Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2016; 22(46): 10148-10157
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10148
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10148
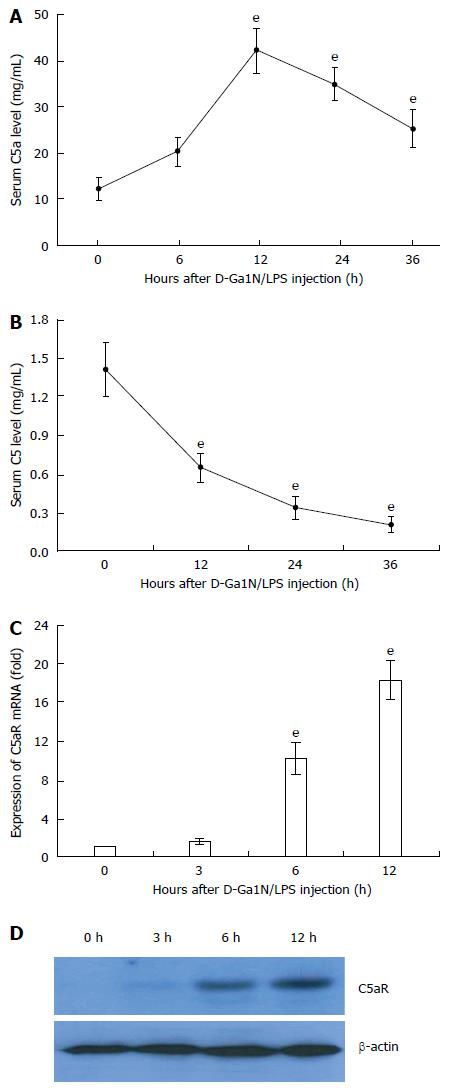
Figure 1 Excessive activation of C5 and up-regulation of C5aR in liver tissue of mice with acute liver failure.
Acute liver failure was induced in BALB/c mice using D-GalN (600 mg/kg) and LPS (10 μg/kg). A: Serum levels of C5a at 12, 24 and 36 h increased significantly compared with that at 0 h (42.8 ng/mL ± 4.77 ng/mL, 35.22 ng/mL ± 3.62 ng/mL, 25.52 ng/mL ± 4.02 ng/mL vs 12.23 ng/mL ± 2.55 ng/mL, t = 19.31, 17.2, and 9.67, respectively, eP < 0.001); B: Serum levels of C5 at 12, 24 and 36 h increased significantly compared with that at 0 h (0.65 mg/mL ± 0.117 mg/mL, 0.343 mg/mL ± 0.09 mg/mL, 0.211 mg/mL ± 0.06 mg/mL vs 1.413 mg/mL ± 0.209 mg/mL, t = 11.03, 16.29, and 19.15, respectively, eP < 0.001); C and D: Expression of C5aR mRNA and protein in liver tissue. The mean ± SE of three independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error).
