Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2015; 21(47): 13250-13258
Published online Dec 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13250
Published online Dec 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13250
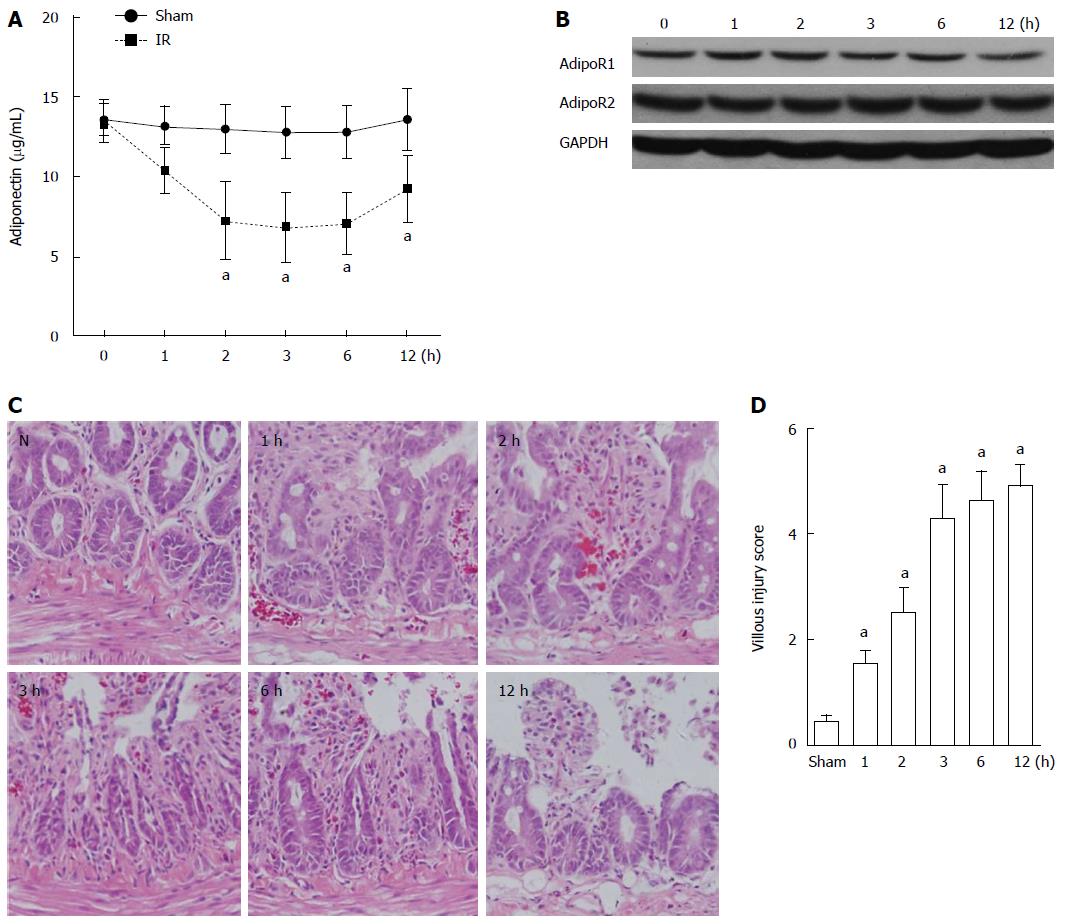
Figure 1 Adiponectin levels in rats in the sham and ischemia reperfusion injury groups.
A: ELISA was used to determine the adiponectin serum levels in the sham and ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury rats. Data are presented as mean ± SD obtained from five independent experiments; B: Western blot analysis of the expression of adiponectin receptor 1 and adiponectin receptor 2 in the small intestine of rats with I/R injury; C: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of the small intestine at different time points after I/R injury; D: Villous injury scores of C. Necrosis was the major damage after intestinal I/R. N: Colon tissue in normal control rat. aP < 0.05 vs sham.
