Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2017; 23(37): 6802-6816
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6802
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6802
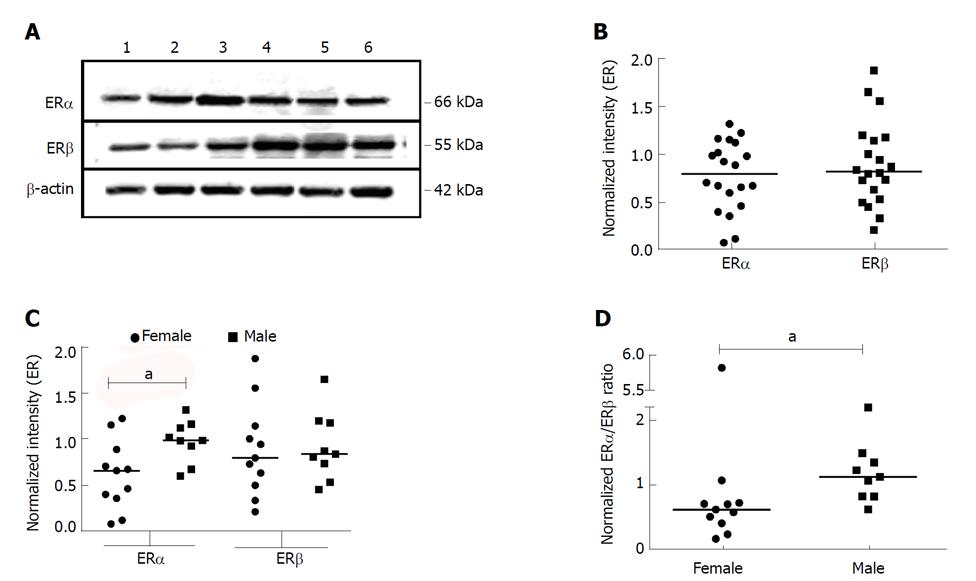
Figure 1 Expression of estrogen receptor subtypes in whole tissue lysates from normal male and female subjects.
A: Whole tissue lysates from liver tissues of normal donors were subjected to Western blotting and probed with antibodies against ERα, ERβ and β-actin. A representative blot is shown. B-D: The bands corresponding to ERα, ERβ and β-actin were quantified by densitometric analyses using ImageJ. Each symbol represents one individual. Expression of the ER subtypes was normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted (B). Gender-based ER subtype expression was evaluated by segregating the gender and plotted (C). The ERα:ERβ expression ratio was also plotted for each gender group (D). aP < 0.05 was considered significant. ER: Estrogen receptor.
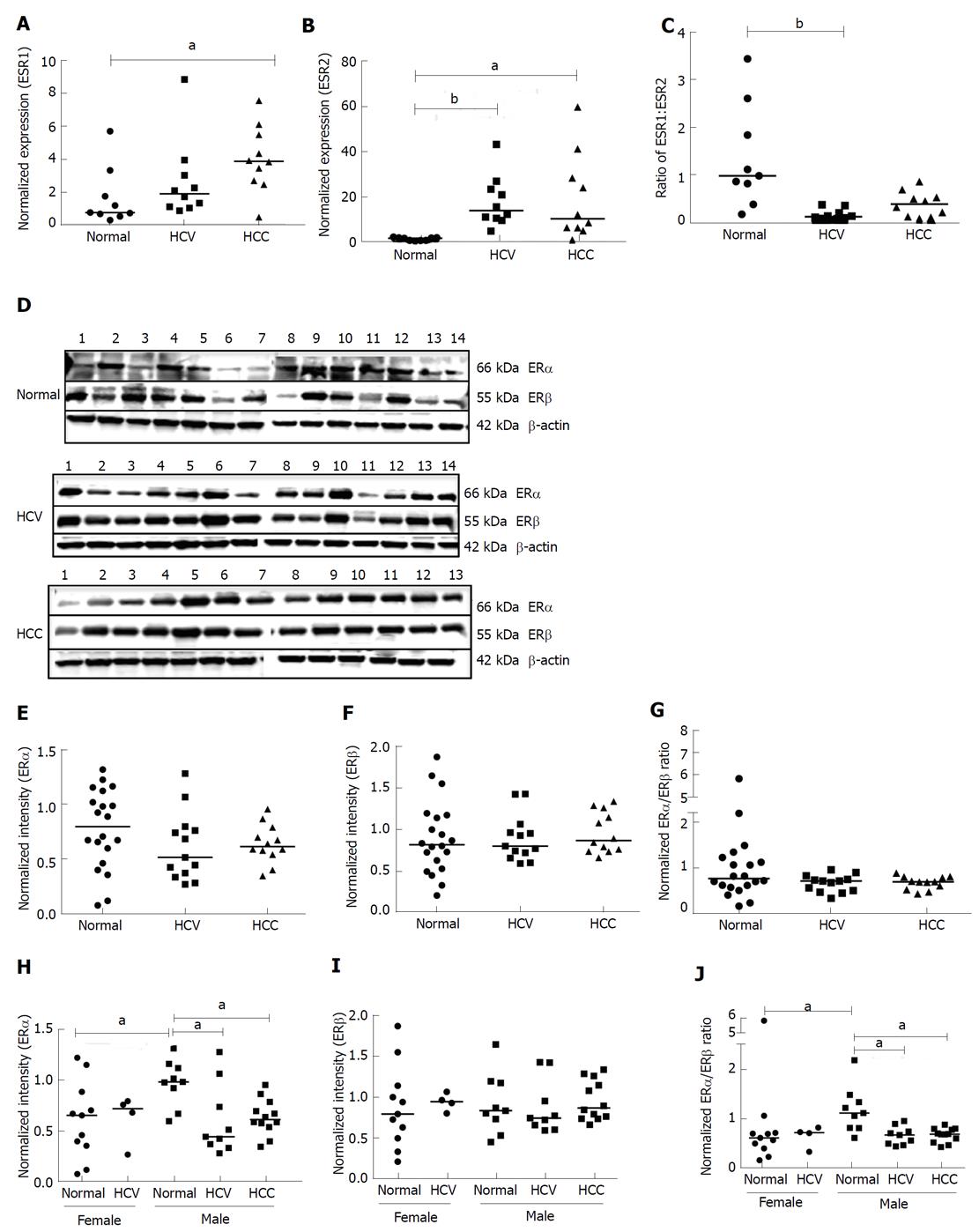
Figure 2 Expression of estrogen receptor subtypes from normal and diseased subjects.
A-C: Total RNA extracted from normal, HCV-related cirrhosis and HCV-related HCC livers was subjected to RT-PCR. The abundance of ESR1 (A) and ESR2 (B) transcripts was determined by real time PCR and normalized to the expression of HPRT. ESR1:ESR2 expression ratio was also plotted for the three groups (C). aP < 0.05 or bP < 0.001 was considered significant. D: Whole tissue lysates from liver tissues of normal, HCV and HCC subjects were subjected to Western blotting and probed with antibodies against ERα, ERβ and β-actin. Representative blots for each group are