Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2015; 21(33): 9727-9735
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727
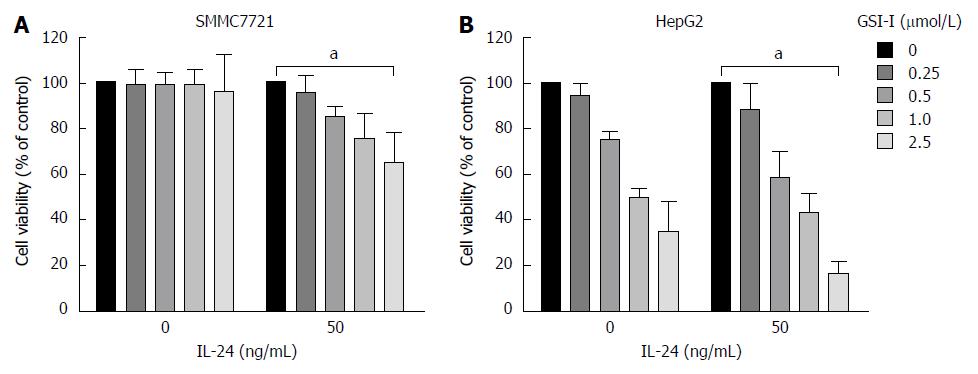
Figure 1 γ-secretase inhibitor-I/interleukin-24 combined treatment induces apoptotic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Cytotoxic effects exerted on SMMC7721 cells by γ-secretase inhibitor-I (GSI-I) employed alone or in combination with recombinant interleukin (IL)-24. After treatment for 24 h cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay as reported in Materials and Methods; B: Cytotoxic effects exerted on HepG2 cells by GSI-I employed alone or in combination with recombinant IL-24. After treatment for 24 h cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay as reported in Materials and Methods. The data represent mean ± SD; aP < 0.05 vs control cells.
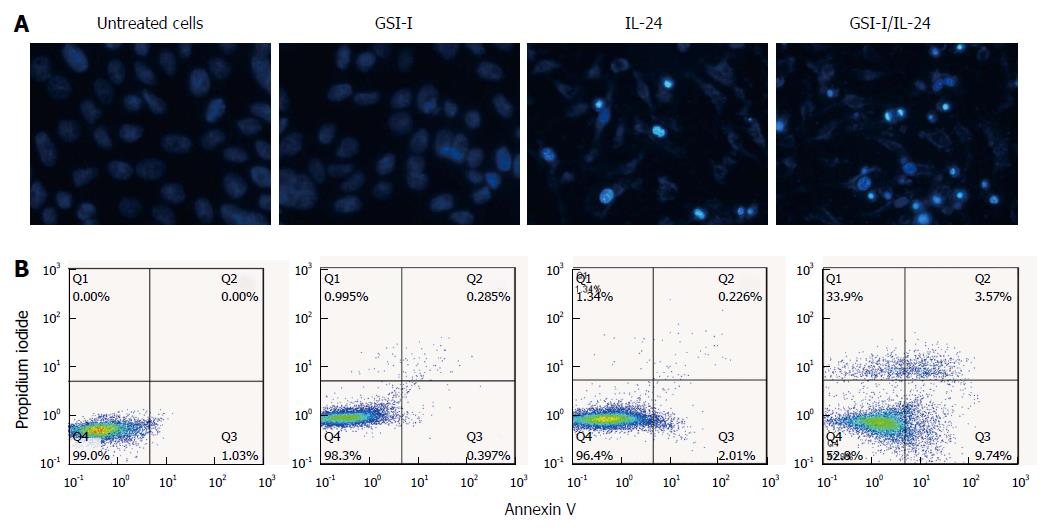
Figure 2 γ-secretase inhibitor-I/interleukin-24 combined treatment induces apoptotic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Apoptotic effects induced by treatment of HepG2 cells with GSI-I and/or IL-24 for 24 h. Apoptotic morphology was evaluated by staining of the cells with Hoechst 33258 (magnification × 200); B: Annexin V positive cells were quantified by flow cytometric analysis after double staining of cells with Annexin V and propidium iodide at 6 h of treatment. Results are representative of three independent experiments. GSI-I: γ-secretase inhibitor-I; IL: Interleukin.
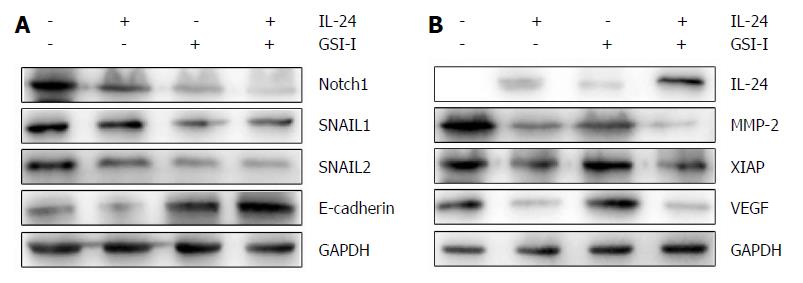
Figure 3 Cytotoxic effects of interleukin-24 and γ-secretase inhibitor-I assessed by Western blot analysis.
