Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4559-4568
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4559
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4559
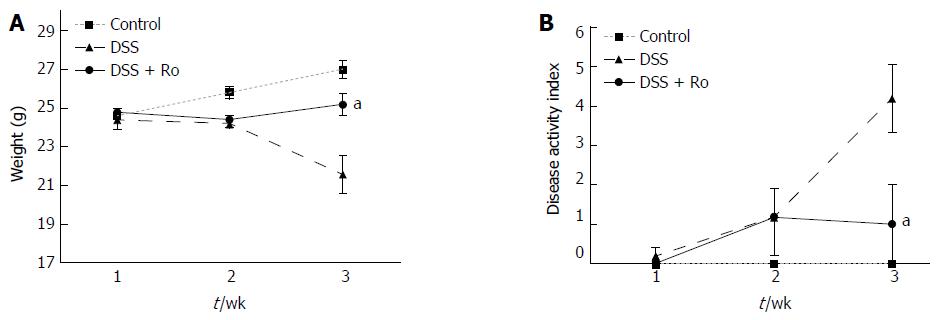
Figure 1 Rosuvastatin attenuated changes in body weight and the disease activity index in dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis model.
In mice, acute colitis was induced by oral DSS administration in drinking water for 7 d. Rosuvastatin (0.3 mg/kg per day) was administered orally before and after DSS administration for 21 d in the rosuvastatin-treated group. A: Changes in body weight during DSS administration in mice treated with and without rosuvastatin. Mice in the rosuvastatin group showed less weight loss than mice in DSS-induced colitis model; B: Disease activity index (sum of weight change, gross bleeding, and stool consistency scores) in mice treated with and without rosuvastatin. The rosuvastatin group had a lower disease activity index than untreated mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs DSS group. DSS: Dextran sodium sulphate; Ro: Rosuvastatin.
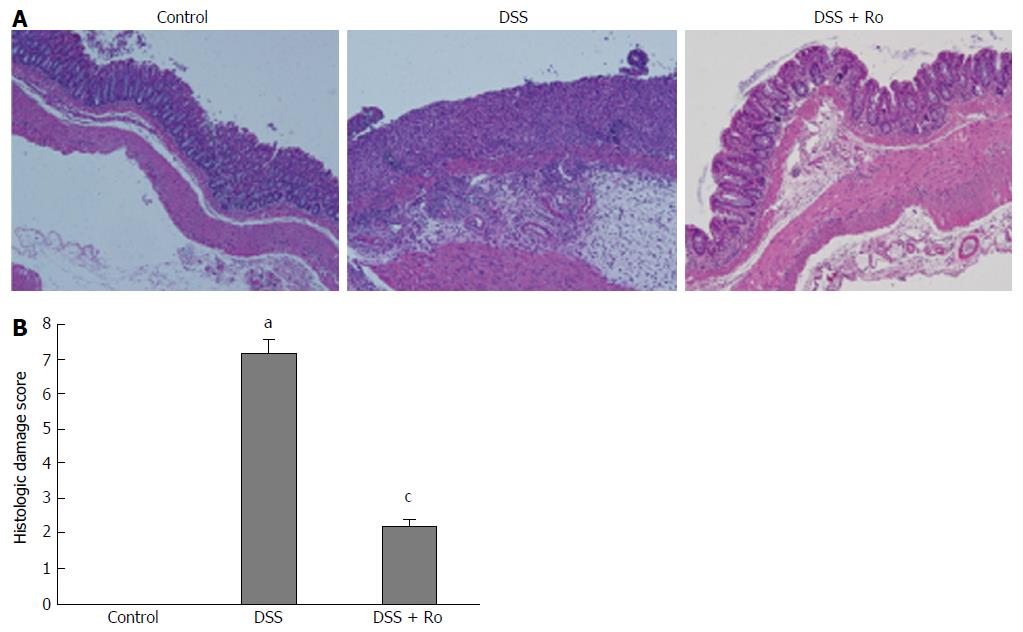
Figure 2 Rosuvastatin alleviated dextran sodium sulphate-induced histologic damage.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained colon sections from DSS-induced colitis mouse models treated with and without rosuvastatin. Magnification × 4; B: Histologic damage score. Rosuvastatin-treated mice had lower histological damage scores than untreated mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs DSS group. DSS: Dextran sodium sulphate; Ro: Rosuvastatin.
