Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2015; 21(32): 9554-9565
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9554
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9554
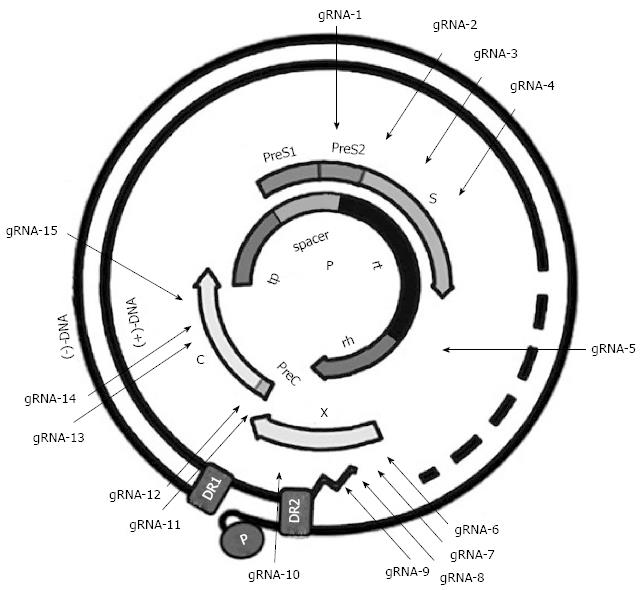
Figure 1 Illustration of the gRNA-targeted sequences located in the hepatitis B virus genome.
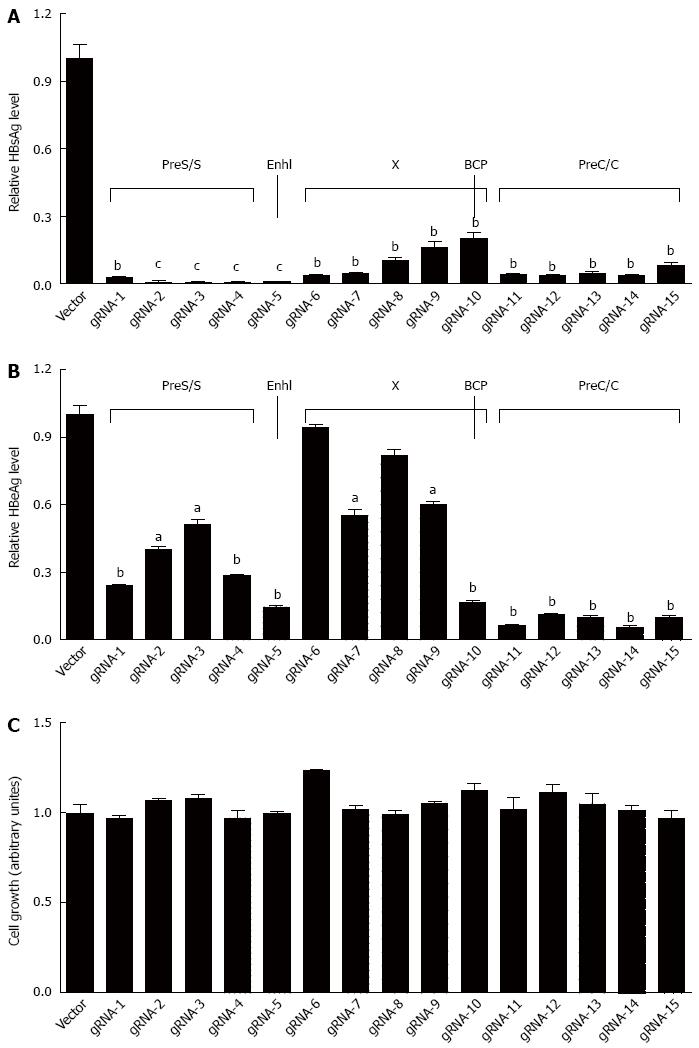
Figure 2 Fifteen hepatitis B virus-specific gRNAs could efficiently suppress the production of hepatitis B virus surface antigen or hepatitis B virus e antigen.