A, B: HepG2 cells were treated for 48 h in the presence of GSI-I and/or IL-24. The levels of the proteins were determined by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies as indicated. GAPDH blots were included to show equal protein loading for all of the samples. Results are representative of three independent experiments. GSI-I: γ-secretase inhibitor-I; IL: Interleukin.
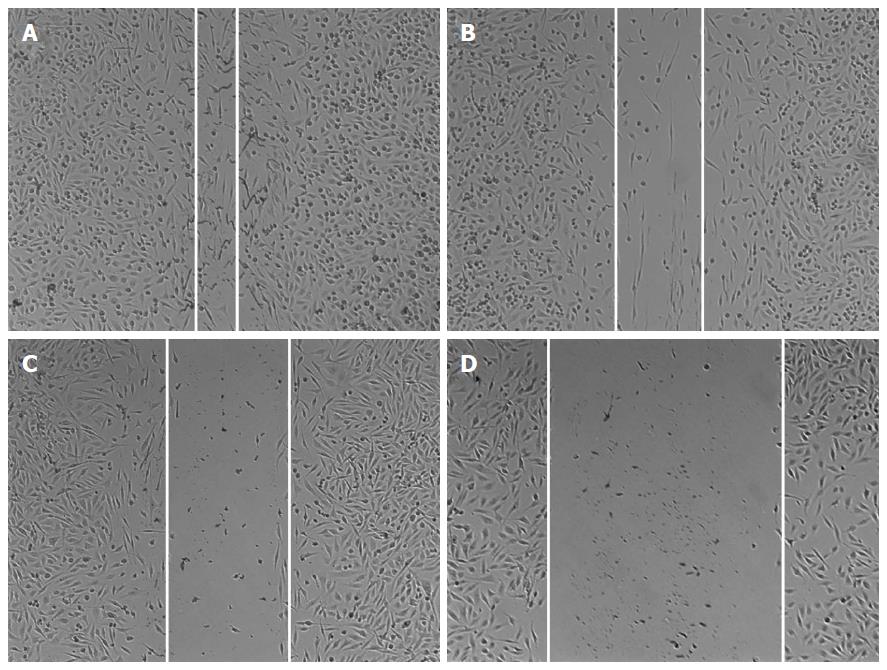
Figure 4 Wound healing in HepG2 cells treated with γ-secretase inhibitor-I and/or interleukin-24.
Representative wounds after scratch wounding and after healing were recorded with a microscope (A-D). A: Control HepG2 cells; B: HepG2 cells treated with GSI-I; C: HepG2 cells treated with IL-24; D: HepG2 cells treated with GSI-I and IL-24. GSI-I: γ-secretase inhibitor-I; IL: Interleukin.
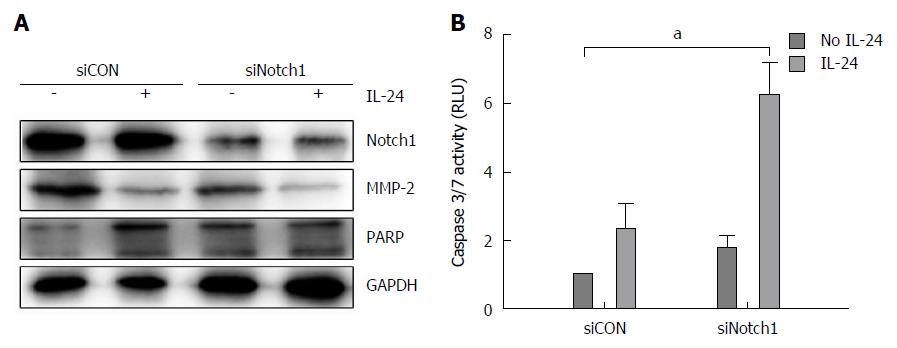
Figure 5 RNA interfering against Notch-1 in combination with interleukin-24 treatment in HepG2 cells.
HepG2 cells were transfected for 48 h with siNotch-1 or siScr. Cells were treated with IL-24 for 48 h. A: Western blot analysis of the levels of Notch-1, MMP-2 and PARP was performed after siCON or siNotch1 treatment as reported in Materials and Methods; B: Caspase 3/7 activity was estimated by luminescent assay. aP < 0.05 vs siCON in HepG2 cells.
- Citation: Han B, Liu SH, Guo WD, Zhang B, Wang JP, Cao YK, Liu J. Notch1 downregulation combined with interleukin-24 inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(33): 9727-9735
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i33/9727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727