Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2017; 23(11): 2012-2022
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.2012
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.2012
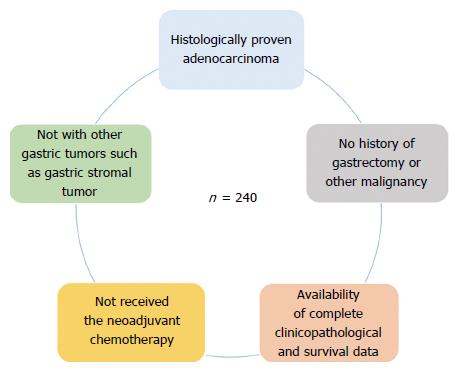
Figure 1 Eligibility criteria for patient inclusion.
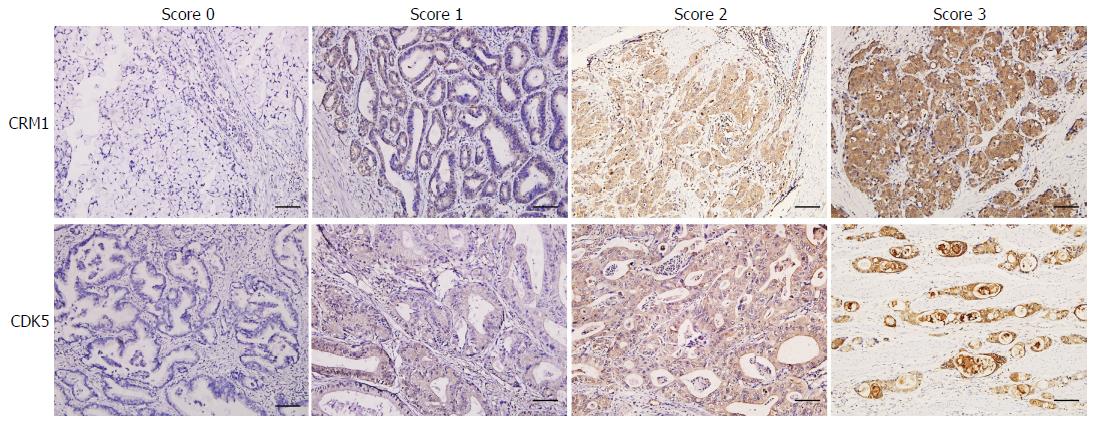
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining of CRM1 and CDK5 expression in gastric cancer tissue and the criteria for immunohistochemistry scoring.
Score 0: no staining, Score 1: weak staining, Score 2: moderate staining, Score 3: strong staining. The protein expression was considered low if the score was ≤ 1 and high if it was ≥ 2. Scale bar = 100 μm.
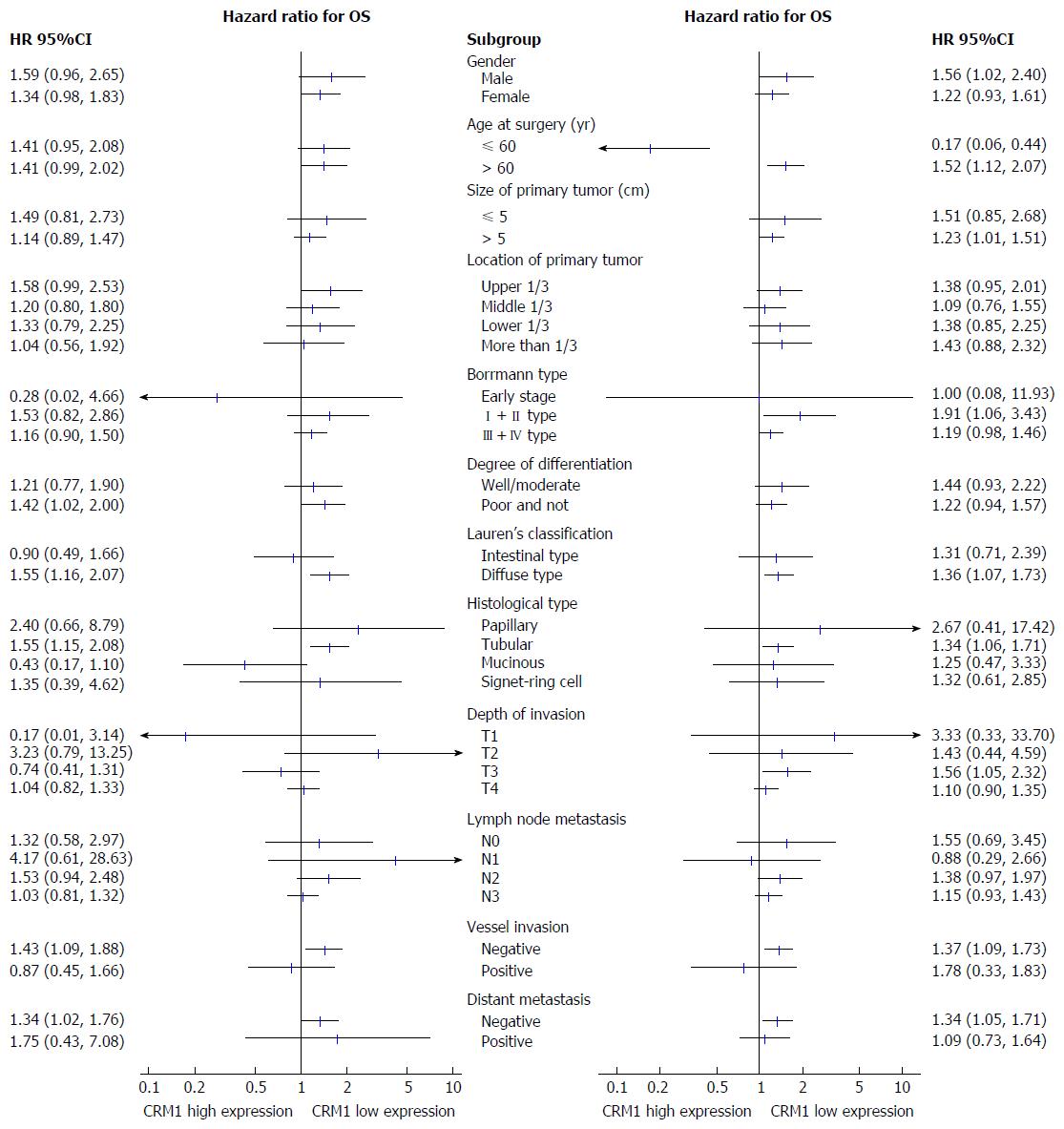
Figure 3 Forest plot showing hazard ratios (oblongs) and 95%CI (bars) for overall survival of subgroups from the 240 gastric cancer patients with different CRM1 (left) and CDK5 (right) expression status.
HR: Hazard ratio; OS: Overall survival; CRM: Chromosomal maintenance; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase.
