Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2016; 22(7): 2357-2365
Published online Feb 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2357
Published online Feb 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2357
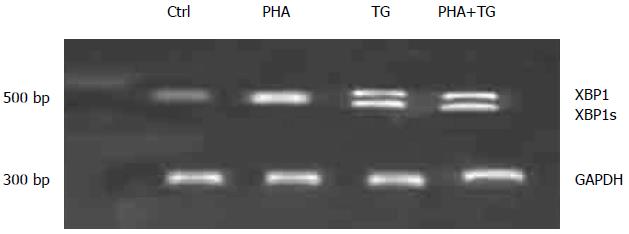
Figure 1 Expression detection of X-box binding protein 1 splicings in the phytohemagglutinin-thapsigargin co-stimulation group.
After PHA-TG co-stimulation, the expression of XBPIs in the co-stimulation group was significantly greater than the Ctrl group. PHA: Phytohemagglutinin; TG: Thapsigargin; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1 splicing.
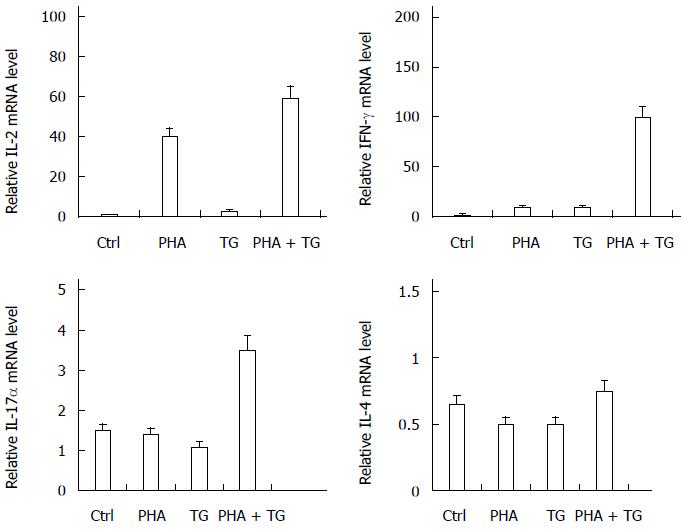
Figure 2 Expression of IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-17α in the phytohemagglutinin-thapsigargin co-stimulation group.
After PHA-TG co-stimulation, the mRNA expression of IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-17α in the co-stimulation group were significantly increased, while that of IL-4 did not change. PHA: Phytohemagglutinin; TG: Thapsigargin.
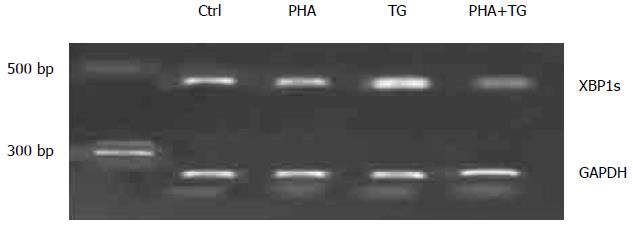
Figure 3 XBPIs detection after phytohemagglutinin-thapsigargin co-stimulation in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of normal participants.
XBPIs showed no significant change after the PHA-TG co-stimulation among the groups. PHA: Phytohemagglutinin; TG: Thapsigargin.
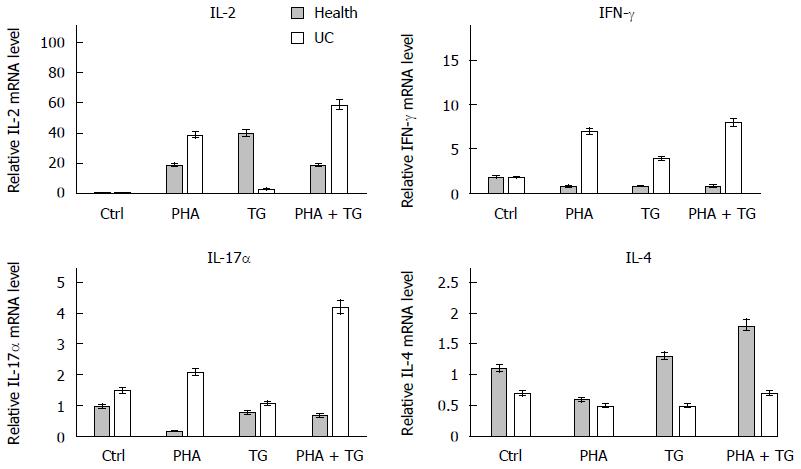
Figure 4 Comparison of the expression of IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-17α in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of normal healthy people and ulcerative colitis patients after phytohemagglutinin and thapsigargin stimulation.
The mRNA expression levels in the normal healthy people and ulcerative colitis (UC) patients all exhibited changes after TG and PHA + TG stimulation, while the expression of IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-17α in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of UC patients was higher than that in normal volunteers. PHA: Phytohemagglutinin; TG: Thapsigargin.
- Citation: Li N, Wang XM, Jiang LJ, Zhang M, Li N, Wei ZZ, Zheng N, Zhao YJ. Effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in patients with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(7): 2357-2365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i7/2357.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2357