Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2018; 24(40): 4565-4577
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565
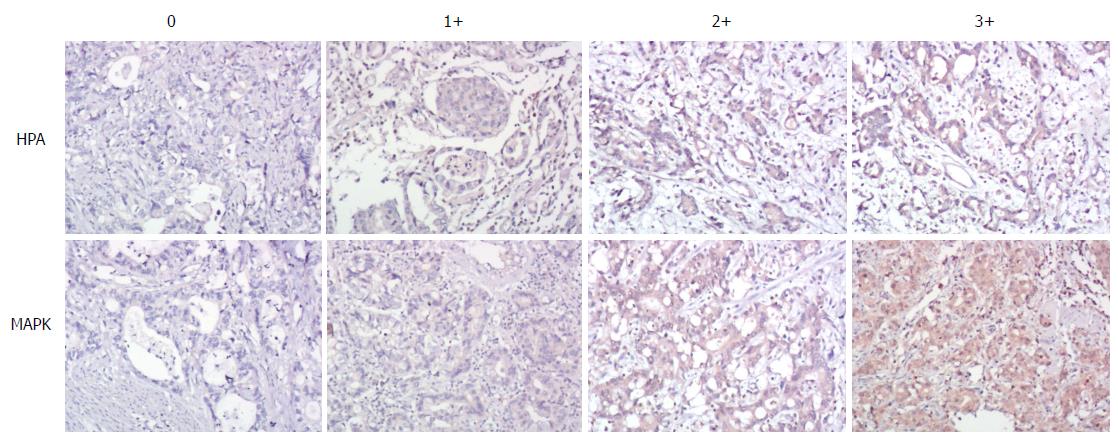
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical analysis of heparanase and mitogen-activated protein kinase protein expression in gastric cancer.
Expression of heparanase (HPA) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) was detected by immunohistochemical staining in normal gastric tissue. Representative immunohistochemical staining images are shown (magnification, 200 ×). HPA: Heparanase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
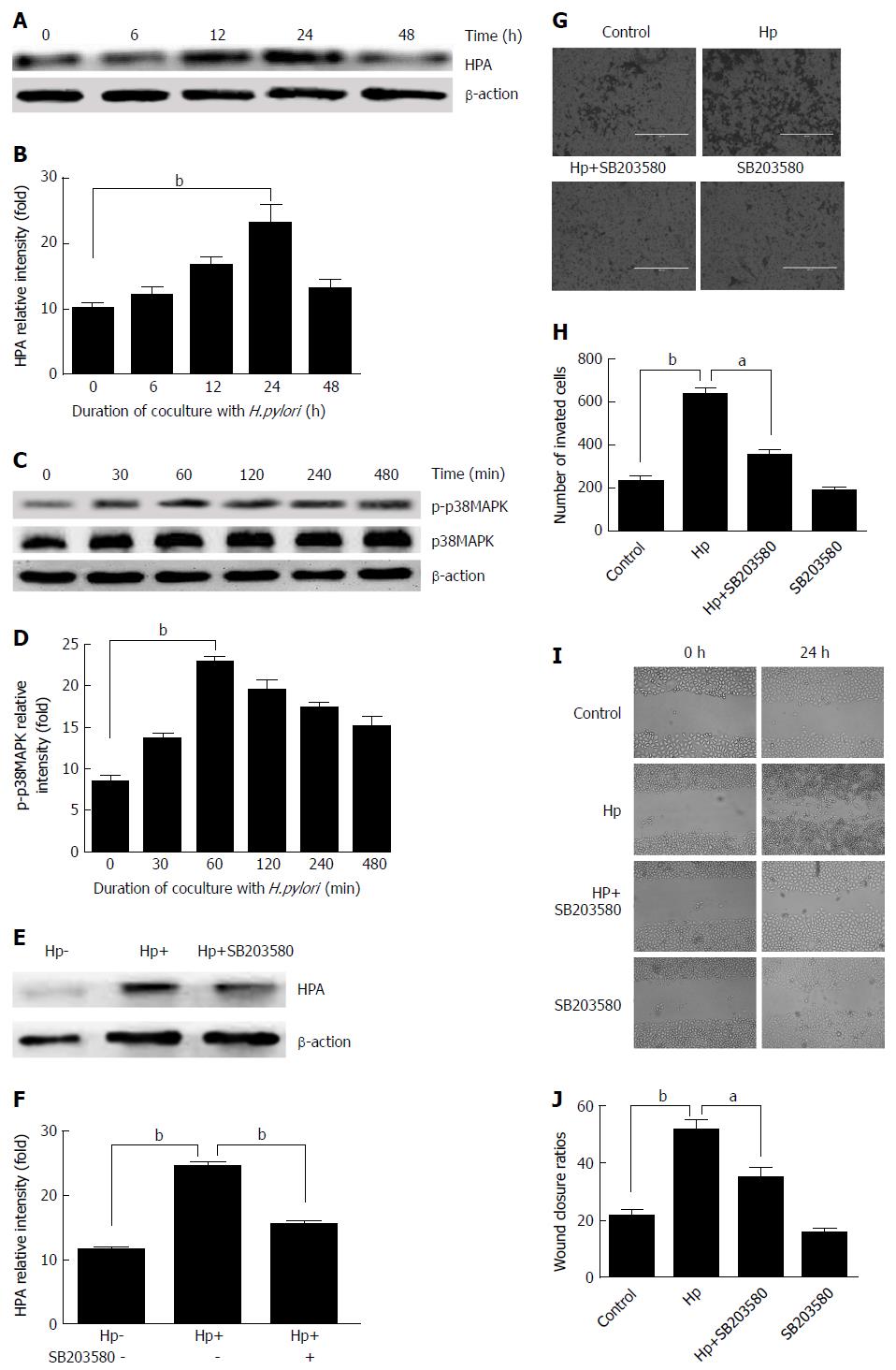
Figure 2 Heparanase protein expression following Helicobacter pylori infection in MKN-45 gastric cancer cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
