Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2016; 22(39): 8760-8769
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8760
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8760
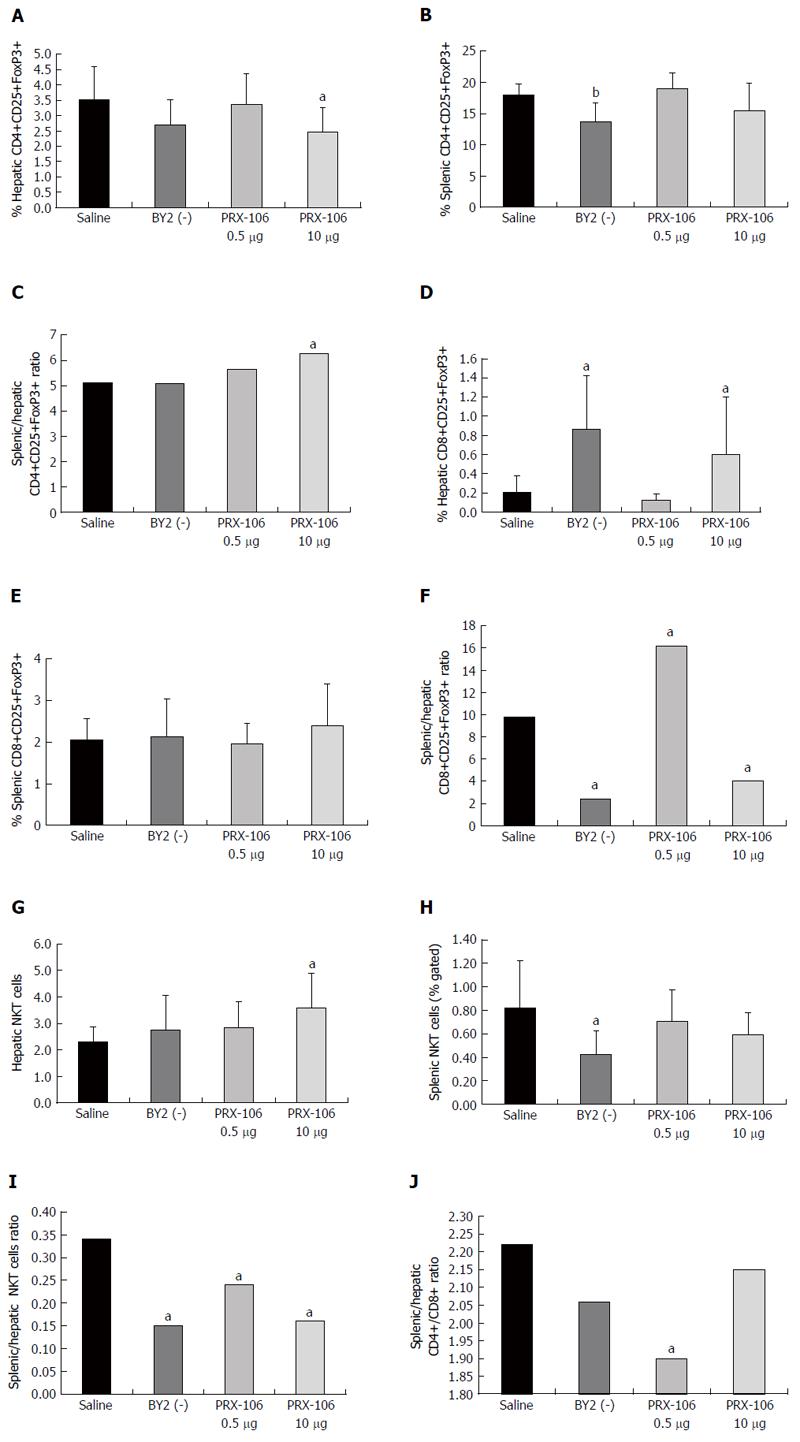
Figure 1 FACS analysis was performed on lymphocytes harvested from the spleens and livers of all mice from the experimental and control groups.