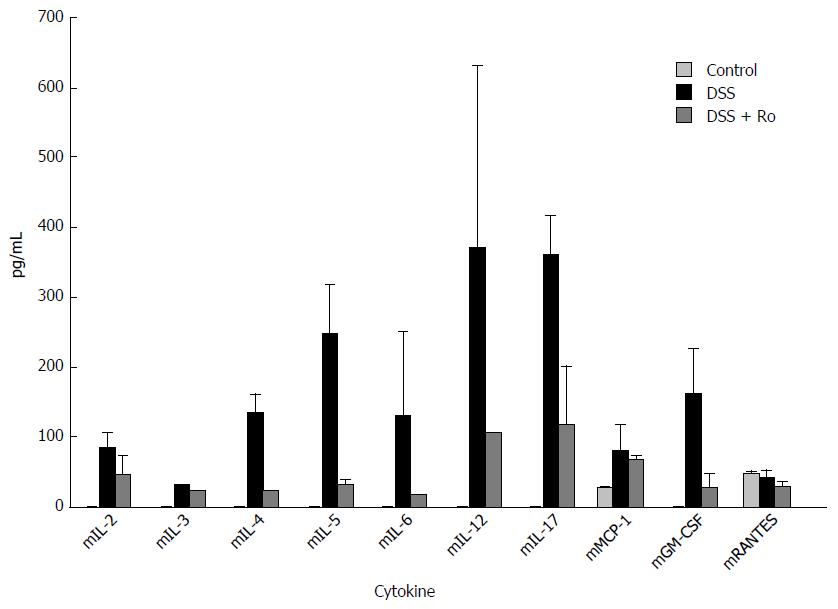
Figure 3 Rosuvastatin reduced the levels of dextran sodium sulphate-induced serum inflammatory cytokines.
Analysis of multiplex ELISA showed that the levels of serum IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-12 and IL-17, and G-CSF were markedly decreased in the rosuvastatin-treated group. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. DSS: Dextran sodium sulphate; Ro: Rosuvastatin.
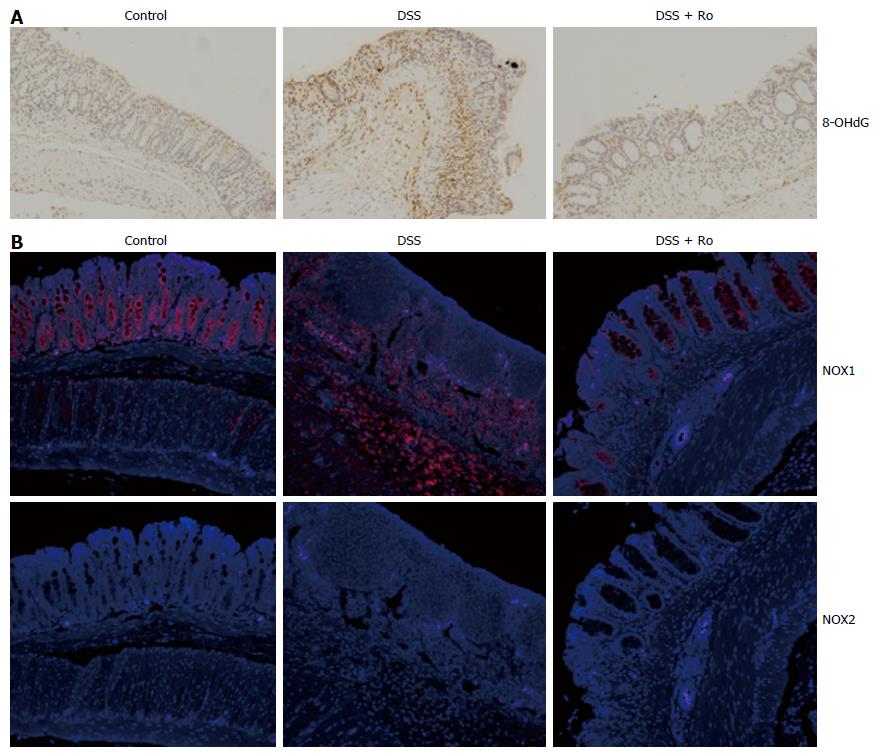
Figure 4 Rosuvastatin attenuated the expression of 8-OHdG and NOX1, but not of NOX2, in a dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis model.
A: 8-OHdG expression in colon sections from DSS-induced colitis mice treated with and without rosuvastatin by immunohistochemistry. 8-OHdG expression was attenuated in the rosuvastatin-treated group. Magnification × 10; B: NOX1 and NOX2 expression in colon sections from DSS-induced colitis mice treated with and without rosuvastatin by immunofluorescence. NOX1 expression was attenuated in the rosuvastatin-treated group. NOX2 expression levels were not different in DSS-induced colitis mice and control mice. Magnification × 10. DSS: Dextran sodium sulphate; 8-OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine; NOX: NADPH oxidase.
