Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2017; 23(17): 3184-3192
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3184
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3184
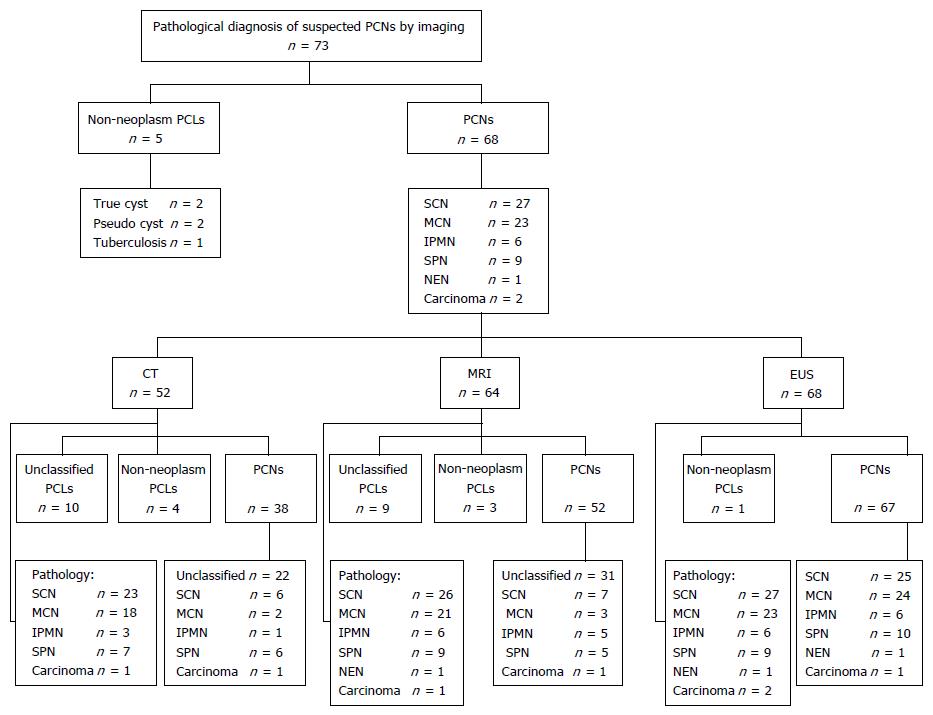
Figure 1 Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms by pathology and imaging.
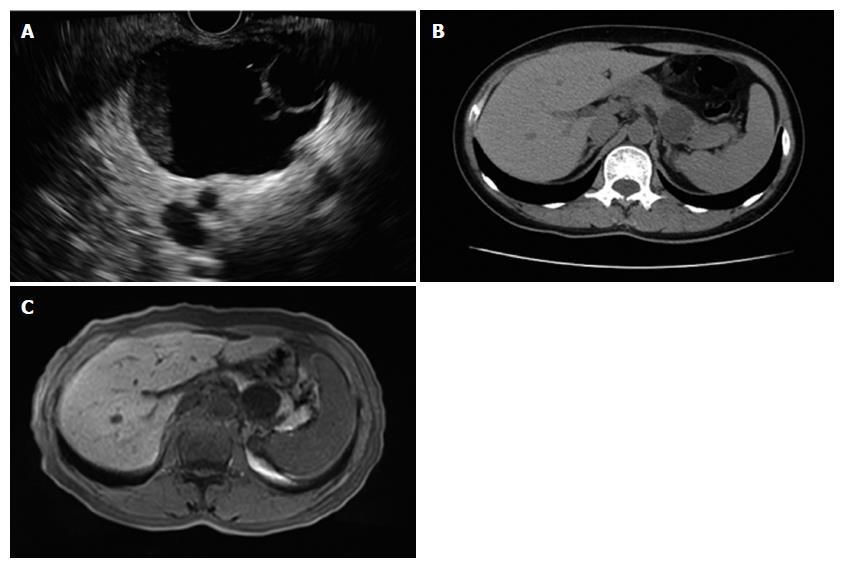
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
A: EUS view. The mother cyst of 4.6 cm × 3.8 cm in the pancreatic tail consisted of two daughter cysts. B: CT image. No daughter cyst was revealed by CT in the same patient. C: MRI image. No daughter cyst was revealed by MRI in the same patient. EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Du C, Chai NL, Linghu EQ, Li HK, Sun LH, Jiang L, Wang XD, Tang P, Yang J. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of detailed structures of pancreatic cystic neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(17): 3184-3192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i17/3184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3184