Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13555-13565
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13555
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13555
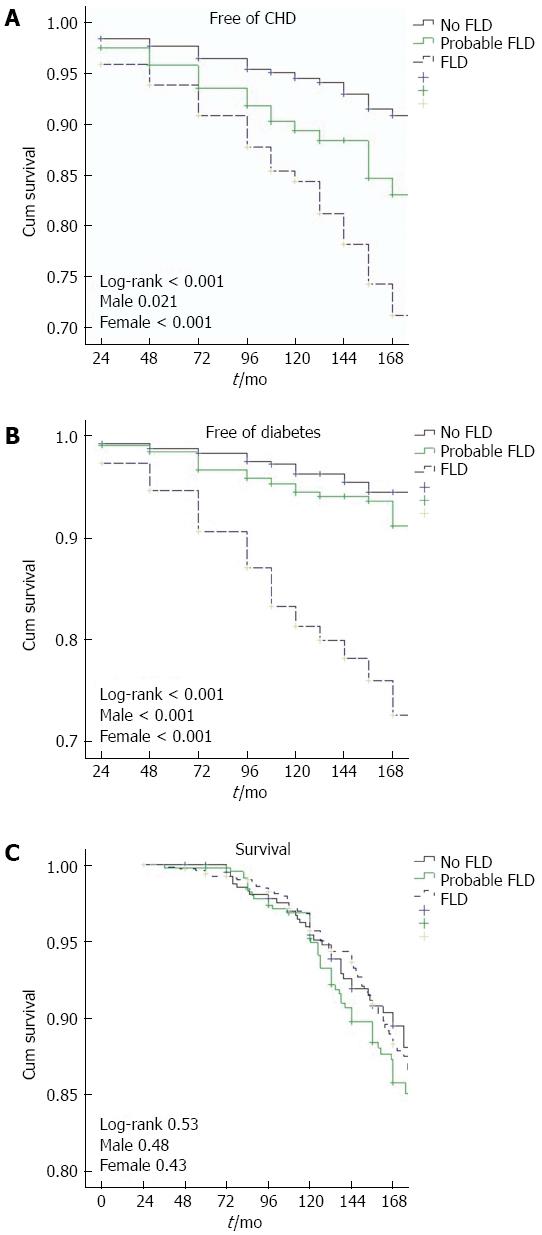
Figure 1 Diagram depicts Kaplan-Meier plots in the whole sample for survival and (exclusive of those with diabetes/coronary heart disease) survival free of diabetes/coronary heart disease.
Significantly (Log-rank < 0.001) lower survival free of diabetes and of incident CHD are noted for participants with FLD at baseline. Subjects categorized as probable FLD separated from those with no FLD in regard to CHD. However, no significant difference was elicited (Log-rank 0.53) with respect to mortality. Log-rank values were similar in the sexes. BP: Blood pressure; CHD: Coronary heart disease; FLD: Fatty liver disease.
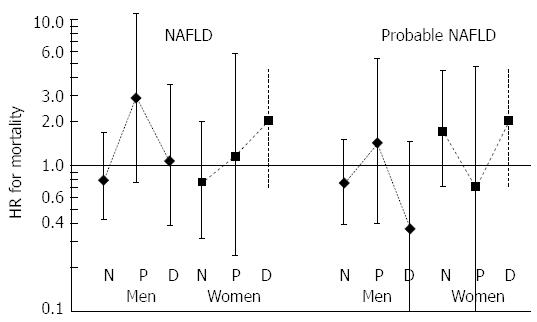
Figure 2 Diagram of multivariable adjusted hazard ratios are depicted for death of fatty liver disease in the 3 glucose categories.
Though significant findings were not obtained, the risk of overall mortality among normoglycemic (N) individuals with fatty liver disease was lower than in subjects with no fatty liver disease. Risk increased in prediabetes (P) and tended so in diabetic (D) women, while declining in men with diabetes. NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Onat A, Can G, Kaya A, Akbaş T, Özpamuk-Karadeniz F, Şimşek B, Çakır H, Yüksel H. Fatty liver disease: Disparate predictive ability for cardiometabolic risk and all-cause mortality. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13555-13565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13555