Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2018; 24(22): 2348-2362
Published online Jun 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i22.2348
Published online Jun 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i22.2348
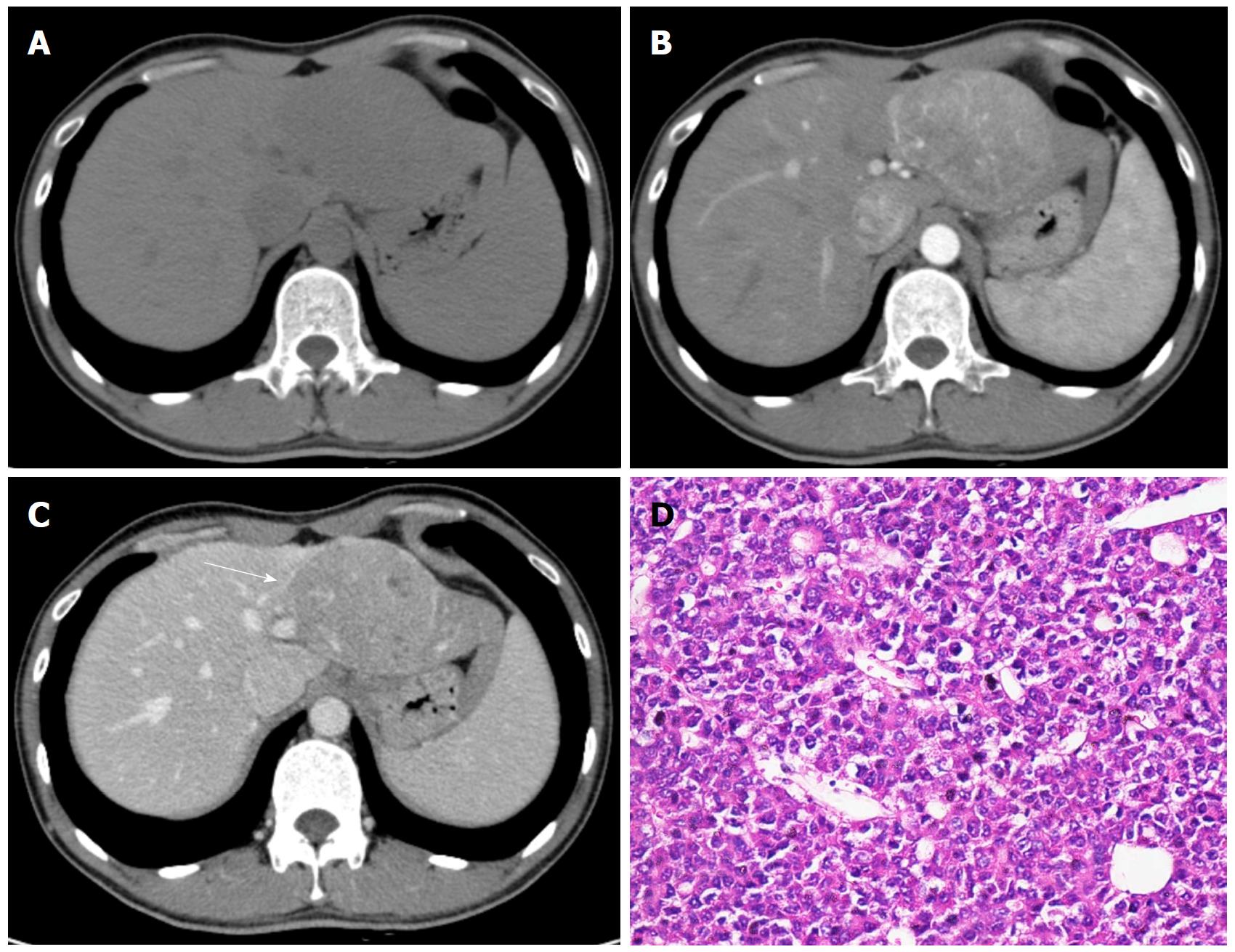
Figure 1 Hepatocellular carcinoma in a 32-year-old male with chronic hepatitis B.
Axial dynamic non-enhanced (A), late arterial phase (B), and portal venous phase (C) CT images show the 8.5 cm mass with arterial phase hyperenhancement and portal venous phase wash-out appearance. The capsule is seen as a hyperattenuating ring on portal venous phase (C, white arrow). The hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of the mass at 200 × magnification proved it to be Edmonson-Steiner grade II (D).
