Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8256-8260
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8256
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8256
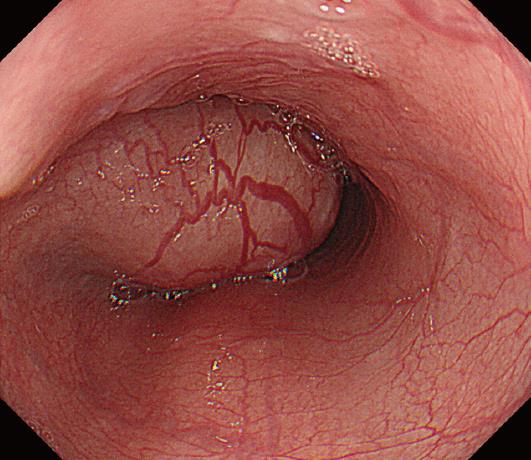
Figure 1 Endoscopic findings.
The submucosal tumor is observed at 27-33 cm from the incisors. The endoscope could be passed beyond the tumor.
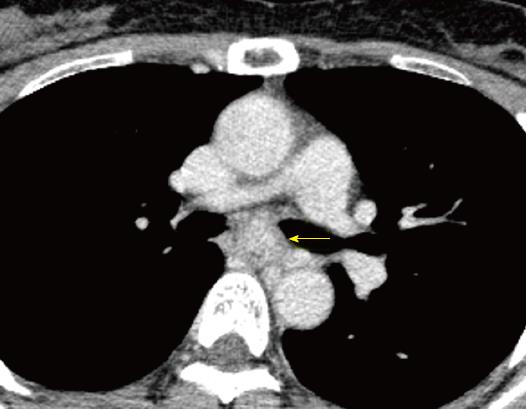
Figure 2 Computed tomography images.
Computed tomography reveals a well demarcated, heterogeneous, esophageal tumor in the mid-thoracic esophagus (arrow). The longitudinal diameter of the tumor was 60 mm.
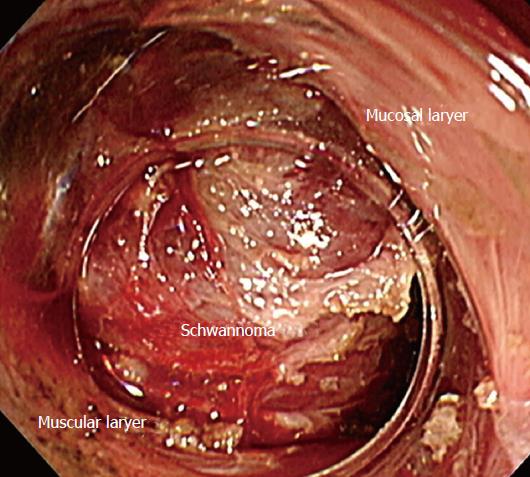
Figure 3 Endoscopic procedure.
The esophageal schwannoma is visible through the submucosal tunnel created proximal to its cranial edge. The mucosal and muscular layers are dissected free of the tumor.
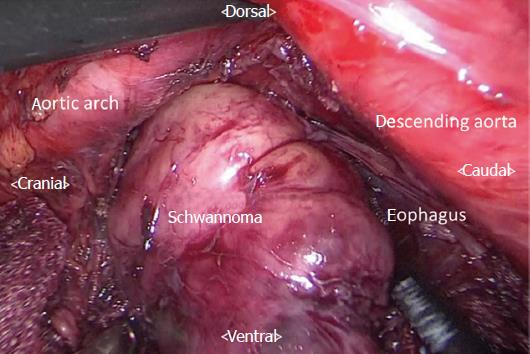
Figure 4 Thoracoscopic procedure in the prone position, with access via the left thoracic cavity.
The cranial aspect of the tumor was already dissected free of the adjacent structures by endoscopic procedure. The part of the esophageal schwannoma that was not dissected endoscopically is removed from the submucosal space after incising the muscular layer of the esophagus, thoracoscopic method.
- Citation: Onodera Y, Nakano T, Takeyama D, Maruyama S, Taniyama Y, Sakurai T, Heishi T, Sato C, Kumagai T, Kamei T. Combined thoracoscopic and endoscopic surgery for a large esophageal schwannoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8256-8260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8256.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8256