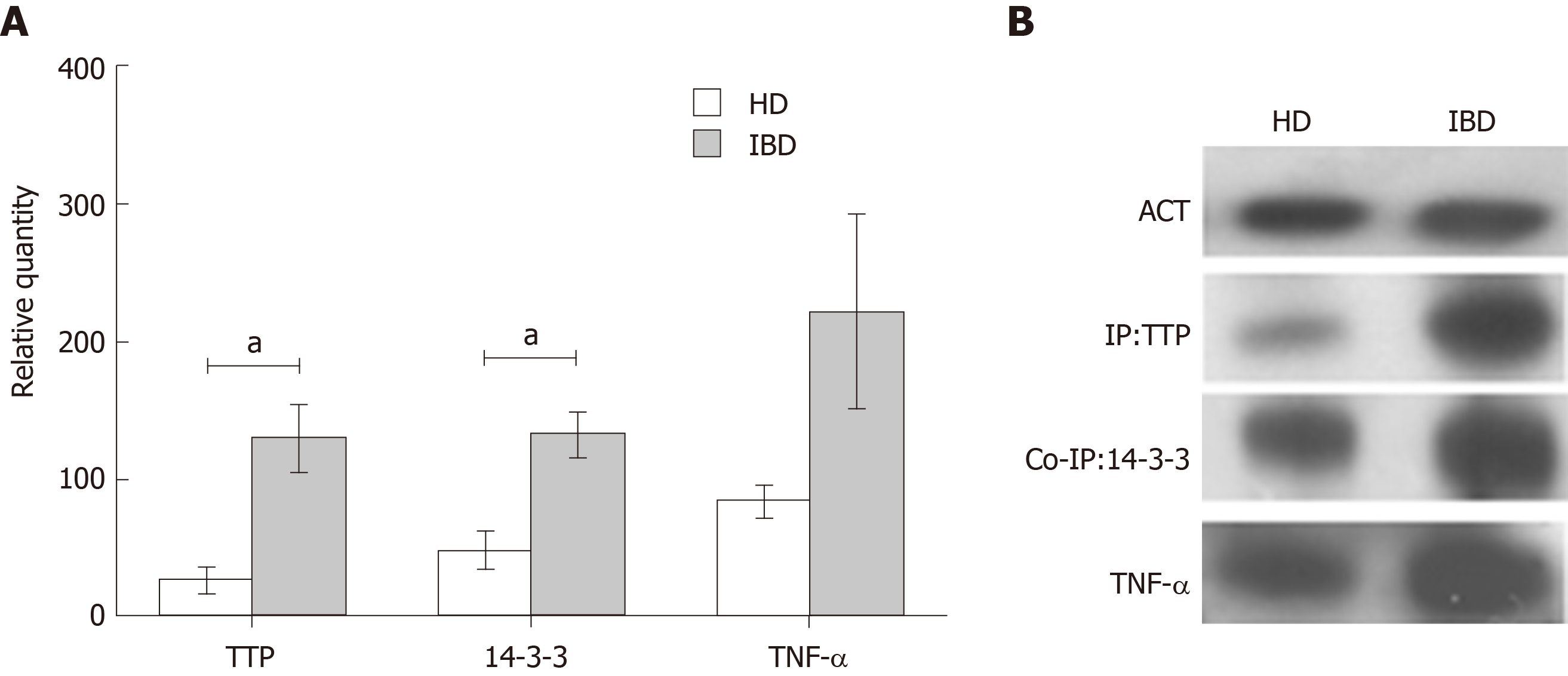
Figure 2 Tristetraprolin, 14-3-3 protein and tumor necrosis factor-α expression in macrophages of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients and healthy donors.
A: Tristetraprolin (TTP) immunoprecipitated, 14-3-3 co-immunoprecipitated and tumor necrosis factor-α expressions were normalized with actin (ACT) used as loading control. Mann–Whitney test TTP aP < 0.05, 14-3-3 aP < 0.05; B: Representative image of immunoblot experiments. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; HD: Healthy donors; TTP: Tristetraprolin; IP: Immunoprecipitated; Co-IP; Co-immunoprecipitated; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ACT: Actin.
- Citation: Di Silvestre A, Lucafò M, Pugnetti L, Bramuzzo M, Stocco G, Barbi E, Decorti G. Role of tristetraprolin phosphorylation in paediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(39): 5918-5925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i39/5918.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5918