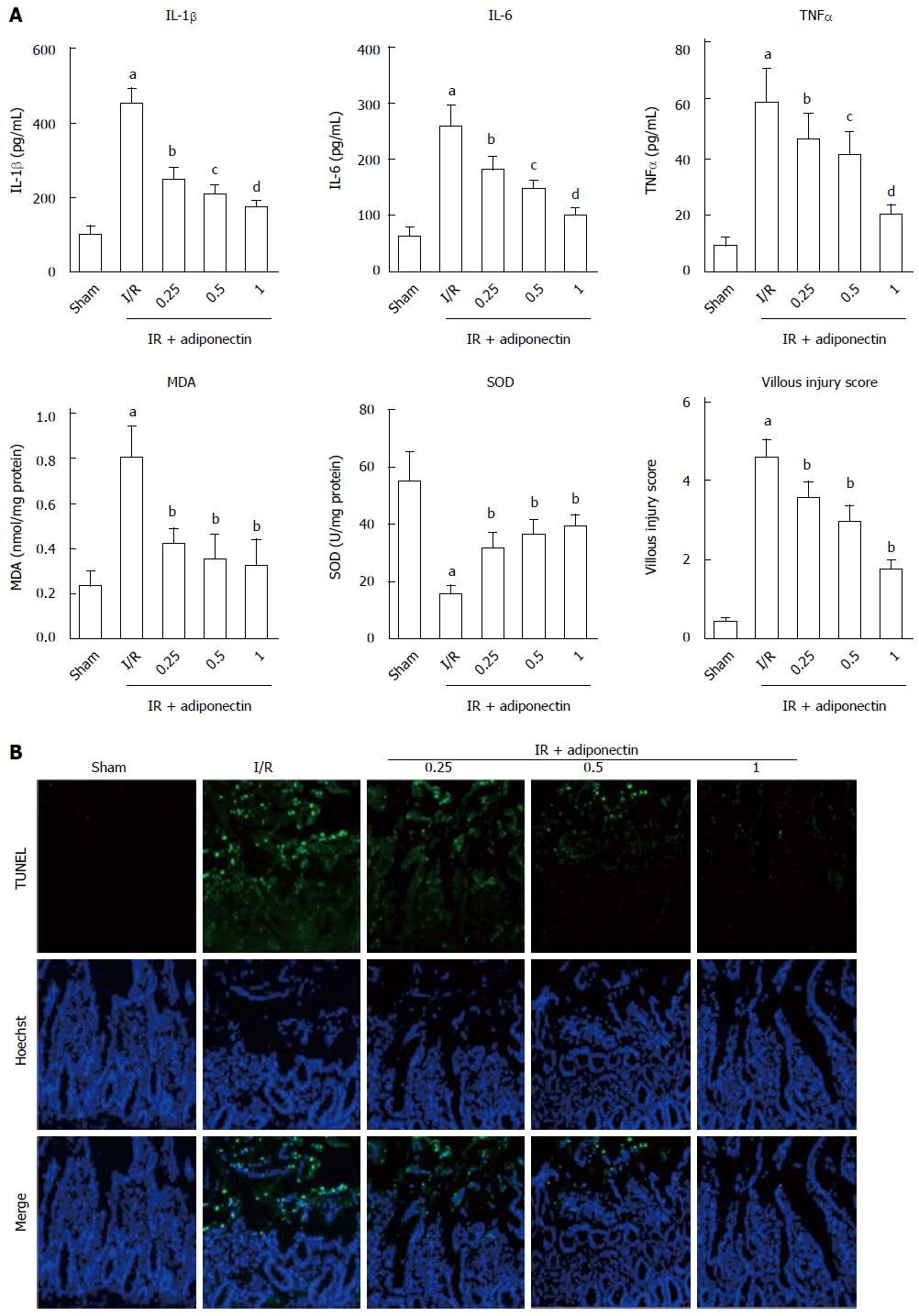
Figure 2 Adiponectin attenuated ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.