A: Heparanase (HPA) expression was determined by Western blot at 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection; B: Quantitative Western blot results of HPA; C: p-p38MAPK expression was determined by Western blot at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 480 min after H. pylori infection; D: Quantitative Western blot results of p-p38MAPK; E: HPA expression when the MAPK inhibitor SB203580 was given to MKN-45 cells before H. pylori infection; F: Quantitative Western blot results of HPA when the MAPK inhibitor SB203580 was given. bP < 0.01 compared with the value at 0 h. G, H: Cell invasion rates in the three groups detected using a Transwell invasion assay. I, J: Migration rates in the three groups detected using a scratch migration assay. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. HPA: Heparanase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
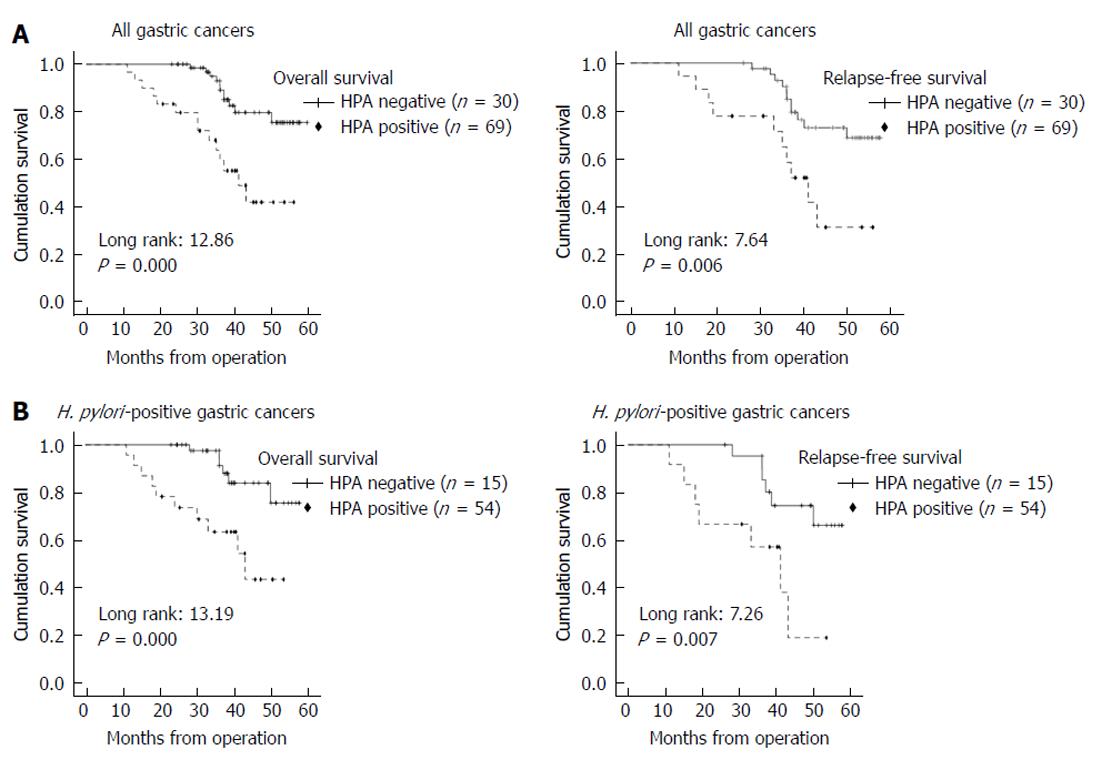
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival plots for overall survival and relapse-free survival according to heparanase expression and Helicobacter pylori infection status.
