Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2018; 24(20): 2191-2202
Published online May 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i20.2191
Published online May 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i20.2191
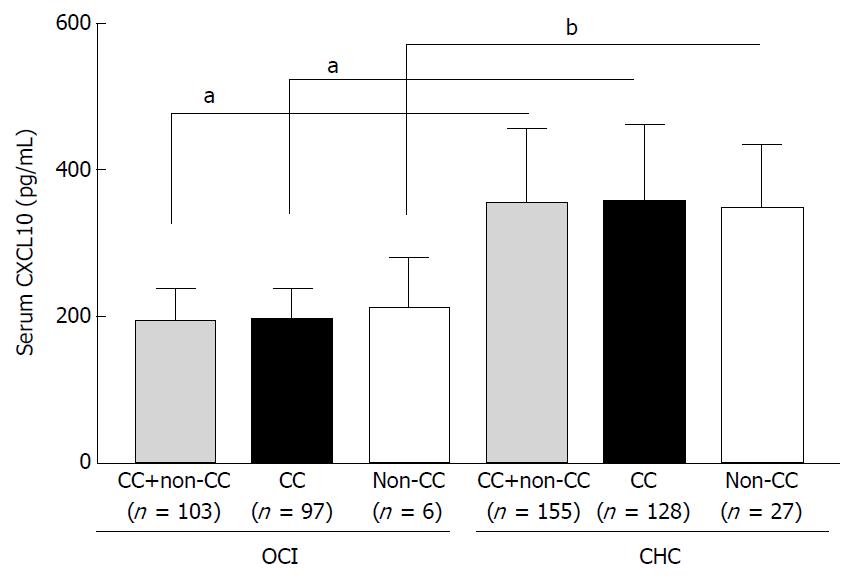
Figure 1 Serum CXCL10 levels in occult hepatitis C virus infection patients with different variants of IL-28B rs12979860 (C/C