Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13447-13456
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447
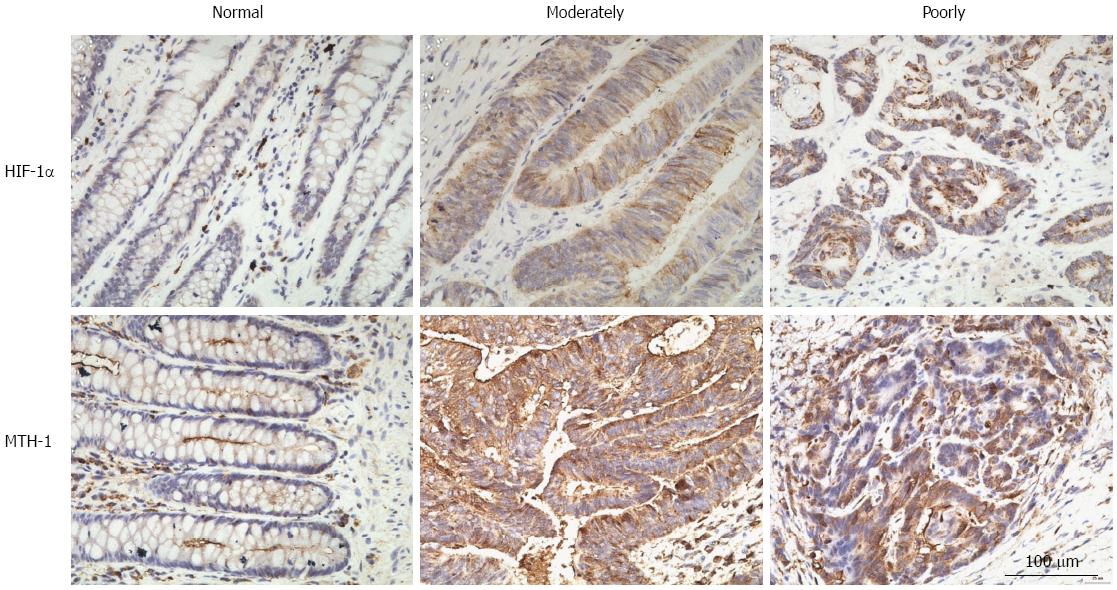
Figure 1 Images of three groups defined by immunohistochemical staining for hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and mutT homolog-1 in normally, moderately, and poorly differentiated colorectal cancer.
No HIF-1α immunoreactivity was detected in normal colorectal mucosa (A). Moderate to strong HIF-1α immunoreactivity was detected in the cytoplasm of tumor cells in moderately or poorly differentiated colorectal adenocarcinoma (B and C). MTH-1 immunoreactivity of normal colon mucosa was faint in the cytoplasm, and strong cytoplasmic immunostaining was observed in lymphoid cells (D). Moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated colorectal adenocarcinoma exhibited strong cytoplasmic staining for MTH-1 protein (E and F). Original magnification, × 400. HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MTH-1: MutT homolog-1.
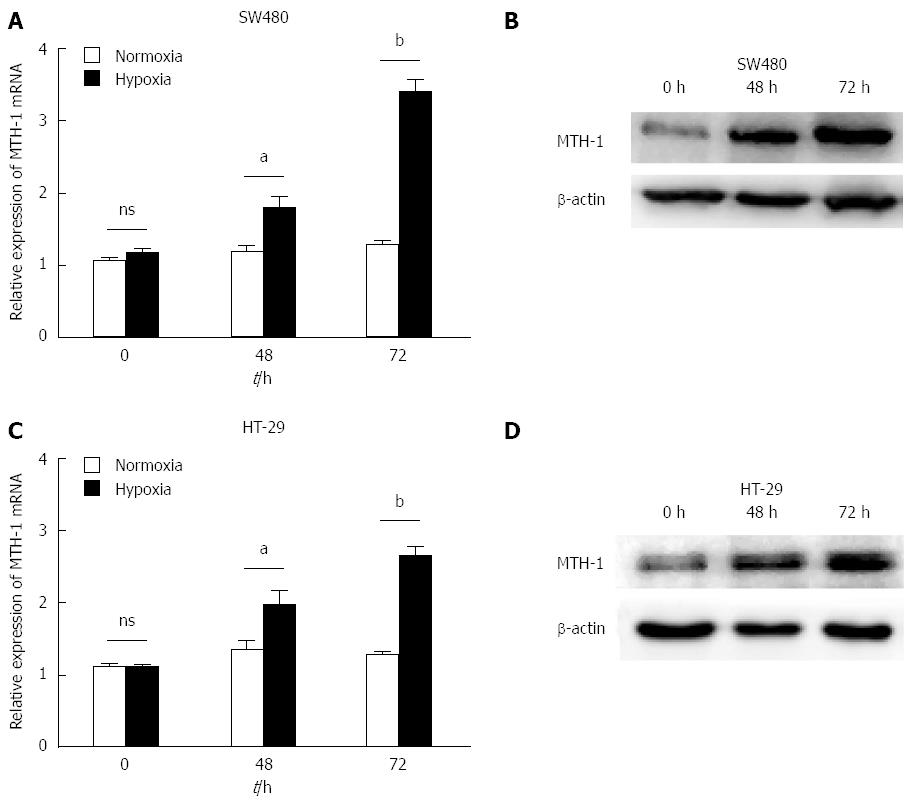
Figure 2 Hypoxic stress-induced mutT homolog-1 expression in colon carcinoma cell lines.