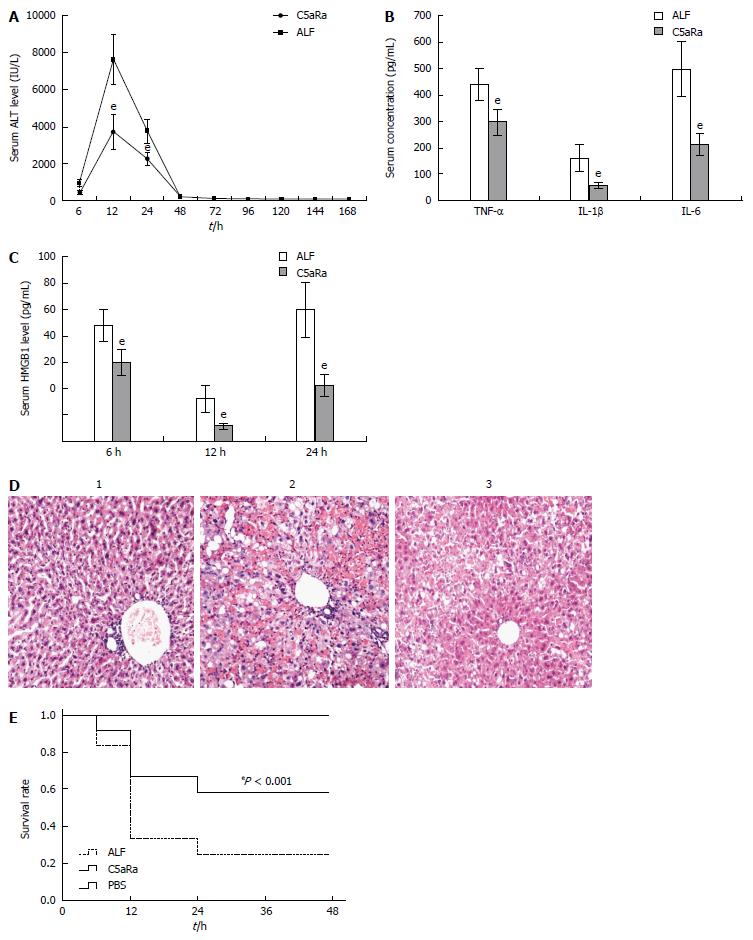
Figure 2 C5aRa attenuates D-GalN/LPS induced acute liver failure in mice.
A: C5aRa decreased serum levels of ALT at 12 h and 24 h significantly (3736.12 IU/L ± 937.98 IU/L vs 7612.78 IU/L ± 1379.21 IU/L, 2225.07 IU/L ± 381.99 IU/L vs 3741.74 IU/L ± 637.53 IU/L, t = 8.05 and 7.07, respectively, eP < 0.001); B: C5aRa reduced serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 at 12 h (299.35 pg/mL ± 50.61 pg/mL vs 439.33 pg/mL ± 63.59 pg/mL, 57.42 pg/mL ± 12.98 pg/mL vs 106.69 pg/mL ± 49.87 pg/mL, 213.52 pg/mL ± 42.69 pg/mL vs 500.87 pg/mL ± 104.14 pg/mL, t = 5.96, 6.94, and 8.84 respectively, eP < 0.001); C: C5aRa reduced HMGB1 levels at 6, 12 and 24 h (18.14 ng/mL ± 4.08 ng/mL vs 60.23 ng/mL ± 5.47 ng/mL; 16.21 ng/mL ± 5.11 ng/mL vs 67.14 ng/mL ± 14.27 ng/mL; 15.42 ng/mL ± 6.23 ng/mL vs 48.71 ng/mL ± 15.6 ng/mL, t = 9.13, 11.64, and 6.85, respectively, eP < 0.001); D: Immune cell infiltration and tissue damage were detected by HE staining at 36 h after onset of ALF (1 = normal mice; 2 = ALF mice; 3 = C5aRa treated mice; magnification, × 100); E: Kaplan-Meier analysis of the effect of C5aRa on survival rates of animals (eP < 0.001, log-rank test, F = 14.06). The mean ± SE of three independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error). ALF: Acute liver failure. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin.
