Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2015; 21(45): 12963-12969
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12963
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12963
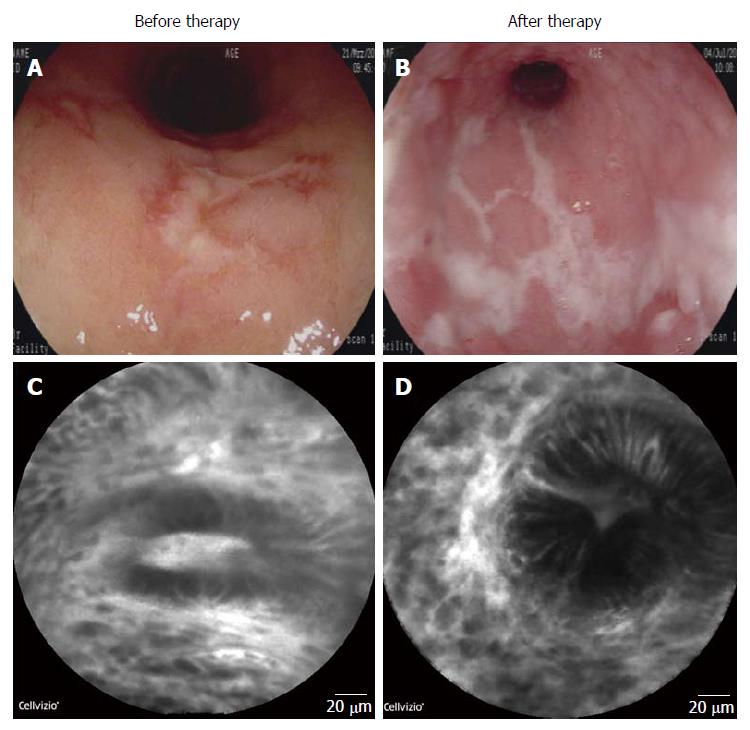
Figure 1 Endoscopic and endomicroscopic evaluation of the mucosa before and after anti-interleukin-6R therapy.
Endoscopy of the sigmoid mucosa of the patient before anti-interleukin (IL)-6R therapy showed strong signs of mucosal inflammation (A); Mayo endoscopy score = 3; Evaluation of the sigmoid after 12 wk of tocilizumab treatment revealed augmented signs of mucosal inflammation and progressive ulcer formation. Mayo endoscopy score = 3 (B); Endomicroscopy with a probe based system (Mauna Kea System) of the sigmoid mucosa of the patient before (C); and after 12 wk of anti-IL-6R therapy (D). There was a marked increase in mucosal inflammation with increased leakage, dilatation of microvessels and disturbed crypt architecture.
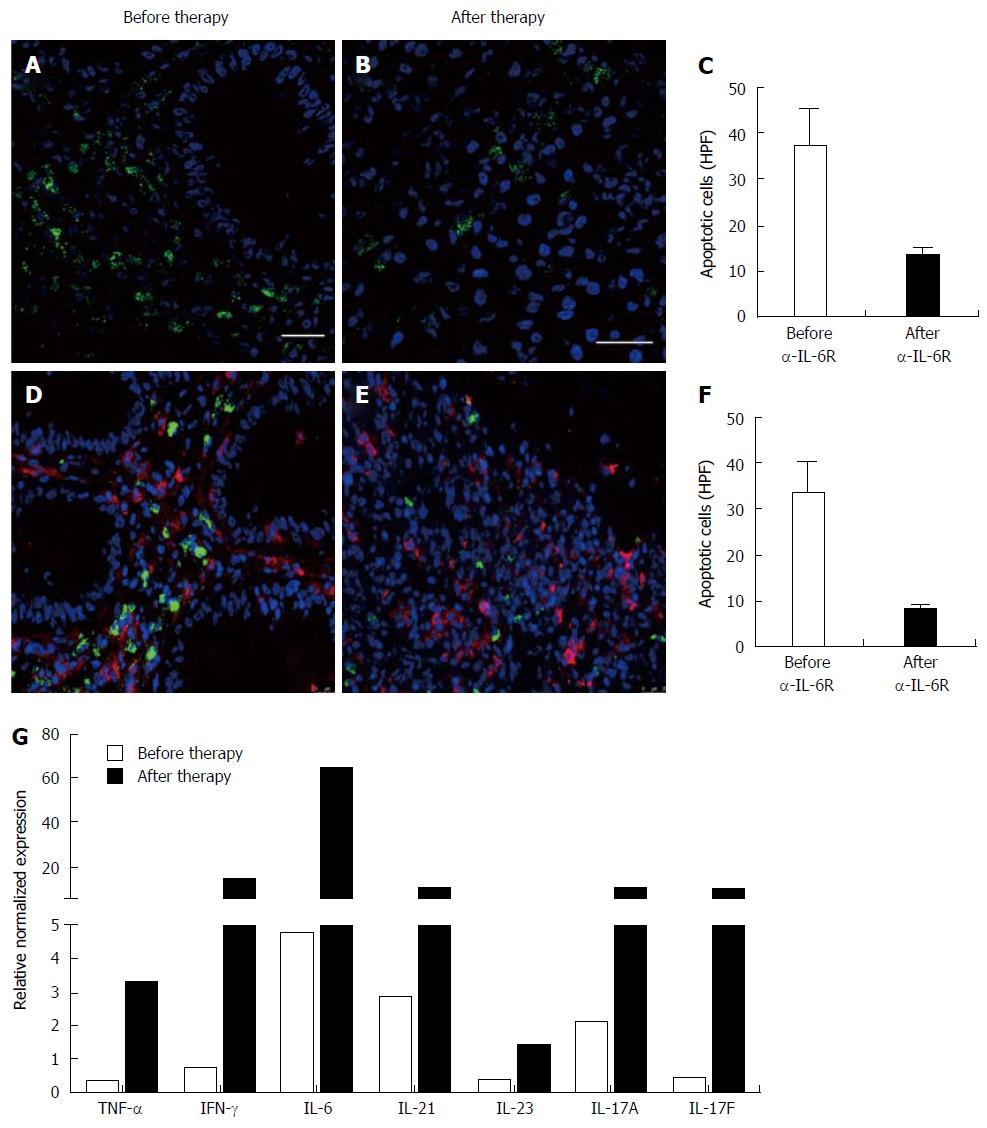
Figure 2 Caspase positive cells and quantitative gene expression profile of mucosal biopsies before and after anti-interleukin-6R therapy.
Pairs of colonic tissue samples taken before (A) and after (B) anti-interleukin (IL)-6R therapy, were stained for caspase and assessed regarding caspase positive cells in 14 high-power fields per slide (C); Histological slides before (D) and after (E) IL-6R inhibition were also stained for caspase and CD4 and quantitatively assessed (F); There was a marked reduction of apoptotic LPMCs and mucosal T cells upon tocilizumab treatment. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars represent 25 μm. Total RNA was isolated from mucosal biopsies taken before (white) and after (black) anti-IL-6R therapy and reverse transcribed (G). Gene expression profiles were analysed by quantitative PCR and normalized to the housekeeping-gene HPRT. There was a marked induction in the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines upon anti-IL-6R treatment.
- Citation: Atreya R, Billmeier U, Rath T, Mudter J, Vieth M, Neumann H, Neurath MF. First case report of exacerbated ulcerative colitis after anti-interleukin-6R salvage therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(45): 12963-12969
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i45/12963.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12963