Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13418-13431
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13418
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13418
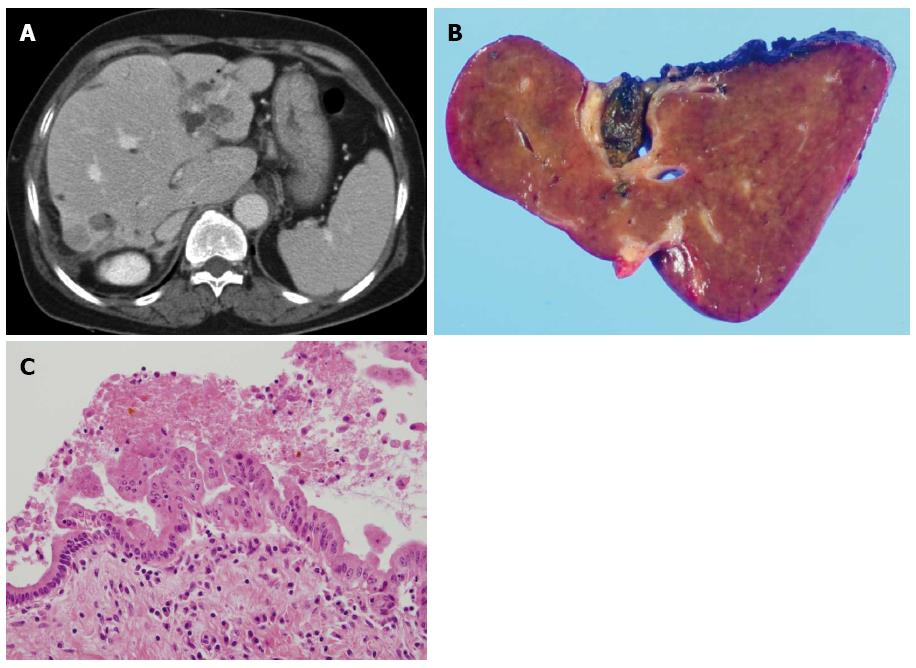
Figure 1 Sixty-seven years old, female was admitted for cholangitis and treated with hepatic resection.
She was followed and underwent second resection 1 year later. A: Abdominal computed tomography demonstrated that B2 IHD dilatation with stones and 2 cm sized low density lesion in liver S7; B: Liver, left, lateral, segmentectomy was done; C: BilIN1 and two were shown on dilated duct with glandular proliferation.
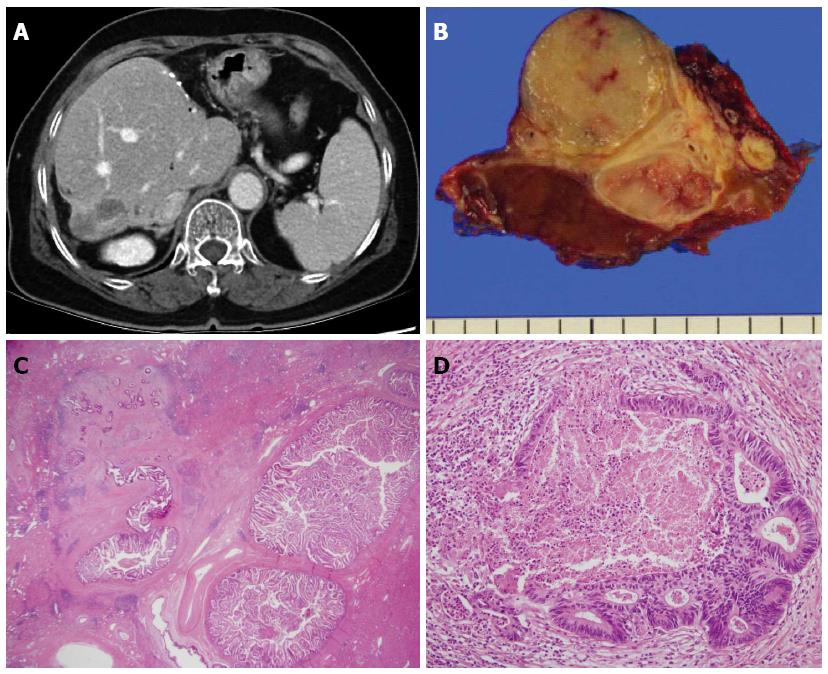
Figure 2 Sixty-seven years old, female was admitted for cholangitis and treated with hepatic resection.