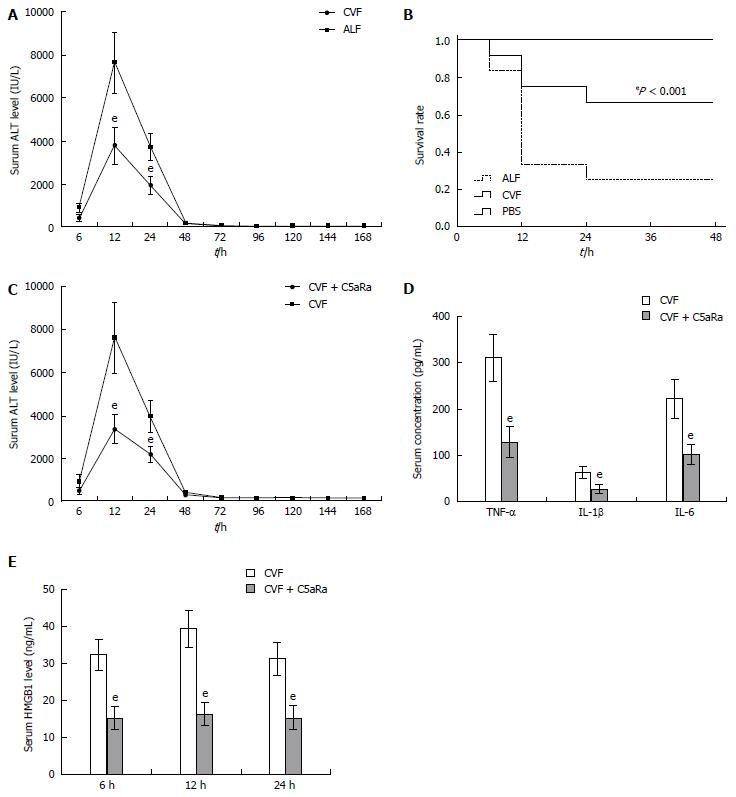
Figure 3 C5aRa further lessens the pathogenic effect on D-GalN/LPS challenged mice receiving cobra venom factor pretreatment.
A: Cobra venom factor (CVF) treatment decreased serum levels of ALT at 12 h and 24 h significantly (3798.28 IU/L ± 839.68 IU/L vs 7612.78 IU/L ± 1379.21 IU/L, 1965.93 IU/L ± 371.74 IU/L vs 3798.28 IU/L ± 839.68 IU/L, t = 8.34 and 8.18, respectively, eP < 0.001); B: Kaplan-Meier analysis of the effect of CVF on survival rates of animals (eP < 0.001, log-rank test, F = 14.84); C: C5aRa further decreased serum levels of ALT at 12 h and 24 h significantly compared with CVF (1668.4 IU/L ± 339.68 IU/L vs 3798.28 IU/L ± 839.68 IU/L, 1069.69 IU/L ± 171.74 IU/L vs 1965.93 IU/L ± 371.74 IU/L, t = 8.14 and 7.58, respectively, eP < 0.001); D: C5aRa further reduced serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 at 12 h significantly compared with CVF (129.67 pg/mL ± 32.79 pg/mL vs 312.19 pg/mL ± 51.25 pg/mL; 27.73 pg/mL ± 8.78 pg/mL vs 63.28 pg/mL ± 13.27 pg/mL; 103.66 pg/mL ± 22.33 pg/mL vs 223.67 pg/mL ± 41.77 pg/mL, t = 10.39, 7.74, and 8.78, respectively, eP < 0.001); E: C5aRa further reduced HMGB1 levels at 6, 12 and 24 h in ALF mice (15.14 ng/mL ± 3.08 ng/mL vs 33.23 ng/mL ± 4.17 ng/mL; 16.21 ng/mL ± 3.11 ng/mL vs 39.44 ng/mL ± 5.07 ng/mL; 15.42 ng/mL ± 3.23 ng/mL vs 31.33 ng/mL ± 4.36 ng/mL, t = 11.49, 13.53, and 10.16, respectively, eP < 0.001). ALF: Acute liver failure. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HMGB1: High-mobility group protein B1.