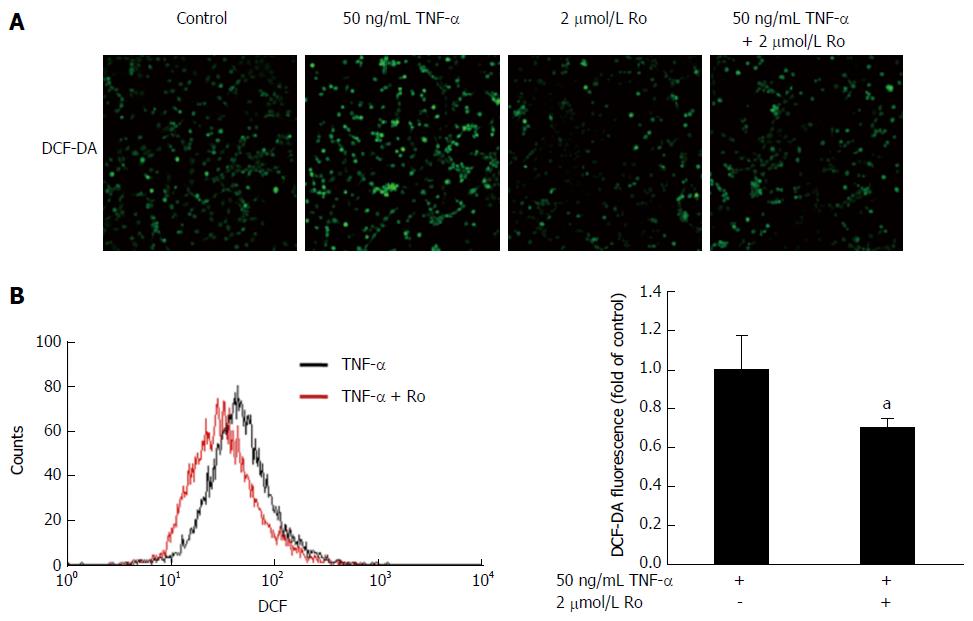
Figure 5 Rosuvastatin attenuated oxidative stress.
IEC-6 cells were treated with 2 μmol/L rosuvastatin for 20 min or 50 ng/mL TNF-α and then stained with 25 μmol/L DCF-DA for 30 min. DCF fluorescence was detected by (A) confocal microscopy and (B) flow cytometry. Rosuvastatin significantly reduced ROS production. aP < 0.05 vs TNF-α -treated IEC-6 cells without rosuvastatin. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; DCF-DA: 2'-7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; R: Rosuvastatin.
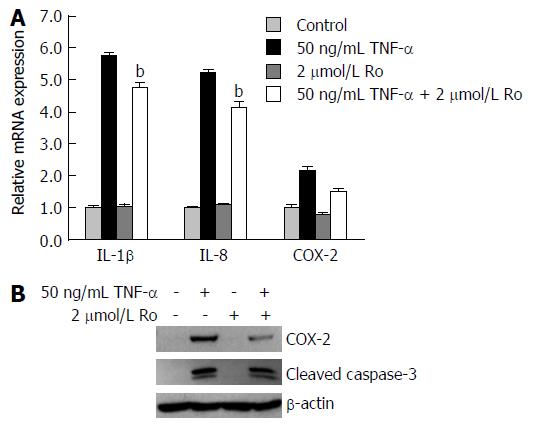
Figure 6 In vitro, rosuvastatin reduced the expression of inflammatory mediators and cleaved caspase-3.
IEC-6 cells were treated with 50 ng/mL and/or 2 μmol/L rosuvastatin for 24 h. (A) qRT-PCR showing mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, IL-8, and COX-2. Rosuvastatin significantly attenuated mRNA levels of IL-1β, IL-8, and COX-2 in TNF-α-treated IEC-6 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. (B) Western blot showing protein expression levels of COX-2 and cleaved caspase-3. Rosuvastatin significantly attenuated COX-2 and cleaved caspase-3 protein expression in 50 ng/mL TNF-α-treated IEC-6 cells. bP < 0.01 vs TNF-α-treated IEC-6 cells without rosuvastatin. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; COX: Cyclooxygenase; Ro: Rosuvastatin.
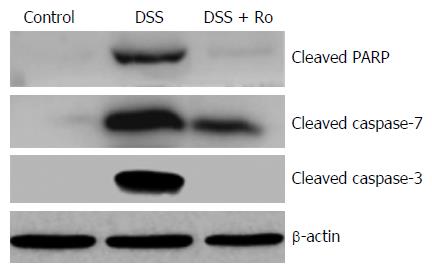
Figure 7 Rosuvastatin attenuated apoptosis in a dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis model.
Western blot showing protein levels of cleaved caspase-3, caspase-7, and PARP. Rosuvastatin attenuated the increase in cleaved caspase-3, caspase-7, and PARP in DSS-treated mice. PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; DSS: Dextran sodium sulphate; Ro: Rosuvastatin.
- Citation: Shin SK, Cho JH, Kim EJ, Kim EK, Park DK, Kwon KA, Chung JW, Kim KO, Kim YJ. Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of rosuvastatin by regulation of oxidative stress in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4559-4568
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4559.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4559