or non-C/C) as compared to chronic hepatitis C virus infection patients.
aP < 0.0001; bP = 0.001. OCI: Occult hepatitis C virus infection; CHC: Chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
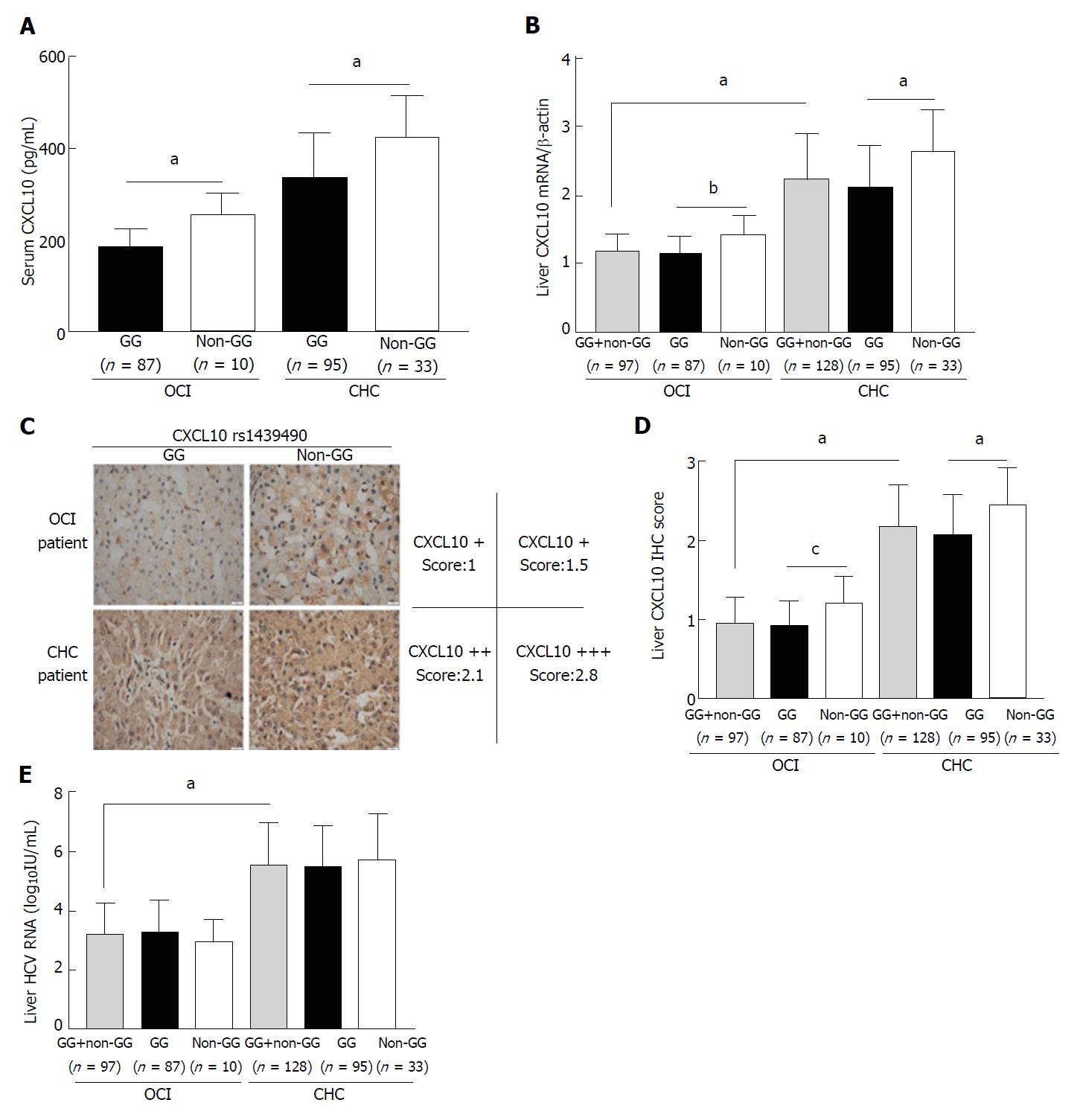
Figure 2 Comparison of serum CXCL10 levels (A), liver CXCL10 mRNA levels (B), representative (C) and grouped (D) liver CXCL10 IHC scoring, and liver hepatitis C virus