Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3735-3745
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3735
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3735
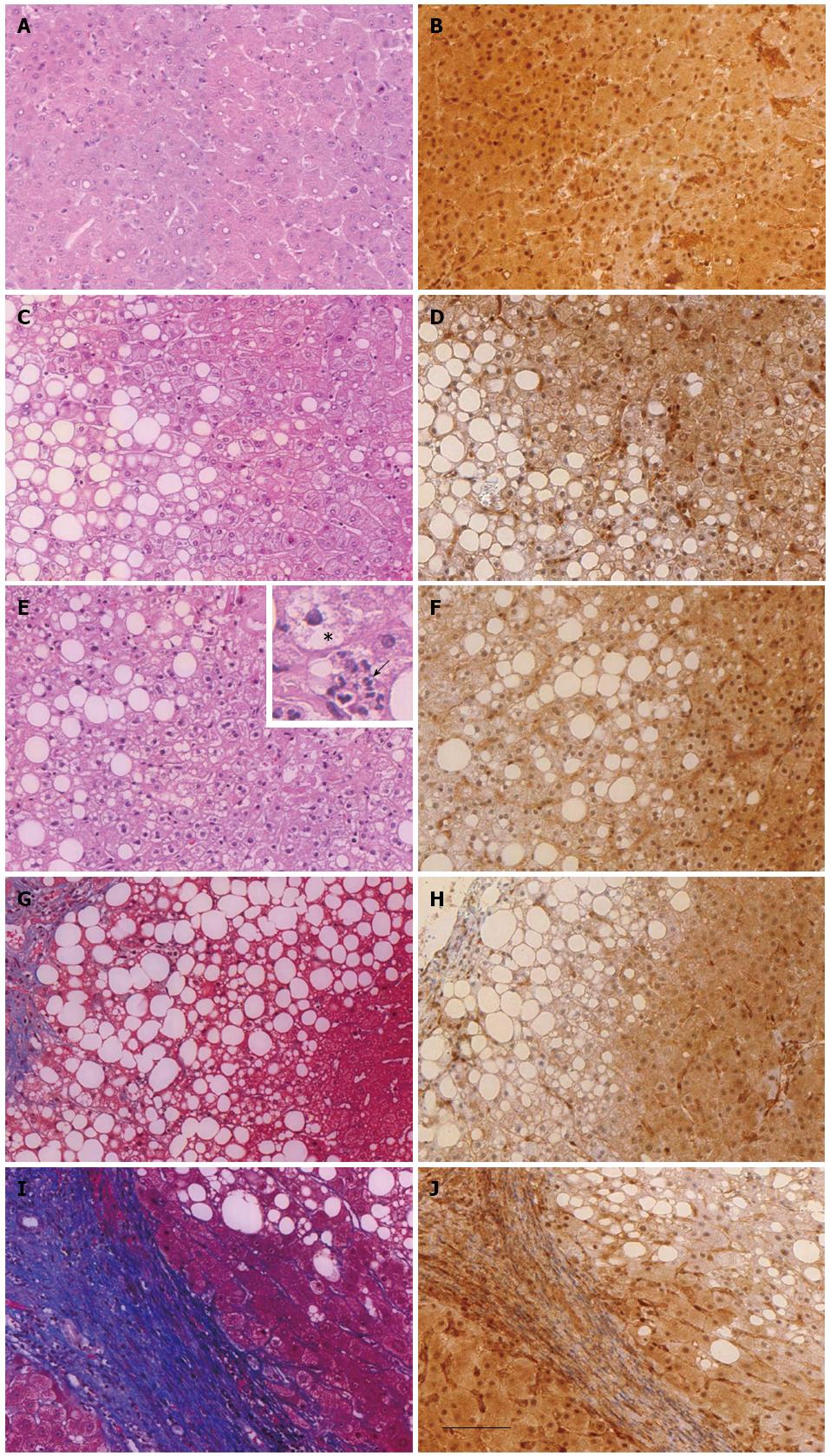
Figure 1 General histology and immunohistochemical detection of phosphatase and tensin homolog protein expression in the liver of healthy donor (hepatic resections) or patients with different stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (liver biopsies).
Liver sections of healthy donors (A and B) or of obese patients with steatosis (n = 10, C and D), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (n = 14, E and F), fibrosis (n = 12, G and H) and cirrhosis (n = 8, I and J) were either stained with hematoxylin eosin (A, C, E), Masson’s trichrome (G and I) or immunostained with anti-PTEN antibody (B, D, F, H and J). The inset in image (E) shows hepatic intralobular inflammation characterized by neutrophils (arrow) and ballooning hepatocyte (star). Scale bar = 100 μm. PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog.
