Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2015; 21(6): 1972-1981
Published online Feb 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1972
Published online Feb 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1972
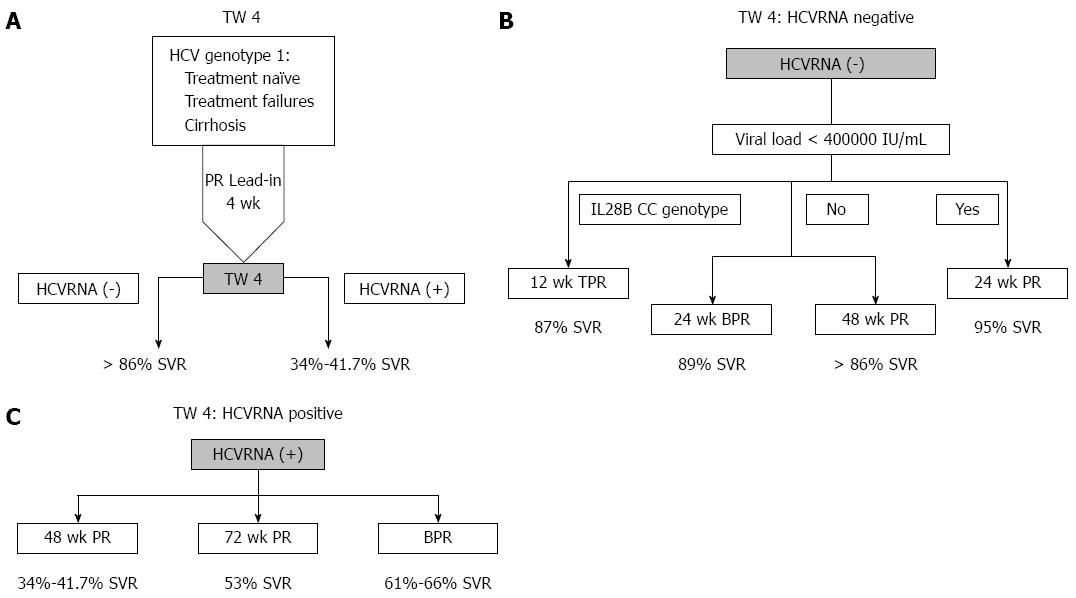
Figure 1 Treatment week 4 (A), hepatitis C virus RNA negative (B) and hepatitis C virus RNA positive (C).
A: All patients eligible for PR therapy regardless of whether they are treatment naïve, previous treatment failures or cirrhotics. Patients who achieve RVR after 4 wk lead-in either have detectable or undetectable HCVRNA. Those with undetectable HCVRNA have SVR > 86% while those with detectable HCVRNA have SVR 34%-41.7%; B: These patients have a high possibility of SVR so PR therapy can be shortened to 24 wk if they have baseline viral load < 400000 IU/mL). If they do not have good baseline predictors, therapy can also be shortened by addition of boceprevir (4 wk lead-in, 24 wk boceprevir + PR). If they also have IL28B CC genotype, telaprevir and PR can be used for 12 wk as well. Alternatively, they can continue on to 48 wk PR; C: These patients have a low possibility of SVR (41.7%) hence the alternative is to extend PR to 72 wk (53% SVR) or to add boceprevir (61%-66% SVR). TW: Treatment week; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PR: Pegylated interferon and ribavirin; SVR: Sustained virological response.
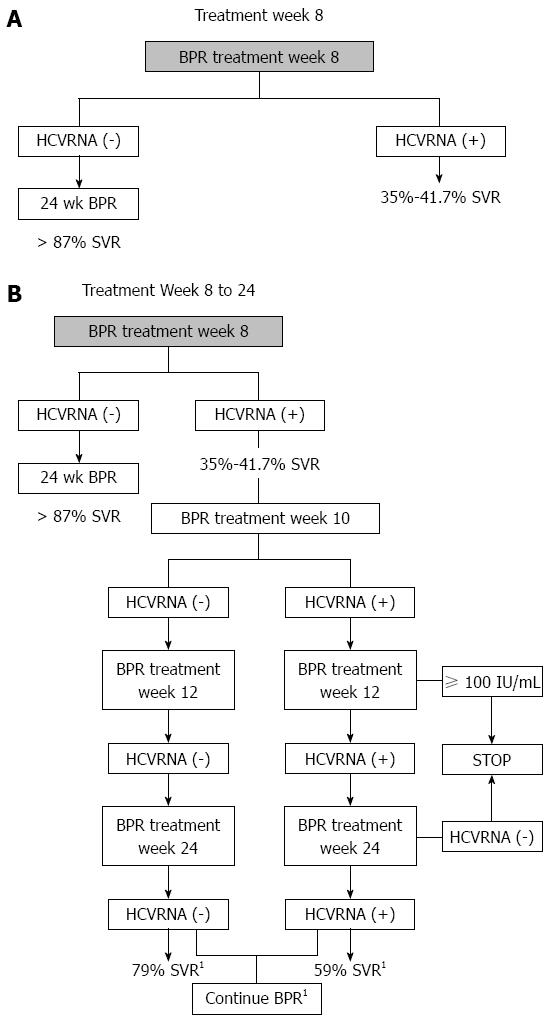
Figure 2 Treatment week 8 (A) and treatment week 8 to week 24 (B).
