Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2016; 22(31): 7111-7123
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7111
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7111
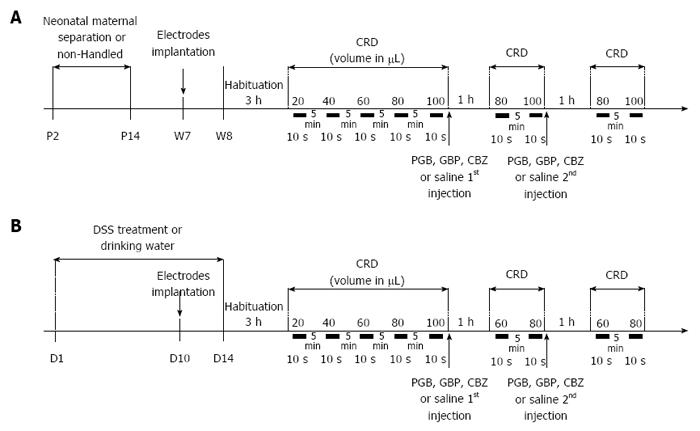
Figure 1 Experimental design of anticonvulsant treatment assessment on colonic hypersensitivity.
A: Non-inflammatory hypersensitivity was induced by neonatal maternal separation from day 2 to day 14 (P2 to P14). At week seven, electrodes were surgically implanted in abdominal muscle. On week eight, mice were accustomed to restraint device for 3 h before probe insertion for the colorectal distension (CRD). Balloon was inflated from 20 to 100 μL to assess basal colonic sensitivity. Then mice were subcutaneously injected with a first dose of anticonvulsants [carbamazepine (CBZ) 10 mg/kg, gabapentin (GBP) 30 mg/kg or pregabalin (PGB) 10 mg/kg] or saline and colonic sensitivity was assessed 1 h later for the two distension volumes displaying the highest significant differences in visceromotor response (VMR) between control and sensitized groups (80 and 100 μL). A second subcutaneous injection was performed to reach the second dose of anticonvulsants (CBZ 30 mg/kg, GBP 100 mg/kg or PGB 30 mg/kg) or saline and the same protocol was repeated; B: A moderate intestinal inflammation was induced by replacing drinking water by 1% DSS at D1 for 14 d. At D10, electrodes were surgically implanted in abdominal muscle. On the last day of treatment (D14), mice were accustomed to restraint device for 3h before probe insertion for the CRD. Balloon was inflated from 20 to 100 μL to assess basal colonic sensitivity. Then mice were subcutaneously injected with a first dose of anticonvulsants (CBZ 10 mg/kg, GBP 30 mg/kg or PGB 10 mg/kg) or saline and colonic sensitivity was assessed 1h later for the two distension volumes displaying the highest significant differences in VMR between control and sensitized groups (60 and 80 μL). A second subcutaneous injection was performed to reach the second dose of anticonvulsants (CBZ 30 mg/kg, GBP 100 mg/kg or PGB 30 mg/kg) or saline and the same protocol was repeated. CRD: Colorectal distension.
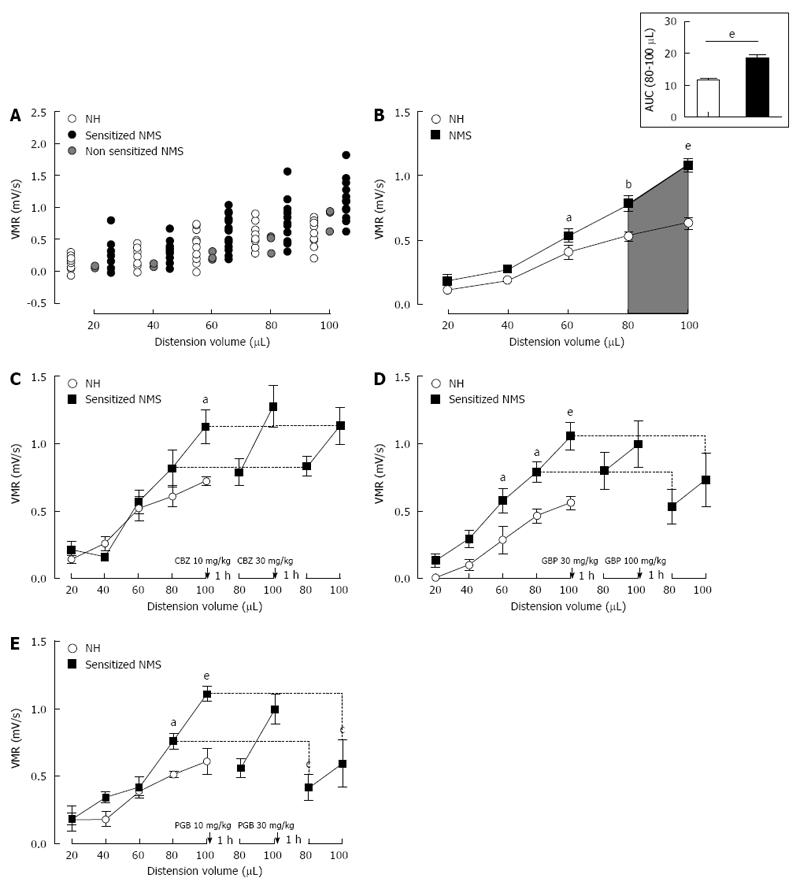
Figure 2 Mouse model of non-inflammatory colonic hypersensitivity and assessment of pregabalin, gabapentin and carbamazepine treatments.