depicted. E-J: The bands corresponding to ERα, ERβ and β-actin were quantified by densitometric analyses using ImageJ. Expression of the ERα and ERβ was normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted (E and F). The ERα:ERβ expression ratio was also plotted for normal, HCV and HCC group (G). Expression of ER subtypes and ERα:ERβ expression ratio in the male population of normal, HCV and HCC groups was plotted separately (H-J). aP < 0.05 was considered significant. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor.
Figure 3 Expression of estrogen receptor subtypes in nuclear and cytoplasmic tissue lysates from normal and diseased subjects.
A: Lysates prepared from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of liver tissues from normal, HCV and HCC subjects were subjected to Western blotting and probed with antibodies against ERα, ERβ, β-actin, histone (nuclear lysates only) and GAPDH (cytoplasmic lysates only). Representative blots for each group are depicted. B-G: The bands corresponding to ERα, ERβ and β-actin were quantified by densitometric analyses using ImageJ. Expression of the ERα and ERβ was normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted with (B and C). The ERα:ERβ expression ratio was also plotted for normal, HCV and HCC group (D). Expression of ER subtypes and ERα:ERβ expression ratio in the male population of normal, HCV and HCC groups was plotted separately (E-G). aP < 0.05 or bP < 0.001 was considered significant. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor.
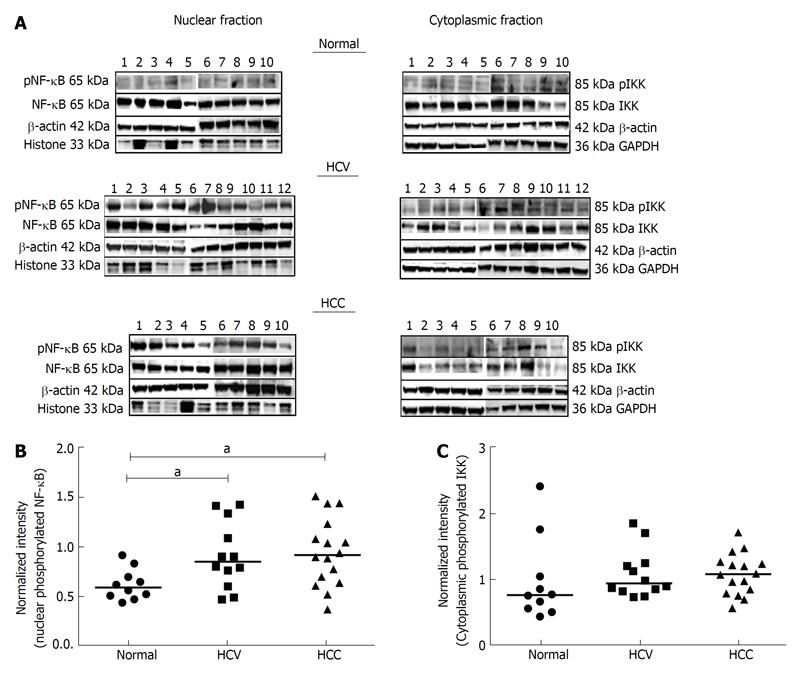
Figure 4 Expression of pNF-κB and pIKK in nuclear and cytoplasmic tissue lysates from normal and diseased subjects.
