Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2016; 22(6): 1935-1942
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1935
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1935
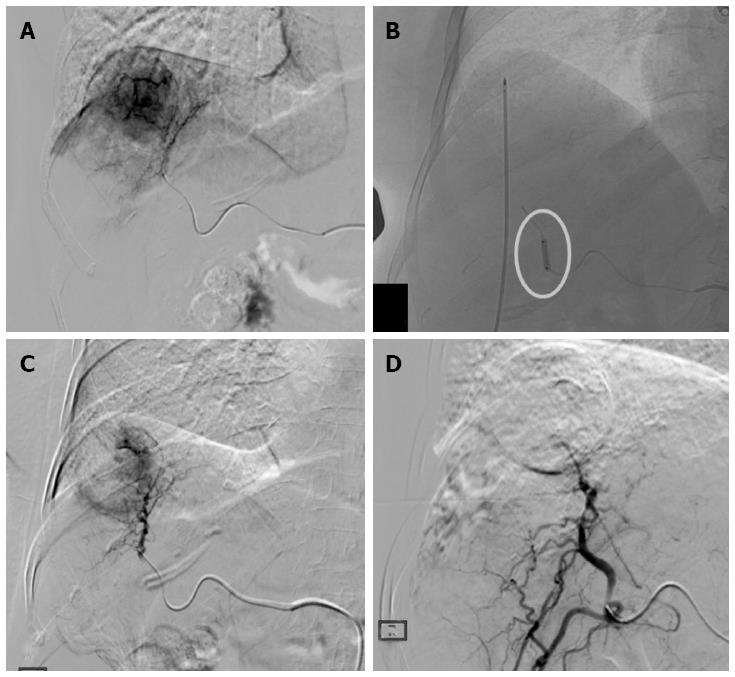
Figure 1 Treatment procedure.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma in SVIII (4.5 cm in size) confirmed on digital subtraction angiography; B: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) electrode placed into the tumor under ultrasonography-guidance with ablation performed during balloon-occlusion (circle); C: Post-RFA digital subtraction angiography showing the central devascularized area with peripheral reactive hyperemia; D: Complete devascularization obtained with superselective Drug-eluting bead trans-arterial chemoembolization.
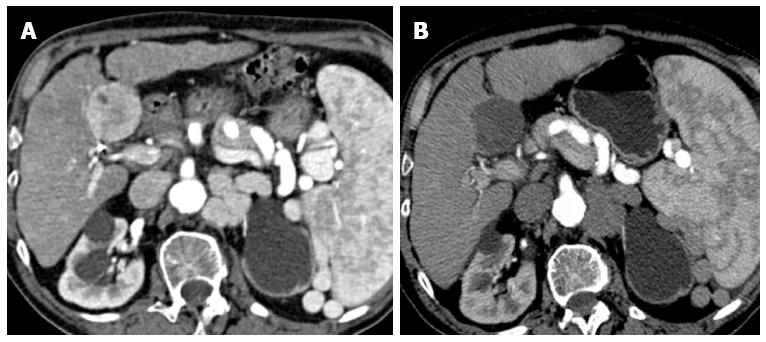
Figure 2 Complex lesion.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma in SV (5 cm in size), located on the intra-abdominal free-surface, adjacent to a gastrointestinal structure; B: Combined treatment allows obtaining a central safe necrosis with radiofrequency ablation (RFA); subsequent post-RFA trans-arterial chemoembolization was used to treat a peripheral portion of the tumor, obtaining a safe complete response.
- Citation: Iezzi R, Pompili M, Posa A, Coppola G, Gasbarrini A, Bonomo L. Combined locoregional treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: State of the art. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(6): 1935-1942
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i6/1935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1935