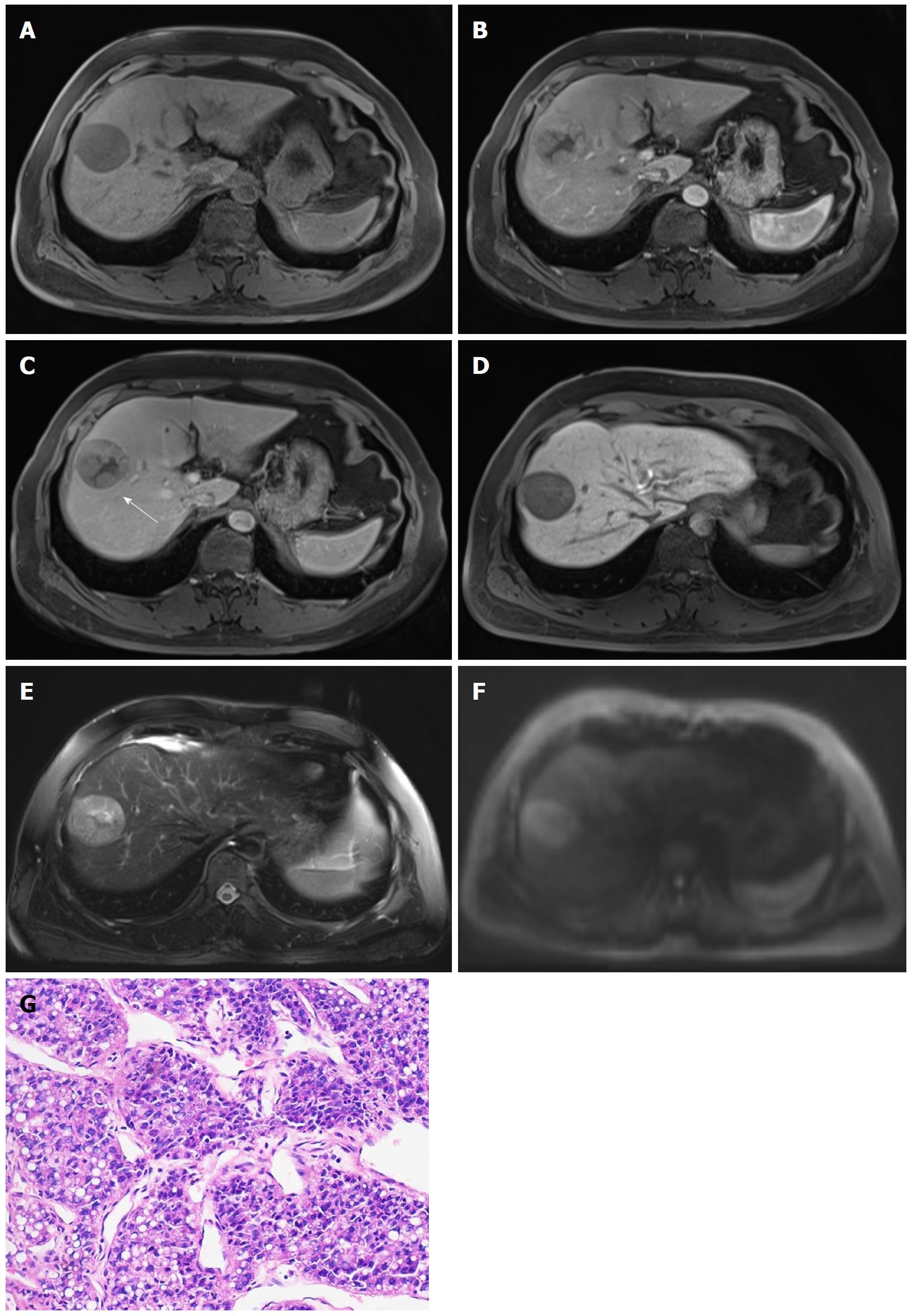
Figure 2 Hepatocellular carcinoma in 47-year-old male with chronic hepatitis B.
4.7-cm-sized mass in right anterior hepatic section shows hypointensity on unenhanced T1-weighted image (A), hyperenhancement in arterial phase (B), hypointensity relative to the surrounding liver parenchyma in portal venous phase (C), and 20 min hepatobiliary phase (D). An enhancing capsule (white arrow, the peripheral rim of smooth enhancement) in portal venous phase, mosaic architecture, intermediate hyperintensity on T2-weighted images (E), and restricted diffusion (F) are also visible. The mass was confirmed as Edmonson-Steiner grade II at 200 × magnification with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining (D).
