Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2017; 23(32): 5829-5835
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5829
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5829
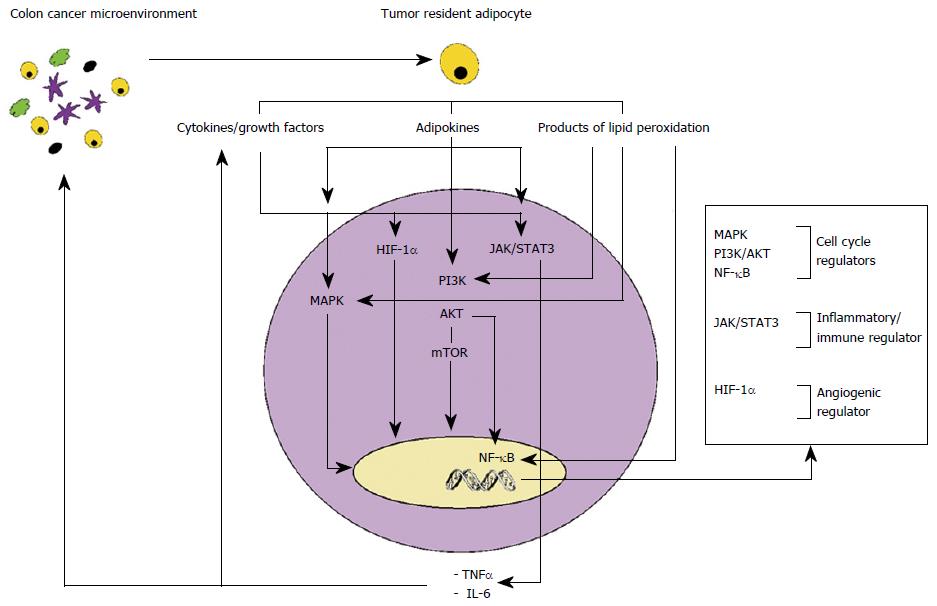
Figure 1 Signalling pathways activated by tumour resident adipocytes secreted factors.
Tumour resident adipocytes secreted factors activate cell cycle regulators and inflammatory/immune/angiogenic regulators. Cancer cell secreted inflammatory cytokines activate host cells of TME constituting a paracrine/autocrine loop. MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein Kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; JAK/STAT3: Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
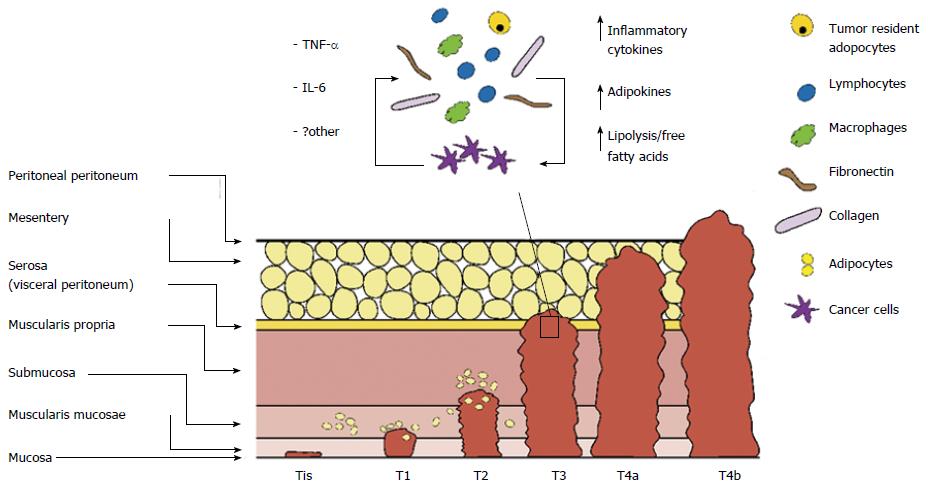
Figure 2 Colon cancer progression and tumour microenvironment.
Bi-directional cross-talk between host cells of tumour microenvironment (TME) contributes to colon cancer progression. Activated tumour resident adipocytes increase secretion of cytokines, growth factors, adipokines and release lipid metabolites promoting colon cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer cells secrete inflammatory factors which repopulate TME, further enhancing cancer cell proliferation. Tis: carcinoma in situ; T1: Tumour invades submucosa; T2: Tumour invades muscularis propria; T3: Tumour invades through muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues; T4a: Tumour penetrates to the surface of the visceral peritoneum; T4b: Tumour directly invades or is adherent to other organs or structures.
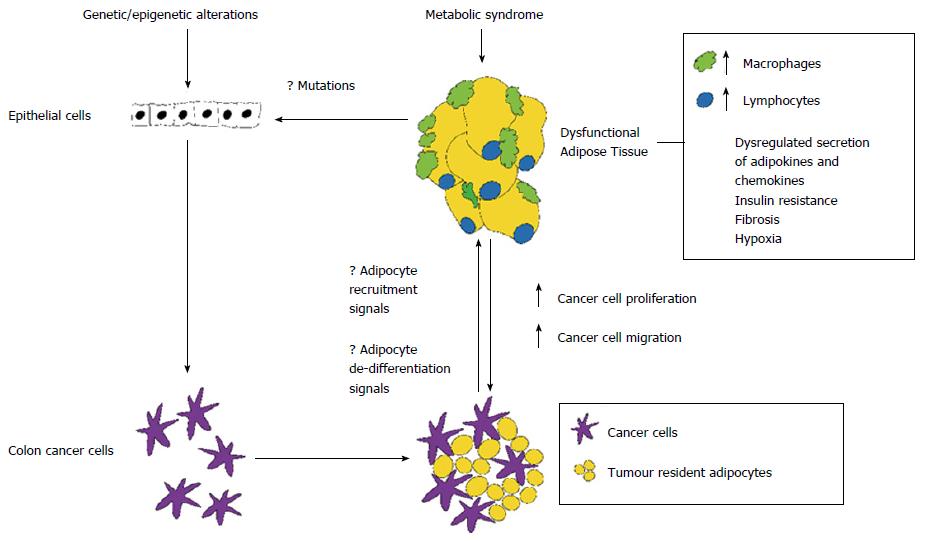
Figure 3 Paracrine interactions between dysfunctional adipose tissue, colon cancer cells and normal epithelial cells.
Dysfunctional adipose tissue induces recruitment of macrophages and lymphocytes creating a favourable microenvironment for tumour initiation and progression. We propose that dysfunctional adipocytes may induce epigenetic mutations in neighbouring epithelial cells. Adipocyte activation and recruitment signals from colon cancer cells are not known.
- Citation: Tabuso M, Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Adya R, Arasaradnam RP. Role of tissue microenvironment resident adipocytes in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(32): 5829-5835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i32/5829.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5829