Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2016; 22(31): 7135-7145
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135
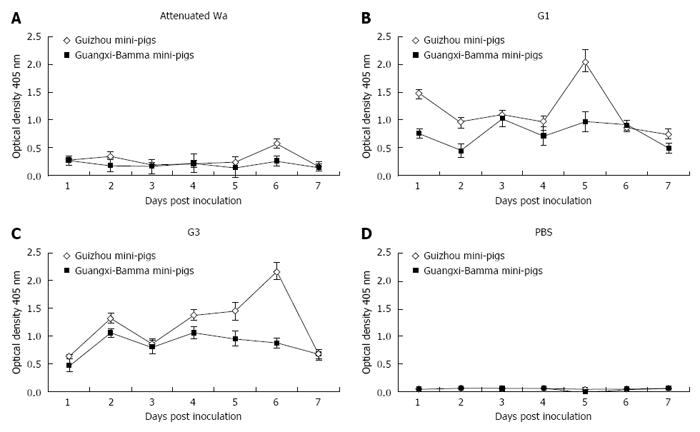
Figure 1 The curves of viral antigen-shedding in fecal samples from 3- to 5-d-old PBS or human rotavirus-inoculated mini-pigs.
The amount of viral antigen in fecal samples from the mini-pigs impregnated with 1 mL of 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human attenuated RV Wa (A), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human RV G1 (B), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human RV G3 (C), and 1 mL of PBS (D). Viral antigen shedding from 0 to 7 DPI was assessed by ELISA and the OD, as net readings, was identified at 450 nm. Only values exceeding 0.1 were considered positive. Fresh fecal samples from mini-pigs were collected every day and were stored at -80 °C. Every virus-inoculated group consisted of three virus-impregnated and one PBS-impregnated mini-pig to supervise transmission among mock-impregnated littermates. All the PBS inoculations were performed before any inoculation with the virus. FFUs: Focus forming units; DPI: Days post infection.
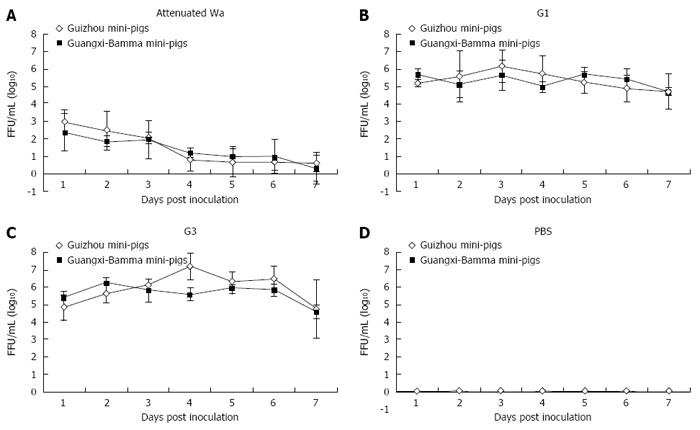
Figure 2 The curves of infectious virus-shedding of 3- to 5-d-old mini-pigs impregnated with 1 mL of human rotavirus or PBS.
The curves of infectious virus-shedding from 3- to 5-d-old mini-pigs impregnated with 1 mL of 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human attenuated rotavirus Wa (A), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human G1 (B), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human RV G3 (C), and 1 mL of PBS (D). Infectious RV shedding in individual fecal samples from 0 to 7 DPI was assessed by FFA and was presented by FFU. FFUs: Focus forming units; DPI: Days post infection.
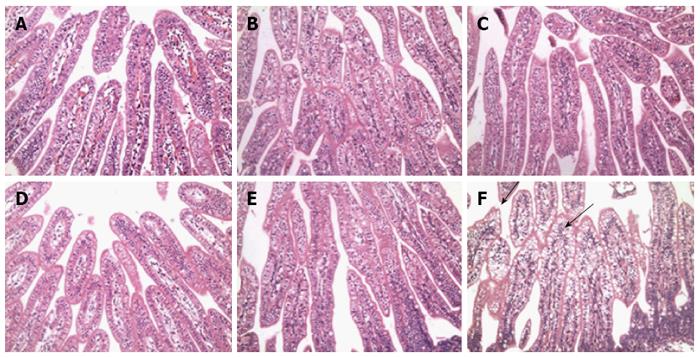
Figure 3 Histopathological lesions in the small intestine during rotavirus infection at 72 hpi.
Sections of the small intestine were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Duodenal (A), jejunal (B), and ileal (C) mucosae collected from mock-infected control newborn mini-pigs or duodenal (D), jejunal (E), and ileal (F) mucosae that were collected from 5-d-old Group A virulent G1-impregnated newborn mini-pigs. Magnification, × 200.
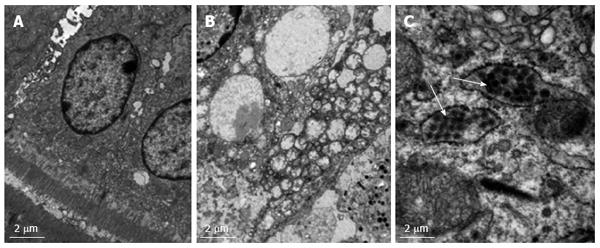
Figure 4 Ultrastructural visualization of the ileum from 5-d-old mini-pigs by electron micrography.
PBS-inoculated (A) and HRV-inoculated (B and C) at 48 hpi. Vacuoles devoid of virus particles (B) and virus particles encapsulated in Golgi-like follicle (white arrow) were observed in HRV-infected neonatal mini-pigs (C). Original magnification, × 40. HRV: Human rotavirus.
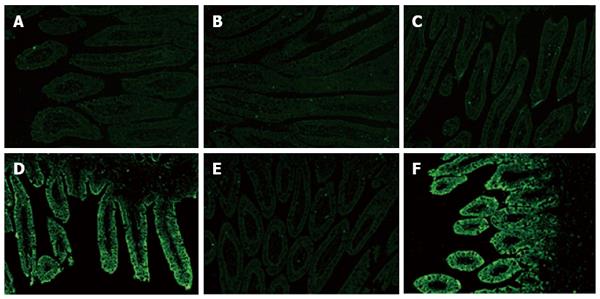
Figure 5 Distribution of immunofluorescence specific to VP6 antigen of rotavirus in the intestine.
The duodenum (A), jejunum (B) or ileum (C) from 5-d-old mock-impregnated control newborn mini-pigs and the duodenum (D), jejunum (E) or ileum (F) from HRV-incubated newborn mini-pigs at 24 hpi. No rotavirus antigen was detected at 24 hpi in any part of the small intestinal epithelium in mock-impregnated control newborn mini-pigs. The expression of rotavirus antigen in the ileum was significantly higher than in the jejunum in HRV-infected neonatal mini-pigs at 24 hpi. HRV: Human rotavirus.
- Citation: Li JT, Wei J, Guo HX, Han JB, Ye N, He HY, Yu TT, Wu YZ. Development of a human rotavirus induced diarrhea model in Chinese mini-pigs. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(31): 7135-7145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i31/7135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135