The results were compared for the following subsets of cells. A: Intrahepatic CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ lymphocytes; B: Intrasplenic CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ lymphocytes; C: The intrasplenic-to-intrahepatic CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ ratio was calculated; D: Intrahepatic CD8+CD25+FoxP3+ lymphocytes; E: Intrasplenic CD8+CD25+FoxP3+ lymphocytes; F: The intrasplenic-to-intrahepatic CD8+CD25+FoxP3+ ratio was calculated; G: Intrahepatic NKT lymphocytes; H: Intrasplenic NKT lymphocytes; I: The intrasplenic-to-intrahepatic NKT ratio was calculated; J: To determine the effect of the treatment on the lymphocyte trapping in the liver, the CD4/CD8 lymphocyte ratio was calculated in the spleen and in the liver. The ratio between the splenic and hepatic CD4/CD8 ratios was calculated. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
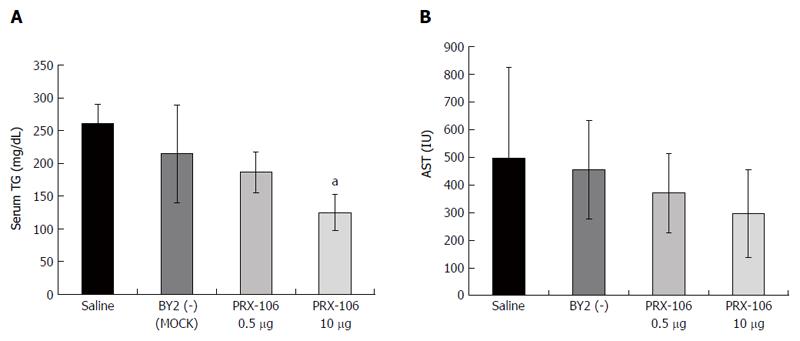
Figure 2 Serum levels of triglycerides (A) and aspartate aminotransferase (B) were measured in all mice from the experimental and control groups.
AST: Aspartate aminotransferase. aP < 0.05.
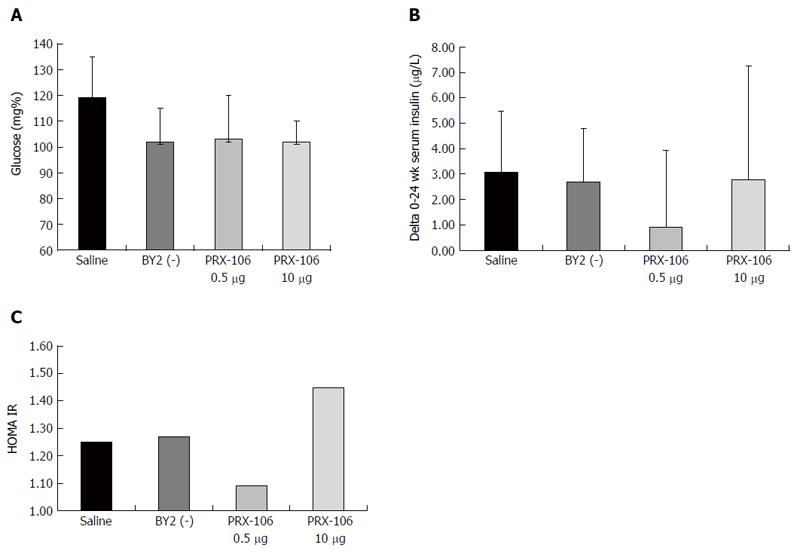
Figure 3 A beneficial effect of oral PRX106 on fasting glucose levels was noted.
Serum glucose levels were measured at the end of the study in all mice (A); the delta between the average serum insulin levels on day 0 and the end of trial was calculated (B); HOMA-IR was calculated for all mice at the end of the study (C).
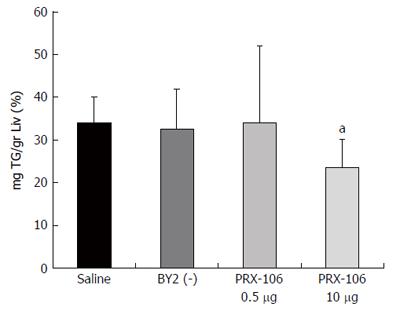
Figure 4 The liver triglyceride content was measured and calculated per liver weight to determine the percentage of fat in the mouse livers.
aP = 0.03.
- Citation: Ilan Y, Ben Ya'acov A, Shabbat Y, Gingis-Velitski S, Almon E, Shaaltiel Y. Oral administration of a non-absorbable plant cell-expressed recombinant anti-TNF fusion protein induces immunomodulatory effects and alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(39): 8760-8769
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i39/8760.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8760