RNA levels (E) among IL-28B rs12979860 C/C patients with different CXCL10 rs1439490 polymorphisms.
aP < 0.0001; bP = 0.003; cP = 0.009. OCI: Occult hepatitis C virus infection; CHC: Chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
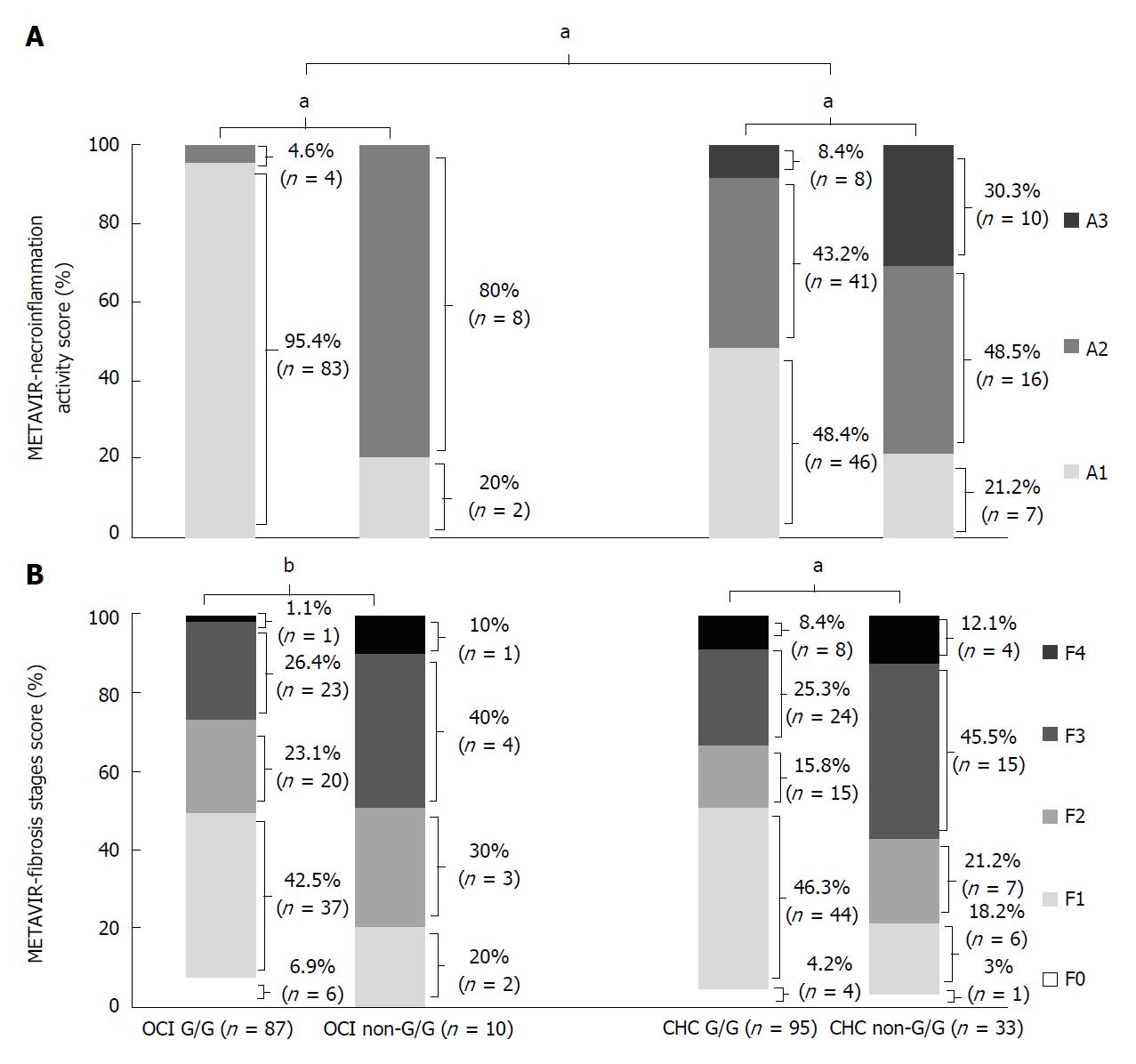
Figure 3 METAVIR necroinflammation activity (A) and fibrosis stage scores of patients with IL-28B rs12979860 CC genotype (B).