SW480 and HT-29 cells were incubated under normal or hypoxic conditions. mRNA relative expression of MTH-1 was evaluated by qRT-PCR, as shown in A and C (48 h: P = 0.013, P = 0.041; 72 h: P = 0.000, P = 0.000). Protein levels of MTH-1 were evaluated by western blotting, as shown in B and D. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, normoxia vs hypoxia. MTH-1: MutT homolog-1; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
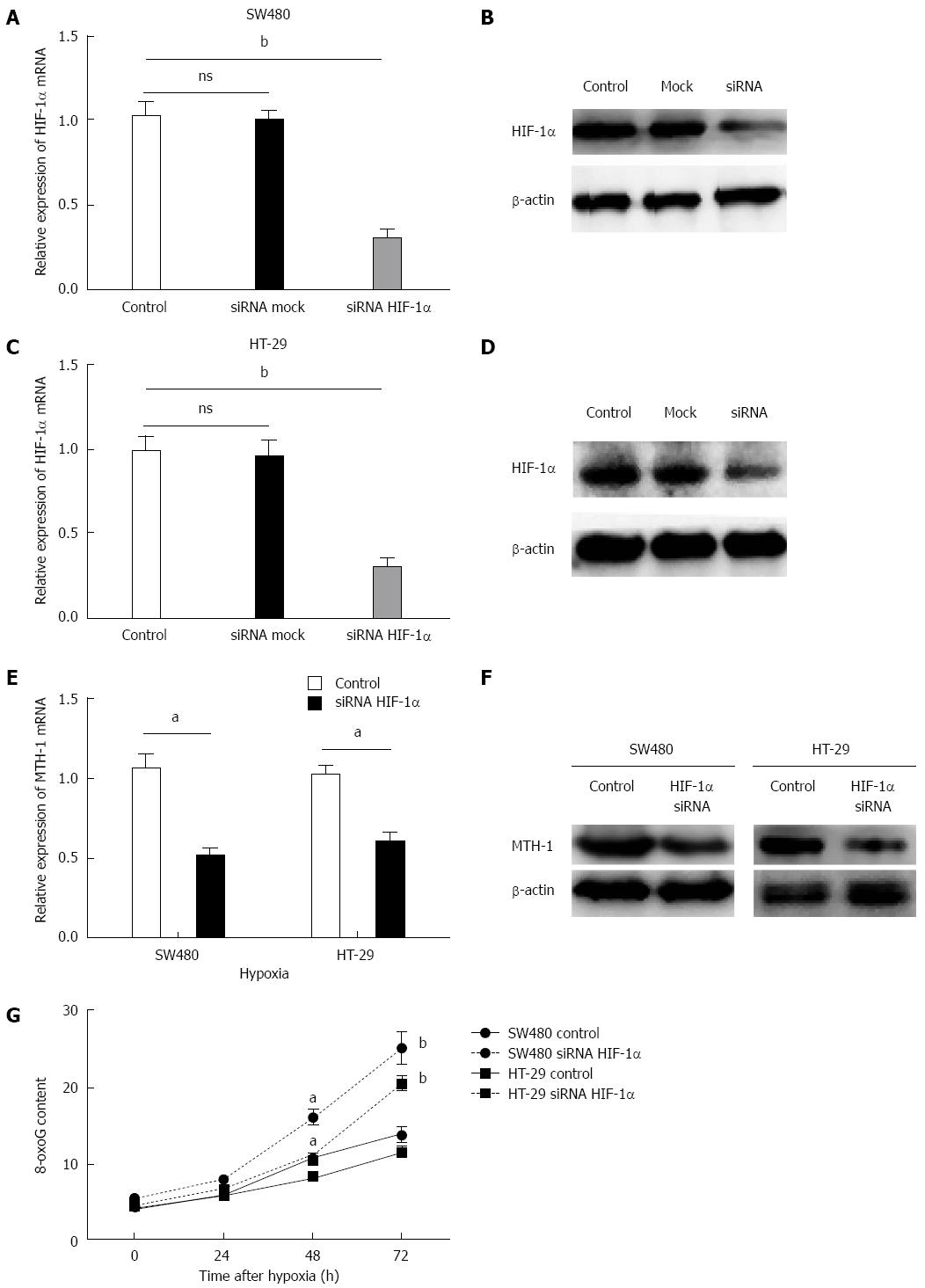
Figure 3 Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is involved in hypoxia-enhanced expression of mutT homolog-1.