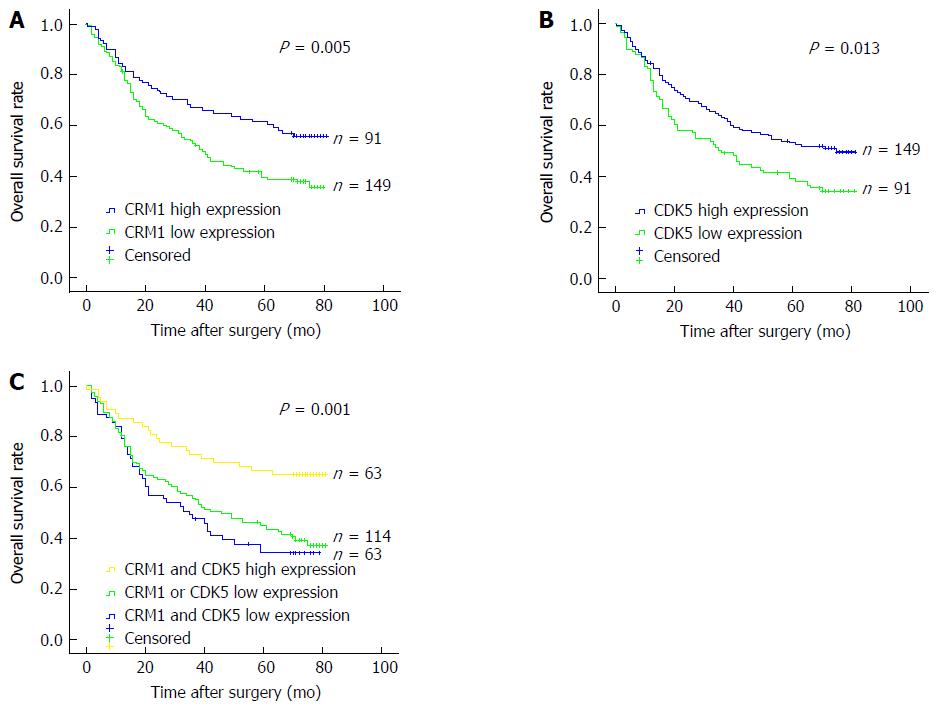
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier analysis of the correlation between expression of CRM1 (A), CDK5 (B) and combined CRM1 and CDK5 expression (C) and the overall survival of gastric cancer patients.
CRM: Chromosomal maintenance; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase.
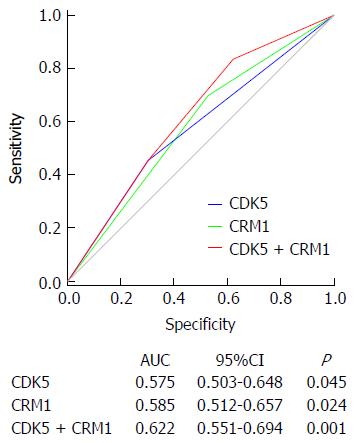
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of the sensitivity and specificity of the predictive value of the combined CRM1 and CDK5 expression model, CRM1 expression model and CDK5 expression model.
CRM: Chromosomal maintenance; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase.
- Citation: Sun YQ, Xie JW, Xie HT, Chen PC, Zhang XL, Zheng CH, Li P, Wang JB, Lin JX, Cao LL, Huang CM, Lin Y. Expression of CRM1 and CDK5 shows high prognostic accuracy for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(11): 2012-2022
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i11/2012.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.2012