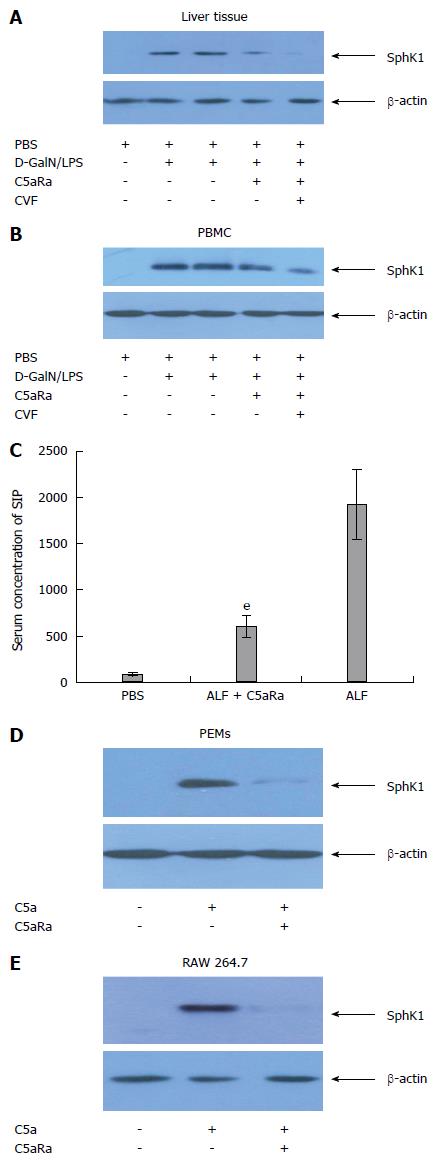
Figure 4 C5a/C5aR signaling is required for the expression of SphK1 during acute liver failure.
A and B: Blocking of C5aR with C5aRa reduced SphK1 expression in liver tissue and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of acute liver failure (ALF) mice; C: Blocking of C5aR by C5aRa reduced S1P level in liver tissue significantly than that of control (ALF group), eP < 0.01; D, E: Recombinant murine C5a (500 ng/mL) induced SphK1 expression in peritoneal exudative macrophages (PEMs) and RAW 264.7 cells, and was abolished by incubation for 60 min with 10 nmol/L C5aRa. The data shown are representative of three separate experiments.
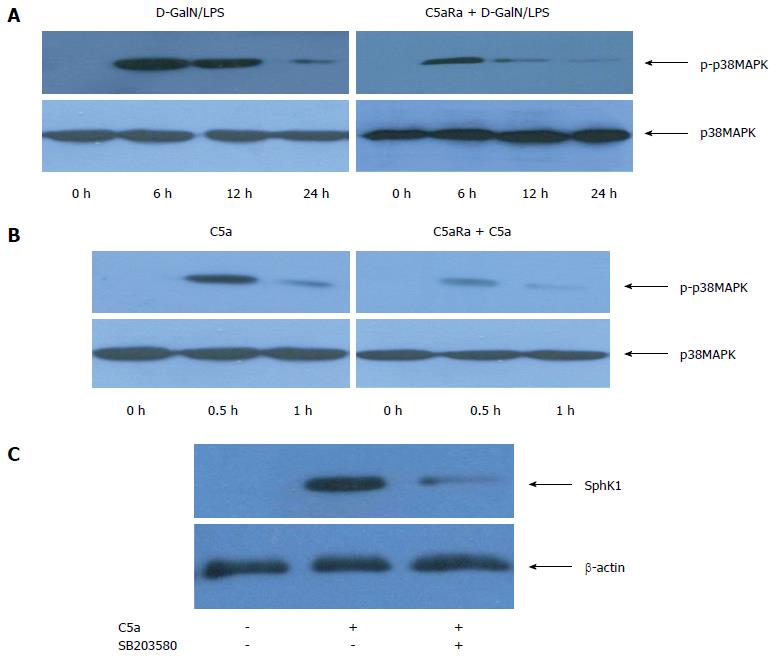
Figure 5 C5aR signaling induces SphK1 expression through activation of p38-MAPK.
A: C5a induced p38-MAPK activation in liver tissue of acute liver failure (ALF) mice; B: PEMs were stimulated with C5a (500 ng/mL) or C5a + C5aRa (pre-incubated 60 min with 10 nmol/L of C5aRa in the presence of C5a); C: Inhibition of p38-MAPK activity with SB203580 down-regulated SphK1 expression in PEMs stimulated with C5a.
- Citation: Lei YC, Lu CL, Chen L, Ge K, Yang LL, Li W, Wu YH. C5a/C5aR pathway is essential for up-regulating SphK1 expression through p38-MAPK activation in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(46): 10148-10157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i46/10148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10148