Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2016; 22(20): 4901-4907
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4901
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4901
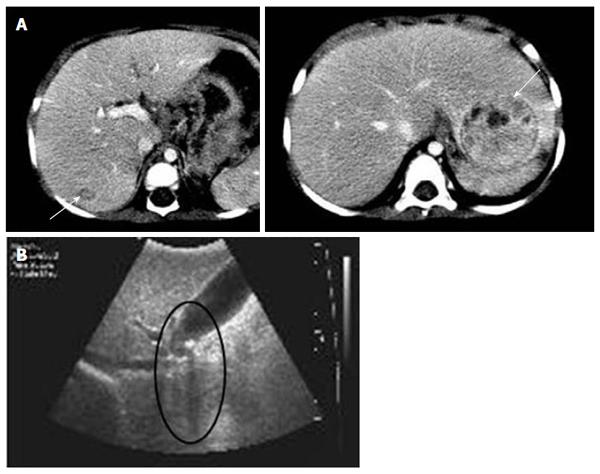
Figure 1 Radiologic hepatic evaluations in patient 1 and 2.
A: Abdominal computed tomography of patient 1 revealed two contrast-enhanced hepatic masses (arrows) at 21 mo of age; B: Gallstone and its posterior shadow (circle) were observed on liver ultrasonography in patient 2.
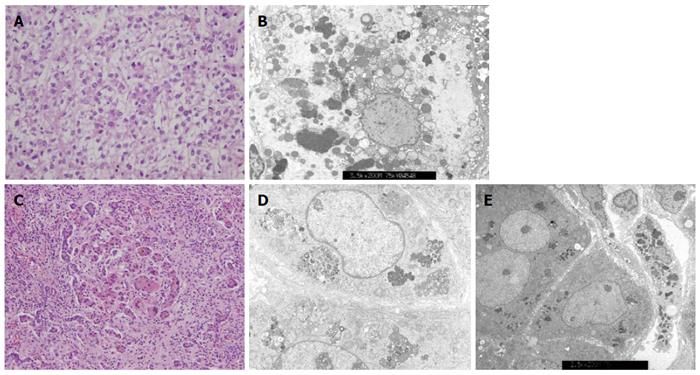
Figure 2 Liver histologic features from infants with chronic intrahepatic cholestasis with normal ranges of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma was confirmed by liver specimen at hepatectomy taken from patient 1 at 24 mo of age. Cellular atypia with trabecular and acinar type was shown. Microvascular invasion was not identified; hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification × 400; B: Electron microscopic examination of liver specimen from patient 2 shows many globular or curly appearance electron dense materials in the cytoplasm with original magnification of × 3.5k; C: Liver biopsy at hepatectomy taken at 6 months of age from patient 3 shows periportal fibrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, intracanalicular bile plugs, giant cell formation, and bile ductular proliferation; hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification × 200; D: Electron microscopic examination of liver specimen from patient 4 at 3.5 mo of age reveals amorphous and coarse granular bile pigments in the dilated bile canaliculi. Original magnification × 5.0k; E: Electron microscopic examination of liver specimen from patient 5 shows aggregated bile pigments in the cytoplasm. Original magnification × 2.5k.
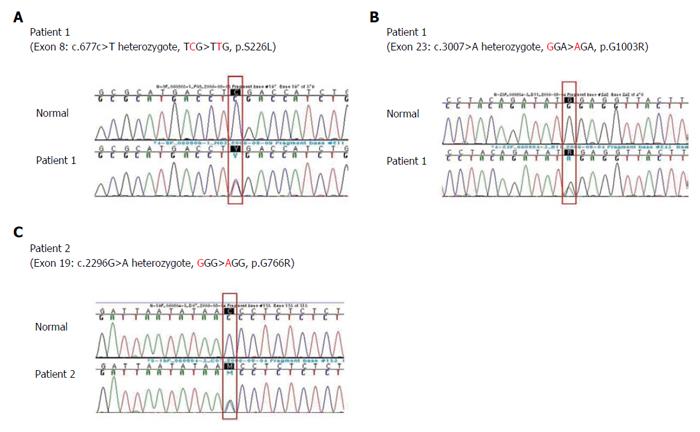
Figure 3 Direct sequencing analysis of the ABCB11 genes demonstrating (A) heterozygous C to T substitution in exon 8 predicting a missense mutation at amino acid position 226(p.
S226L) (B) heterozygous G to A in exon 23 predicting a missense mutation at amino acid position 1003 (p.G1003R), and (C) heterozygous G to A in exon 19 predicting a missense mutation at amino acid position 776(p.G776R), (A) and (B) were detected in ABCB11 gene of patient 1 and (C) was detected in patient 2.
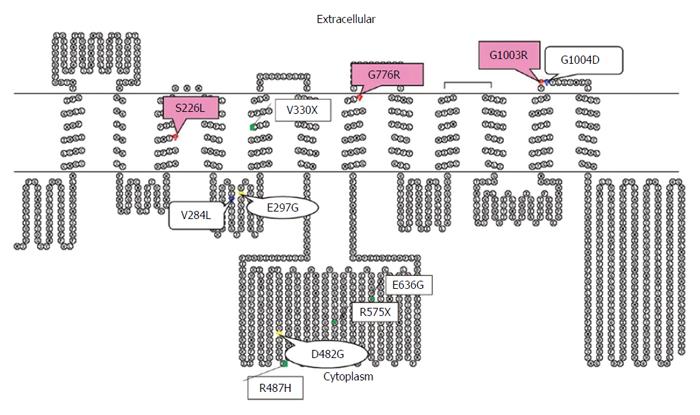
Figure 4 Putative secondary structure of bile salt export pump generated with the TOPO program.
Mutations are represented in red for mutations in patient 1 and 2, green for Japanese, blue for Taiwanese, and yellow for common European mutations. Bile salt export pump alterations in the present study were located at and near the transmembranous space, which was different from most of the mutations from Chinese, Japanese, Taiwanese, and European patients[2,5,7,12].
- Citation: Park JS, Ko JS, Seo JK, Moon JS, Park SS. Clinical and ABCB11 profiles in Korean infants with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(20): 4901-4907
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i20/4901.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4901