Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2017; 23(18): 3367-3373
Published online May 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3367
Published online May 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3367
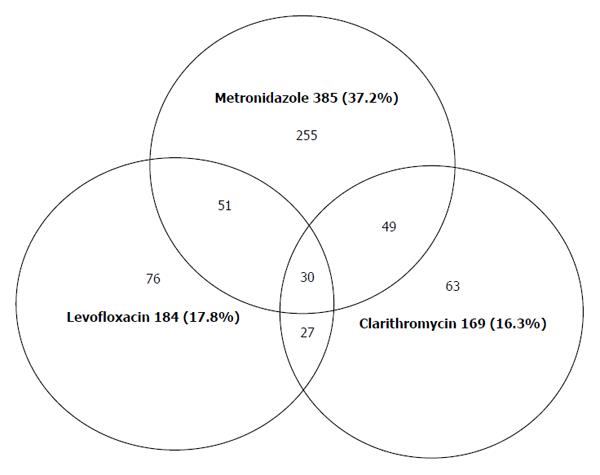
Figure 1 Relation of simultaneous antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori to various antibiotics in Gipuzkoa 2013/2014 (n = 1034).
Figure 2 Flow diagram of screening and follow-up of study subjects.
Susceptibility testing for H. pylori resistance was performed in 1034 consecutive infected patients. A total of 157 patients showed dual (127, 12.3%) or triple (30, 2.9%) antibiotic resistance. Patients from Donosti area were selected for follow up (68 with dual and 12 with triple resistance). 43 patients resistant to clarithromycin and metronidazole but sensitive to levofloxacin were treated with levofloxacin-based triple therapy: omeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1 g, and levofloxacin 500 mg (OAL); 12 patients resistant to both clarithromycin and levofloxacin were treated with metronidazole-based triple therapy: omeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1 g, and metronidazole 500 mg (OAM); 13 resistant patients to metronidazole and levofloxacin were treated with clarithromycin-based triple therapy: omeprazole 20 mg amoxicillin 1 g, and clarithromycin 500 mg (OAC), if the H. pylori-strains werein all cases twice a day for 10 d. 12 patients with triple H. pylori-resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole and levofloxacin received rifabutin-based triple therapy: omeprazole 20 mg b.i.d., amoxicillin 1 g b.i.d., and rifabutin 150 mg b.i.d. (OAR) for 10 d.
- Citation: Cosme A, Montes M, Ibarra B, Tamayo E, Alonso H, Mendarte U, Lizasoan J, Herreros-Villanueva M, Bujanda L. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing before first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with dual or triple antibiotic resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(18): 3367-3373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i18/3367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3367