A: Heparanase (HPA) expression status (negative or positive) and the prognosis of all gastric cancer cases. HPA positive staining includes all cases of 1+, 2+, and 3+. HPA positive expression detected by immunohistochemical staining significantly predicts poor overall survival and relatively poor relapse-free survival; B: Kaplan-Meier survival according to HPA status in Helicobacter pylori positive gastric cancer cases. HPA positive expression significantly predicts poor overall survival as well as relapse-free survival. HPA: Heparanase; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
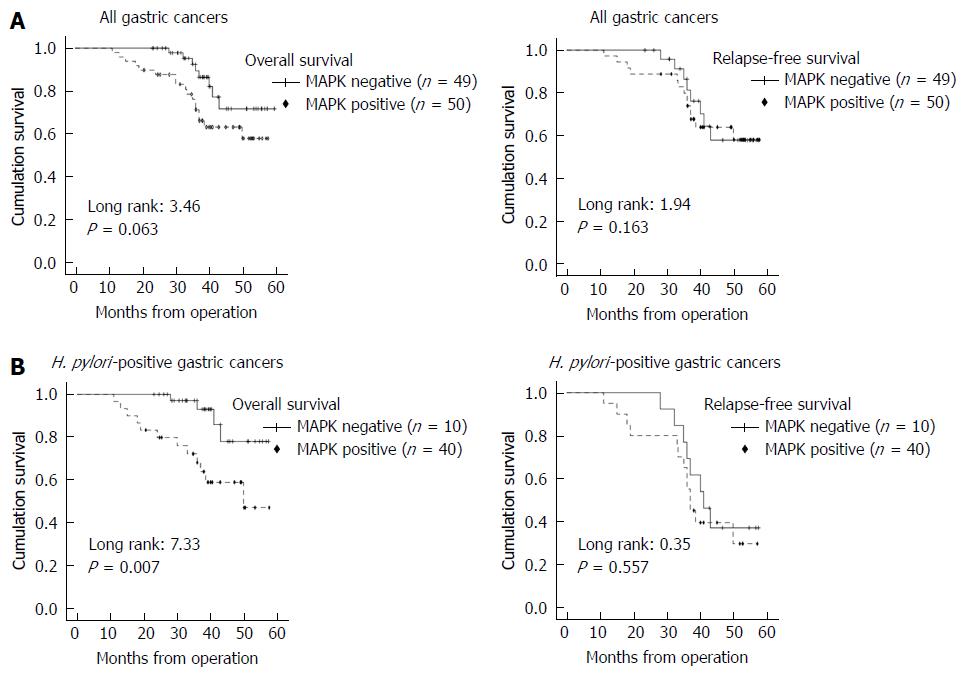
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival plots for overall survival and relapse-free survival according to mitogen-activated protein kinase expression and Helicobacter pylori infection status.
A: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) expression status (negative or positive) and prognosis of all gastric cancer cases. MAPK positive staining includes all cases of 1+, 2+, and 3+. MAPK positive expression detected by immunohistochemical staining cannot predict overall survival or relapse-free survival; B: Kaplan-Meier survival according to MAPK status in Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) positive gastric cancer cases. MAPK positive expression significantly predicts poor overall survival in H. pylori positive gastric cancer cases, but does not predict relapse free survival. MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Liu LP, Sheng XP, Shuai TK, Zhao YX, Li B, Li YM. Helicobacter pylori promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by enhancing heparanase expression. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(40): 4565-4577
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i40/4565.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4565