aP < 0.0001; bP = 0.04. OCI: Occult hepatitis C virus infection; CHC: Chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
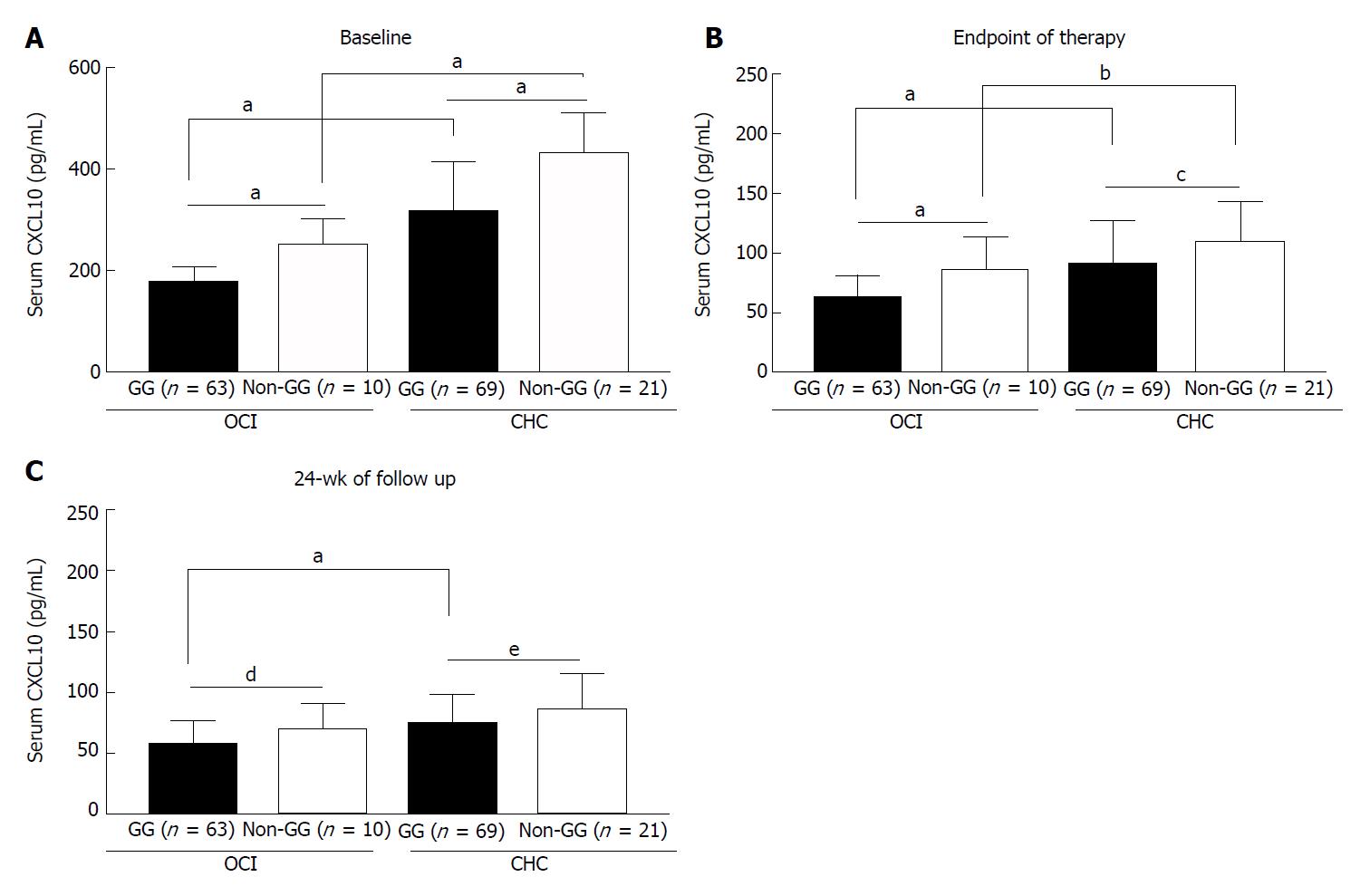
Figure 4 Effect of antiviral therapy on serum CXCL10 levels of IL-28 rs12979860 C/C patients with different CXCL10 G-201A single nucleotide polymorphisms.
A: The baseline serum CXCL10 levels of IL-28 rs12979860 C/C patients who completed the Peg-IFNα plus ribavirin treatment; B-C: The serum CXCL10 levels of the patients at the endpoint of antiviral treatment (B) and at 24 wk follow up (C); aP < 0.0001; bP = 0.038; cP = 0.008; dP = 0.008; eP = 0.009. OCI: Occult hepatitis C virus infection; CHC: Chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
- Citation: Wang X, Wang S, Liu ZH, Qi WQ, Zhang Q, Zhang YG, Sun DR, Xu Y, Wang HG, Li ZX, Cong XL, Zhao P, Zhou CY, Wang JB. Regulatory polymorphism of CXCL10 rs1439490 in seronegative occult hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(20): 2191-2202
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i20/2191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i20.2191