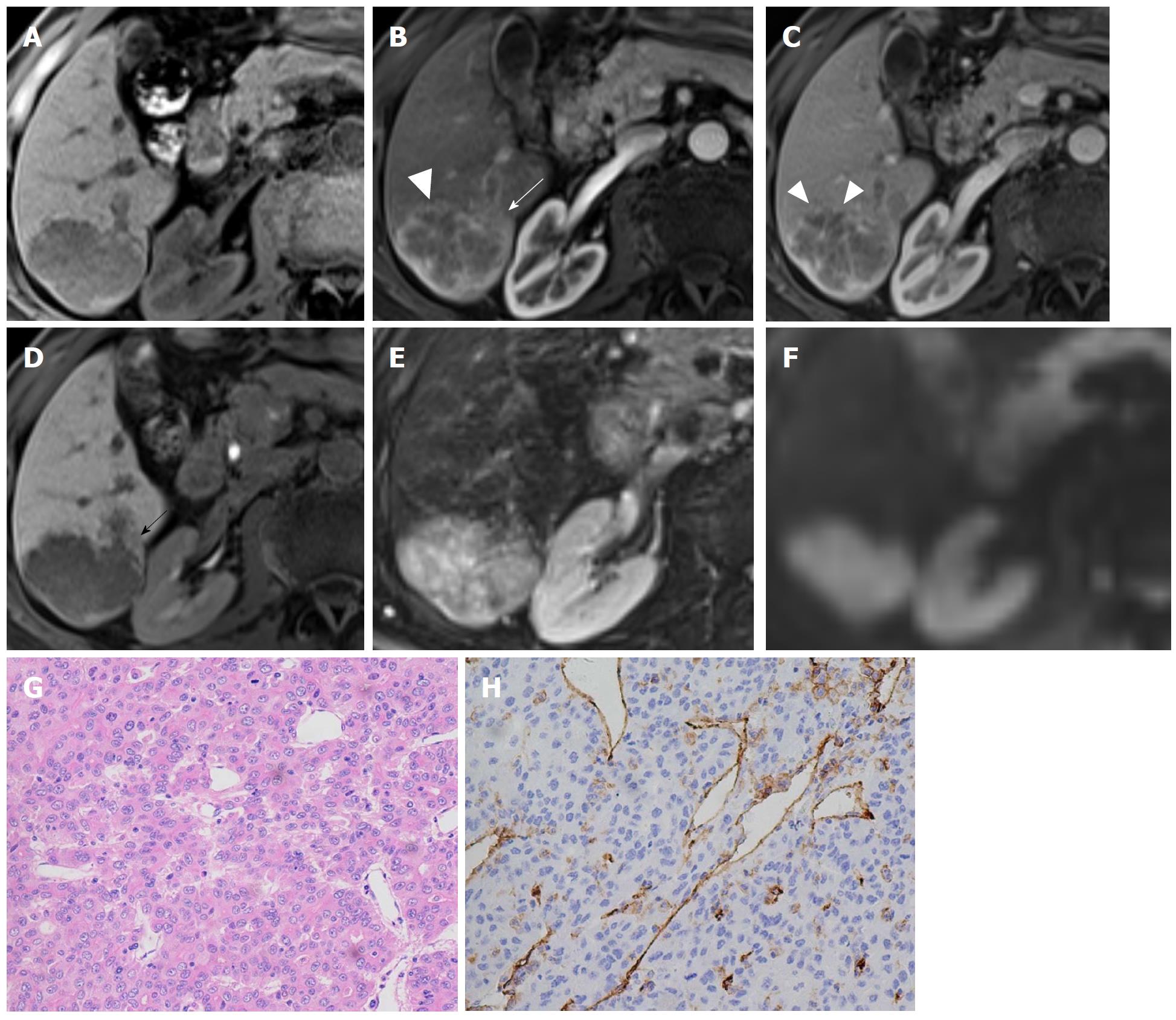
Figure 3 Hepatocellular carcinoma in a 71-year-old male with recognized cirrhosis.
Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR image demonstrates a 5.3 cm lobulated HCC in right posterior section of liver. The lesion shows peritumor enhancement in arterial phase (B, white arrow) and peritumor hypointense (D, black arrow) in hepatobiliary phase. Capsular disruption and non-smooth tumor margin are present (white triangles) in arterial phase (B) and portal venous phase (C). The lesion was histopathologically proven to be Edmonson-Steiner III grade with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining at 200 × magnification (G). Prominent microvascular invasion was detected at 200 × magnification with CD31 immunohistochemical staining (H).
- Citation: Jiang HY, Chen J, Xia CC, Cao LK, Duan T, Song B. Noninvasive imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: From diagnosis to prognosis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(22): 2348-2362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i22/2348.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i22.2348