A: These patients regardless of the treatment week 4 responses have a high possibility of SVR if they are HCVRNA negative (SVR > 87%) and are eligible for shortened therapy but if they are HCVRNA positive, then SVR rates are low, 35%-41.7%; B: After addition of boceprevir, with undetectable HCVRNA, these patients are eligible for shortened therapy (4 wk lead-in, 24 wk boceprevir +PR). However if they are HCVRNA positive then HCVRNA at weeks 10 and 12 are useful to guide therapy. Those who are HCVRNA ≥ 100 IU/mL at week 12 or have detectable HCVRNA at week 24 fulfill the stopping rules. 1Not eligible for shortened therapy - should complete 32 wk BPR ± 12 wk PR or complete 44 wk BPR. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PR: Pegylated interferon and ribavirin; SVR: Sustained virological response.
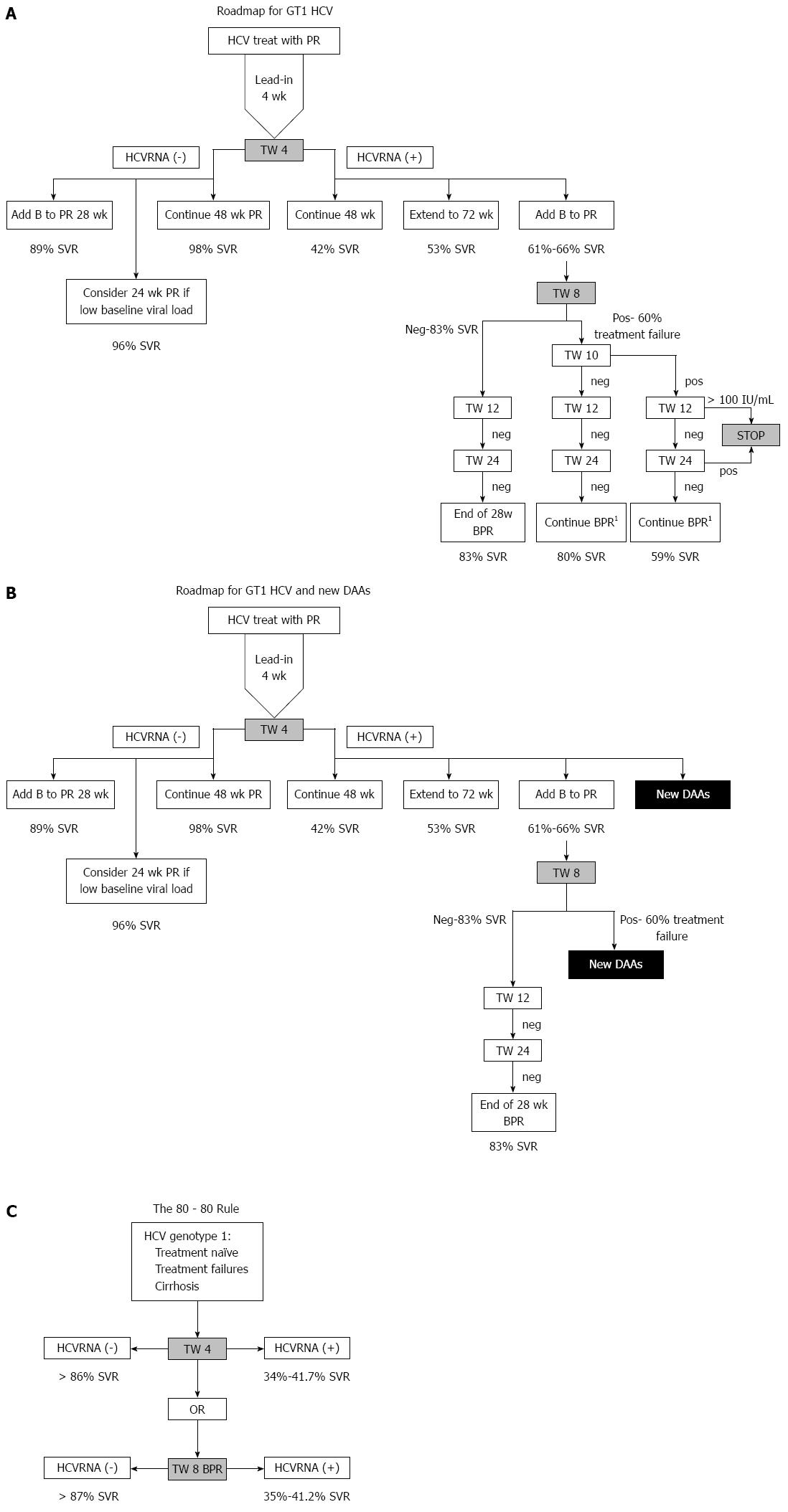
Figure 3 Roadmap for GT1 hepatitis C virus (A), Roadmap for GT1 hepatitis C virus and new direct acting antivirals (B) and the “80-80” Rule (C).
A: Full roadmap showing timepoints, predicted SVR based on undetectable HCVRNA at timepoints, and alternative choices at each timepoint. 1Not eligible for shortened therapy - should complete 32 wk BPR ± 12 wk PR or complete 44 wk BPR; B: Modification of the roadmap showing that new DAAs can be considered at Treatment week (TW)4 or TW8 if HCVRNA is positive; C: Main points of the roadmap showing that if HCVRNA is negative at TW4 (on PR) or 8 (on BPR) then there is > 80% SVR. If HCVRNA is positive at week 4, then there is 41.7% SVR if 48 wk PR is continued, but at week 8, if HCVRNA is positive while on BPR then the possibility of SVR is 35%-41.2%. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PR: Pegylated interferon and ribavirin; SVR: Sustained virological response.
- Citation: Lim SG. Chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 treatment roadmap for resource constrained settings. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(6): 1972-1981
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i6/1972.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1972