SW480 and HT-29 cells transfected with either siRNA targeting HIF-1α or mock siRNA were exposed to hypoxia for 72 h or normoxia. qRT-PCR showed that siRNA targeting HIF-1α significantly inhibited expression of HIF-1α mRNA in colon cancer cells as compared to cells treated with mock siRNA(P = 0.0003, P = 0.0007) (A and C). Western blotting showed that siRNA targeting HIF-1α significantly suppressed expression of HIF-1α protein under hypoxia, but the mock siRNA group was unaffected (B and D). MTH-1 mRNA expression and MTH-1 protein were decreased by silencing of HIF-1α at 72 h (P = 0.002, P = 0.003) (E and F). The residual 8-oxo-dGTP base lesions were markedly higher in the HIF-1α siRNA groups compared to the mock siRNA groups of SW480 and HT-29 cells (G) (48 h: P = 0.011, P = 0.016; 72 h: P = 0.003, P = 0.000). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control. NS: Non-significant; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MTH-1: MutT homolog-1; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
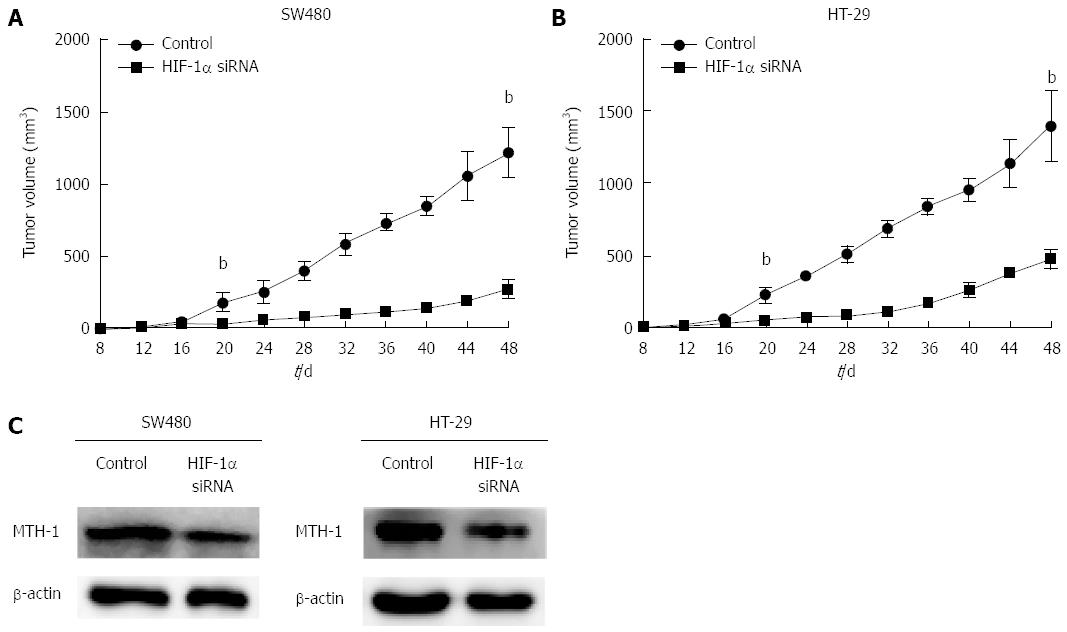
Figure 4 Effects of siRNA of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α on tumor growth and mutT homolog-1 expression in a nude mouse xenograft tumor model.
Tumor volume in the mouse interference group measured by calipers was significantly lower than that in the mock group of SW480 and HT-29 cells (A and B) (20 d: P = 0.004, P = 0.001; 48 d: P = 0.000, P = 0.000). Western blotting revealed that expression of MTH-1 protein was inhibited by silencing of HIF-1α (C). bP < 0.01, vs control. HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; MTH-1: MutT homolog-1.
- Citation: Qiu Y, Zheng H, Sun LH, Peng K, Xiao WD, Yang H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates upregulation of mutT homolog-1 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13447-13456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13447.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447