A: After colorectal distension (CRD) test, three mother-separated mice are considered non-sensitized (grey circles) as described in material and methods and are excluded from the analysis. Distribution of visceromotor response (VMR) values to CRD test highlights an increased response in sensitized neonatal mother-separated (sensitized NMS) (black circles n = 23) compared to non-handled (NH) (white circles n = 17) mice; B: Assessment of colonic sensitivity in sensitized NMS (black squares n = 23) and non-handled (white circles n = 17) mice displays significant differences between groups for highest distension volumes (60, 80 and 100 μL). Top right insert represents the area under the curve (AUC) between 80 μL and 100 μL; C: Carbamazepine (CBZ) administration (10 and 30 mg/kg s.c.) has no effect on VMR response in neonatal mother-separated mice (NMS : n = 8; NH : n = 6); D: Both doses (30 and 100 mg/kg s.c.) of gabapentin (GBP) have no effect on CHS induced by neonatal maternal separation (NMS: n = 8; NH: n = 6); E: Only the highest cumulative dose (30 mg/kg s.c.) of pregabalin (PGB) induces a VMR reduction in response to CRD in NMS mice (NMS : n = 8; NH : n = 6). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, Neonatal Mother-separated vs Non-handled ANOVA 2 Way (Animal housing; Volume) followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons and cP < 0.05 Pre-injection vs Post-injection; ANOVA 2 Way (Treatment; Volume) followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. NMS: Neonatal maternal separation; NH: Non-handled.
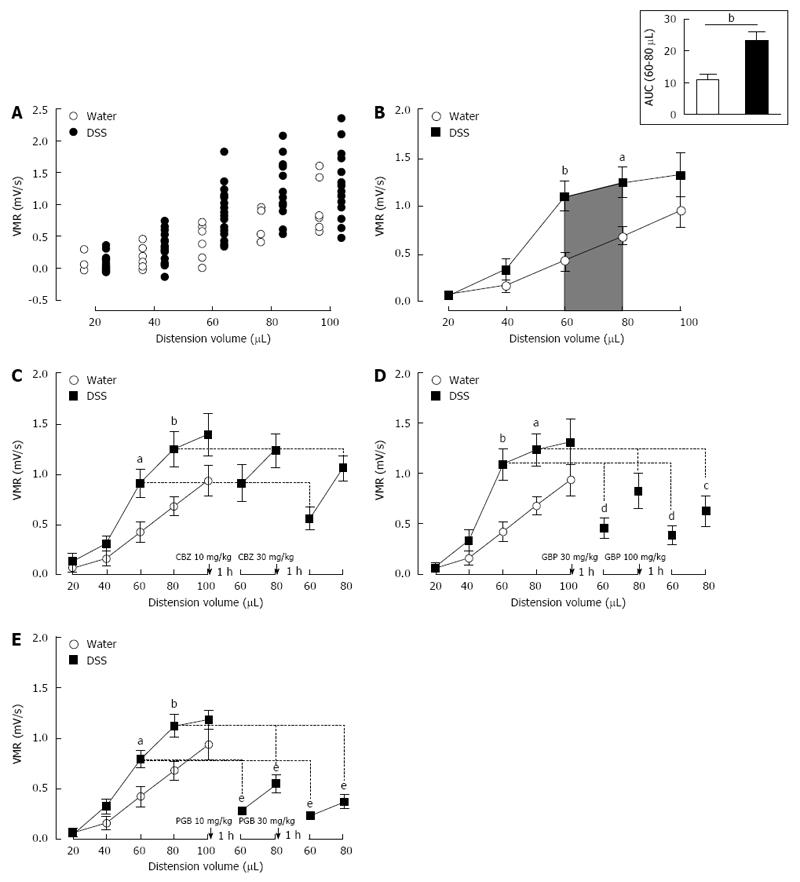
Figure 3 Mouse model of inflammation-associated colonic hypersensitivity and assessment of pregabalin, gabapentin and carbamazepine treatments.