She was followed and underwent second resection 1 year later. A: Follow-up abdominal computed tomography. Exophytic hypodense mass in S7 of the liver was more enlarged with peripheral enhancement; B: Liver, S7, segmentectomy was done; C and D: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) statin (C: × 12.5; D: × 200). Intraductal papillary neoplasm with an associated invasive carcinoma. 6 cm × 3 cm × 3 cm sized intraductal papillary neoplasm including 0.6 cm × 0.5 cm sized invasive tumor.
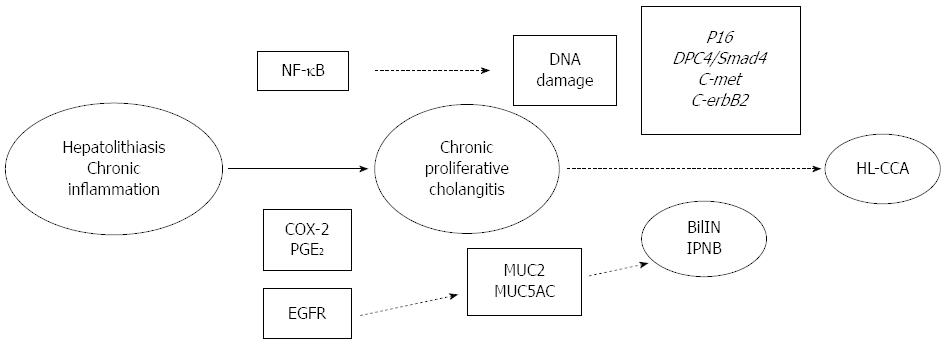
Figure 3 Molecular mechanism of hepatolithiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma.
HL-CCA: hepatolithiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; IPNB: Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct; BilIN: Biliary intraepithelial neoplasia.
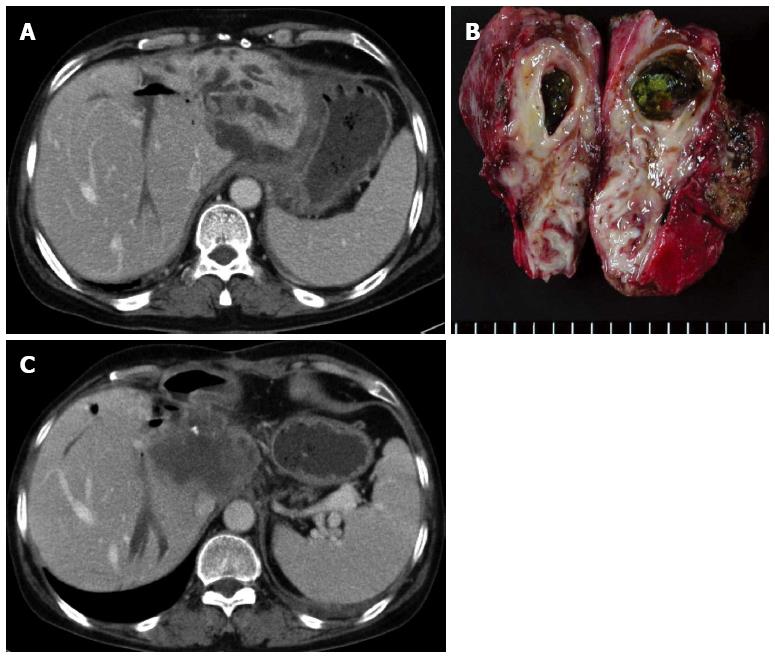
Figure 4 Forty-six years old, female was admitted for cholangitis.
A: Abdominal CT demonstrated that multiple calcified stones are present in the lateral segment of the left lobe; B: Liver, left lobectomy was performed, and there was no cancerous lesion; C: Abdominal computed tomography taken 14 mo after resection demonstrated development of cholangiocarcinoma in the caudate lobe of the liver.
- Citation: Kim HJ, Kim JS, Joo MK, Lee BJ, Kim JH, Yeon JE, Park JJ, Byun KS, Bak YT. Hepatolithiasis and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13418-13431
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13418