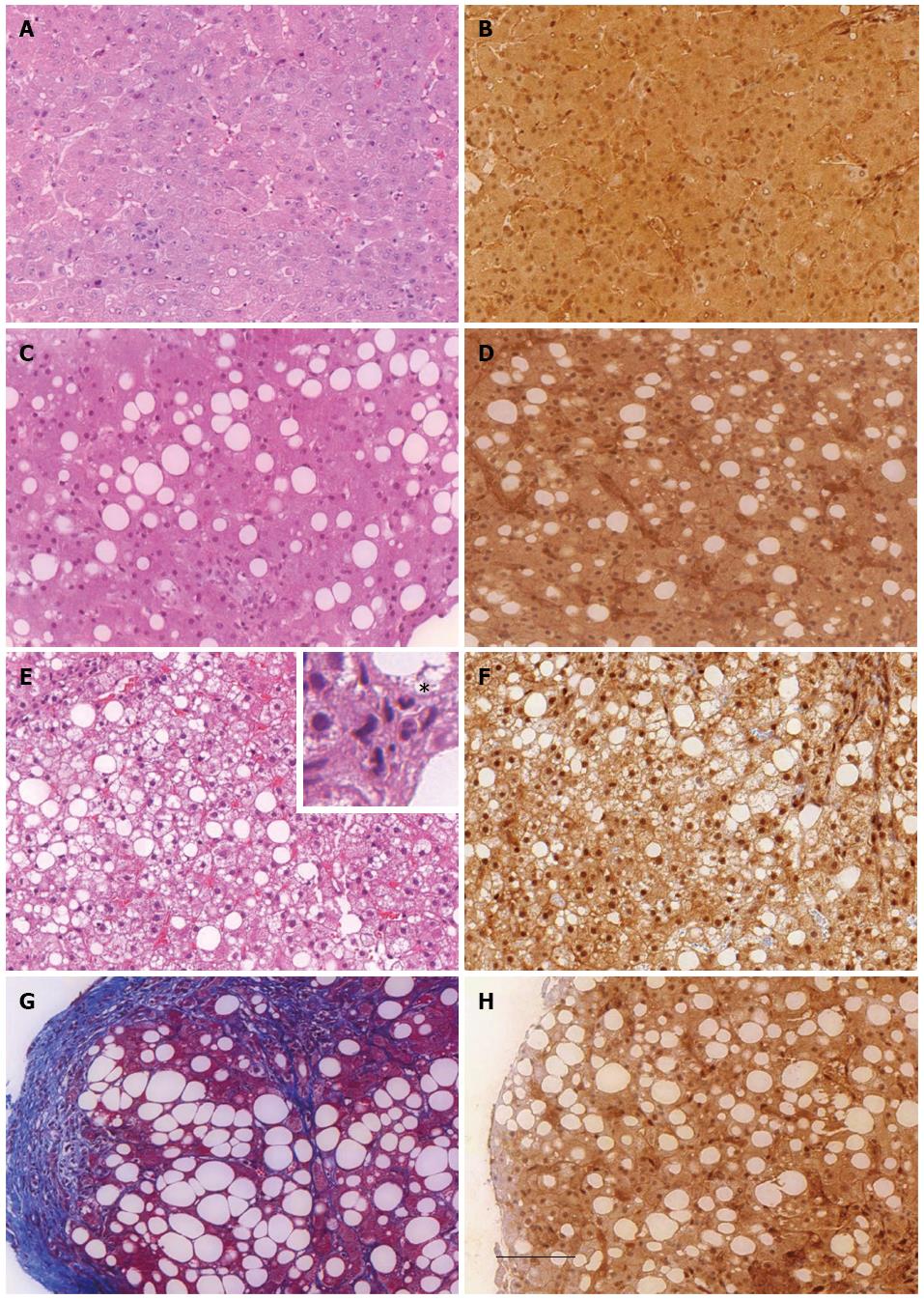
Figure 2 General histology and immunohistochemical detection of phosphatase and tensin homolog protein expression in the liver of healthy donor (hepatic resections) or patients with different stages of alcoholic liver disease (liver biopsies).
Liver sections of healthy donors (A and B) or of patients with alcoholic steatosis (C and D), alcoholic steatohepatitis (E and F) and cirrhotic alcoholic disease (G and H) were stained with hematoxylin eosin (A, C and E), Massson’s trichrome (G) or immunostained with anti-PTEN antibody (B, D, F and H). Scale bar = 100 μm. The inset in image (E) shows hepatic intralobular inflammation characterized by neutrophils (star). Scale bar = 100 μm. PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog.
- Citation: Sanchez-Pareja A, Clément S, Peyrou M, Spahr L, Negro F, Rubbia-Brandt L, Foti M. Phosphatase and tensin homolog is a differential diagnostic marker between nonalcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3735-3745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3735