A: All animals were considered as sensitized by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) treatment. Distribution of visceromotor response (VMR) values highlights an increased response in DSS-treated (black circles n = 22) compared to control (white circles n = 7) mice; B: Assessment of colonic sensitivity in DSS-treated (n = 22) and control mice (n = 7) displays significant differences between groups for 60 and 80 μL distension volumes. Top right insert represents the area under the curve (AUC) between 60 μL and 80 μL; C: Carbamazepine (CBZ) administration (10 and 30 mg/kg s.c.) has no significant effect on VMR response in DSS-treated mice (DSS n = 6; Water n = 7); D: Both doses (30 and 100 mg/kg s.c.) of gabapentin (GBP) induce a VMR reduction in DSS-treated mice (DSS n = 7; Water n = 7); E: Pregabalin (PGB) administration (10 and 30 mg/kg s.c.) induces a highly significant reduction of VMR in response to CRD in DSS-treated mice (DSS n = 9; Water n = 7).aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01, DSS-treated vs Water ANOVA 2 Way (Treatment; Volume) followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons; cP < 0.05; dP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, Pre-injection vs Post-injection ANOVA 2 Way (Treatment; Volume) followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. CRD: Colorectal distension.
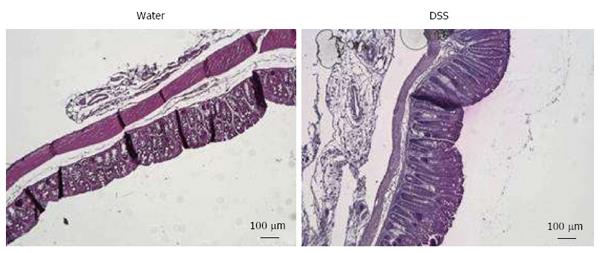
Figure 4 Representative histologic examinations of low dose 1% dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice colons after hematoxylin and eosin-staining (scales bars = 100 μm).
DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
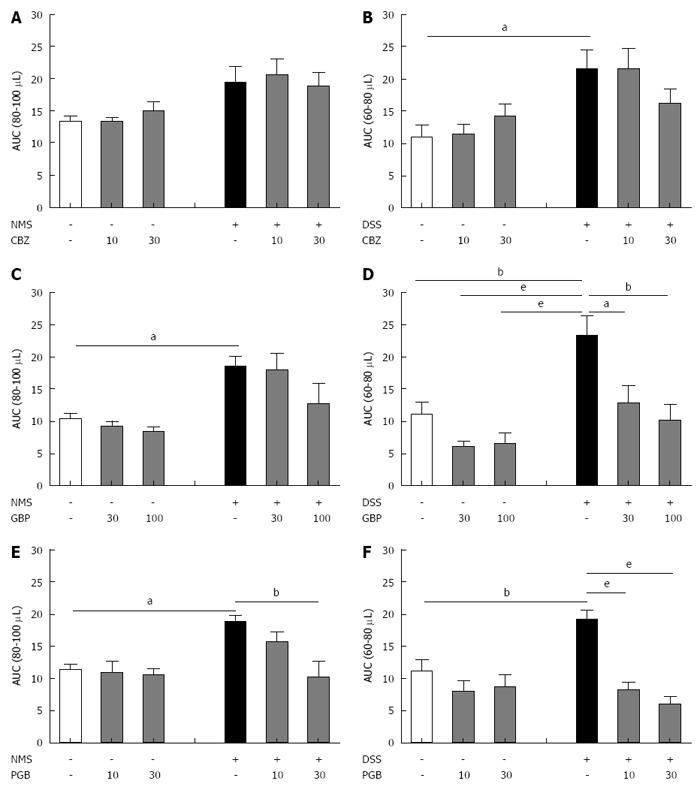
Figure 5 Comparative effect of carbamazepine, gabapentin and pregabalin on visceral hypersensitivity in non-inflammatory and inflammation-associated colonic hypersensitivity mouse models.
The area under the curve (AUC) (A, C and E) between 80 μL and 100 μL for neonatal maternal separation (NMS) model and (B, D and F) between 60 μL and 80 μL for Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) model has been calculated for both doses of (A and B) carbamazepine (CBZ), (C and D) gabapentin (GBP) and (E and F) pregabalin (PGB). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, ANOVA 2 Way (Treatment; Dose) followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons for each treatment in one CHS model. CHS: Colonic hypersensitivity; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
- Citation: Meleine M, Boudieu L, Gelot A, Muller E, Lashermes A, Matricon J, Silberberg C, Theodorou V, Eschalier A, Ardid D, Carvalho FA. Comparative effects of α2δ-1 ligands in mouse models of colonic hypersensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(31): 7111-7123
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i31/7111.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7111