Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2016; 22(31): 7146-7156
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7146
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7146
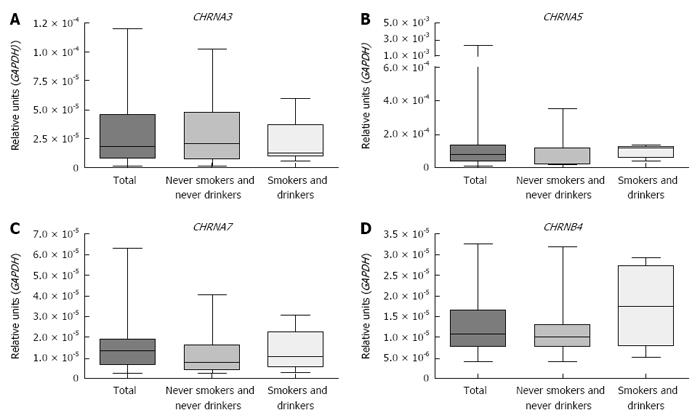
Figure 1 Comparison of CHRNs' expression in esophageal samples from healthy individuals.
A: Evaluation by RT-qPCR of the mRNA expression of CHRNA3; B: CHRNA5; C: CHRNA7 and D: CHRNB4 in esophageal epithelium from healthy individuals (total individuals, never smokers and never drinkers, current smokers and current drinkers).
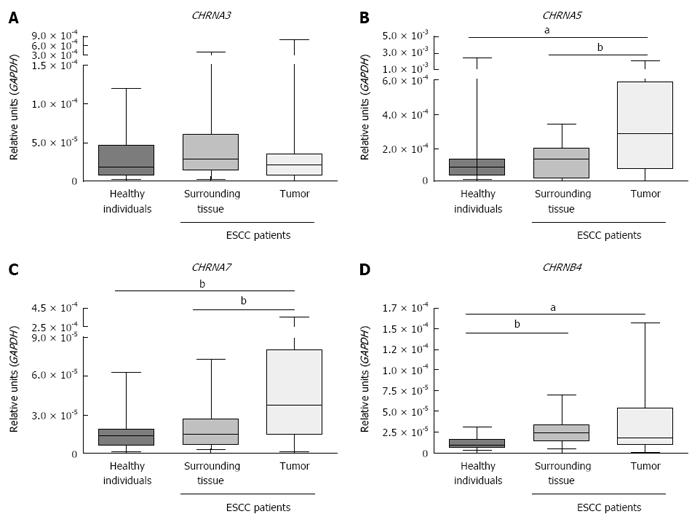
Figure 2 Comparison of CHRNs’ expression in esophageal samples from healthy individuals and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.
A-D: Evaluation by RT-qPCR of the mRNA expression of CHRNA3 (A), CHRNA5 (B), CHRNA7 (C) and CHRNB4 (D) in esophageal epithelium from healthy individuals and ESCC patients (normal surrounding mucosa and tumor tissue). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01.
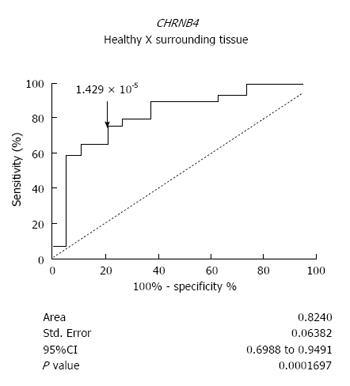
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve for the discrimination of healthy esophagus and normal-appearing surrounding tissue of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients, according to CHRNB4 expression.
The receiver operating characteristic curve was performed for CHRNB4 mRNA expression normalized with GAPDH (number of healthy individuals: 32, number of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients: 19). For a CHRNB4 expression cut-off of 1.429 × 10-5, the area under the curve was 0.824, with a sensitivity of 75.86% and a specificity of 78.95%, P = 0.0002.
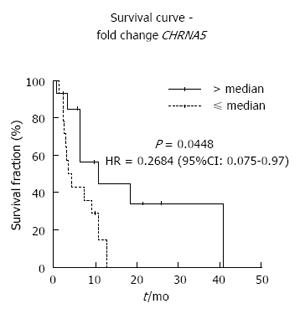
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier curve showing the impact of CHRNA5 mRNA expression on the overall survival of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Kaplan-Meier survival curve according to CHRNA5 expression fold-change (ratio between expression in the tumor and the normal surrounding tissue), with follow-up duration of 5 years after diagnosis (total n = 28). Censored values (+) indicate the last known follow-up time for the corresponding subjects. Adjustments were performed for tumor stage and age.
- Citation: Chianello Nicolau M, Pinto LFR, Nicolau-Neto P, de Pinho PRA, Rossini A, de Almeida Simão T, Soares Lima SC. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors in esophagus: Early alteration during carcinogenesis and prognostic value. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(31): 7146-7156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i31/7146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7146