A: Lysates prepared from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of liver tissues from normal, HCV and HCC subjects were subjected to Western blotting. Nuclear tissue lysates were probed with antibodies against pNF-κB, NF-κB, β-actin, and histones while cytoplasmic tissue lysates were probed with antibodies against pIKK, IKK, β-actin and GAPDH. Representative blots for each group are depicted. B and C: The bands corresponding to pNF-κB, NF-κB, pIKK, IKK and β-actin were quantified by densitometric analyses using ImageJ. The ratio of pNF-κB:NF-κB was normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted (B). The ratio of pIKK:IKK was normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted with gender pooled (C) subjects. aP < 0.05 was considered significant. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor.
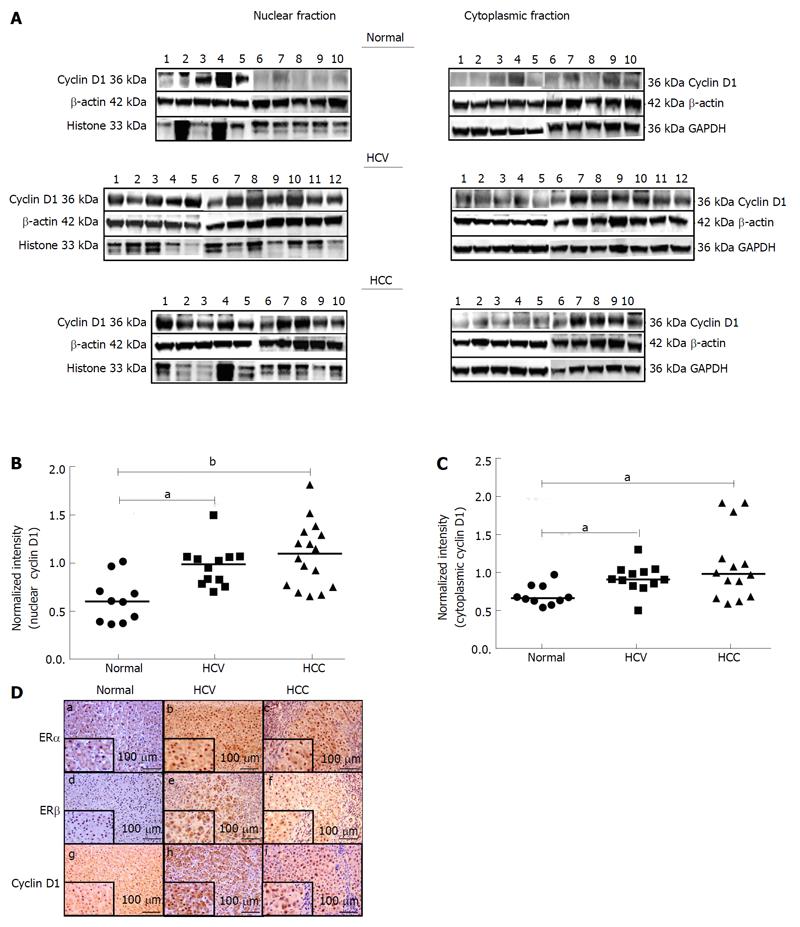
Figure 5 Expression of cyclin D1 in nuclear and cytoplasmic tissue lysates from normal and diseased subjects.
A: Lysates prepared from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of liver tissues from normal, HCV and HCC subjects were subjected to Western blotting and probed with antibodies against cyclin D1, β-actin, histones (nuclear lysates only) and GAPDH (cytoplasmic lysates only). Representative blots for each group are depicted. B and C: The bands corresponding to cyclin D1 and β-actin were quantified by densitometric analyses using ImageJ. Expression of cyclin D1 was normalized to the expression of β-actin in nuclear (B) and cytoplasmic (C) lysates and plotted. aP < 0.05 or bP < 0.001 was considered significant. D: Immunohistochemical staining of ERα, ERβ and cyclin D1 in normal (a, d, g), HCV-related cirrhosis (b, e, h) and HCV-related HCC (c, f, i) is depicted. A magnified region of the stained tissue section is depicted as an inset in each corresponding image. Scale bar = 100 μm. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Iyer JK, Kalra M, Kaul A, Payton ME, Kaul R. Estrogen receptor expression in chronic hepatitis C and hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(37): 6802-6816
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i37/6802.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6802