A: The expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MDA, and SOD, and the villous damage score. The data are expressed as mean ± SD obtained from five independent experiments; B: TUNEL/Hoechst staining was performed to assess the effects of adiponectin treatment on cell apoptosis. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue staining). Apoptotic nuclei were identified by TUNEL staining (green). aP < 0.05 vs sham, bP < 0.05 vs IR, cP < 0.05 vs 0.25 mg/kg group, dP < 0.05 vs 0.5 mg/kg group. SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
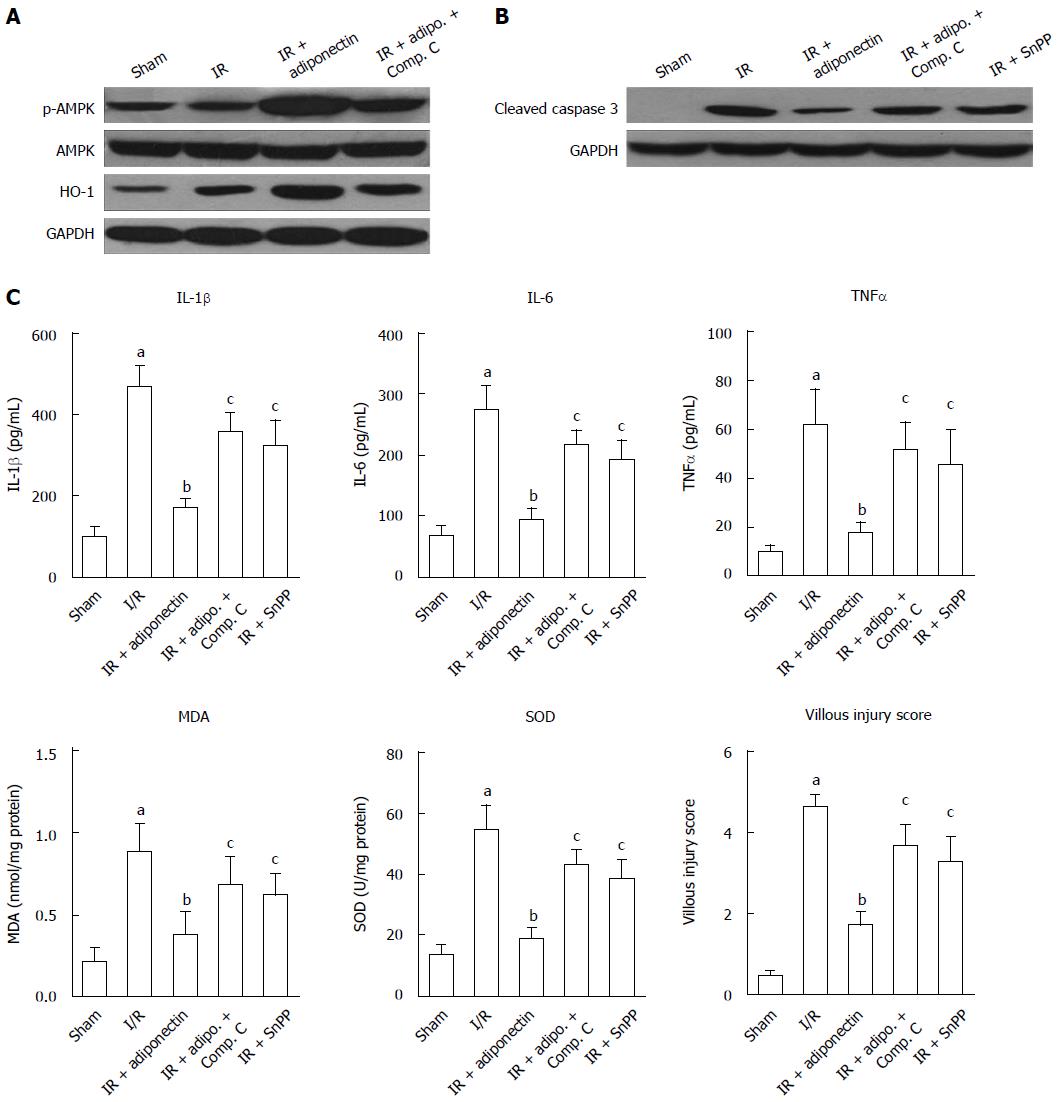
Figure 3 AMPK inhibition attenuated ischemia reperfusion injury.
A: Western blot analysis of the expression of p-AMPK and HO-1; B: Western blot analysis of the expression of cleaved caspase 3; C: The serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MDA, and SOD and the villus damage score. Compound C: AMPK signaling pathway inhibitor; Snpp, HO-1 inhibitor. Adipo: Adiponectin; Compo. C: Compound C; The data are expressed as mean ± SD obtained from 5 independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs sham, bP < 0.05 vs IR, cP < 0.05 vs IR + adiponectin. I/R: Ischemia reperfusion; HO-1: Heme oxygenase 1; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
- Citation: Liu XH, Yang YW, Dai HT, Cai SW, Chen RH, Ye ZQ. Protective role of adiponectin in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(47): 13250-13258
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i47/13250.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13250