A: The plasmid pBB4.5-HBV1.2 (0.5 μg) was co-transfected with each individual gRNA/Cas9 dual expression vector (1.5 μg) to HuH-7 cells. HBsAg level in culture supernatant was measured at 72 h post transfection using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay analysis; B: HBeAg level in culture supernatant was measured using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay analysis as above; C: The cytotoxicity of each HBV-specific gRNA was examined using an MTT assay. Data are shown as mean ± SE of 5 independent experiments. All P-values are from Student’s t-test. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B virus e antigen; MTT: Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
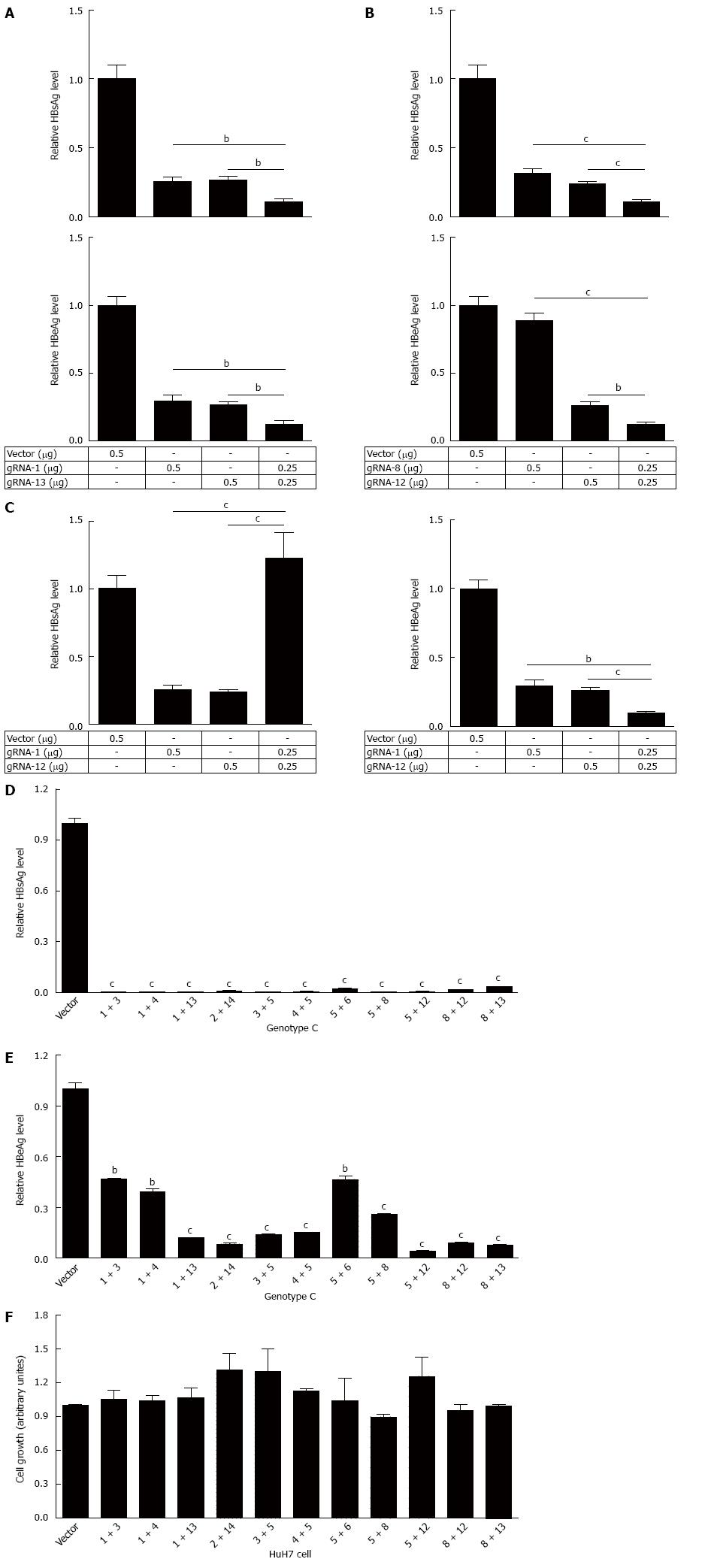
Figure 3 Eleven dual gRNAs could efficiently suppress the production of hepatitis B virus surface antigen or hepatitis B virus e antigen.
The plasmid pBB4.5-HBV1.2 was co-transfected with gRNA-1 and -13 (A), gRNA-8 and -12 (B), or gRNA-1 and -13 (C) expression vectors to HuH-7 cells, alone or in combination. HBsAg and HBeAg levels in cell culture supernatant were measured at 72 h post transfection using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay; D: The plasmid pBB4.5-HBV1.2 (0.5 μg) was co-transfected with different combinations of two gRNAs expression vectors (each 0.75 μg) to HuH-7 cells. HBsAg level in culture supernatant was measured at 72 h post transfection using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay; E: HBeAg level in culture supernatant was measured using time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay as above; F: The cytotoxicity of dual gRNAs was examined using an MTT assay. Data are shown as mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. All P-values are from Student’s t-test. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B virus e antigen; MTT: Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium.
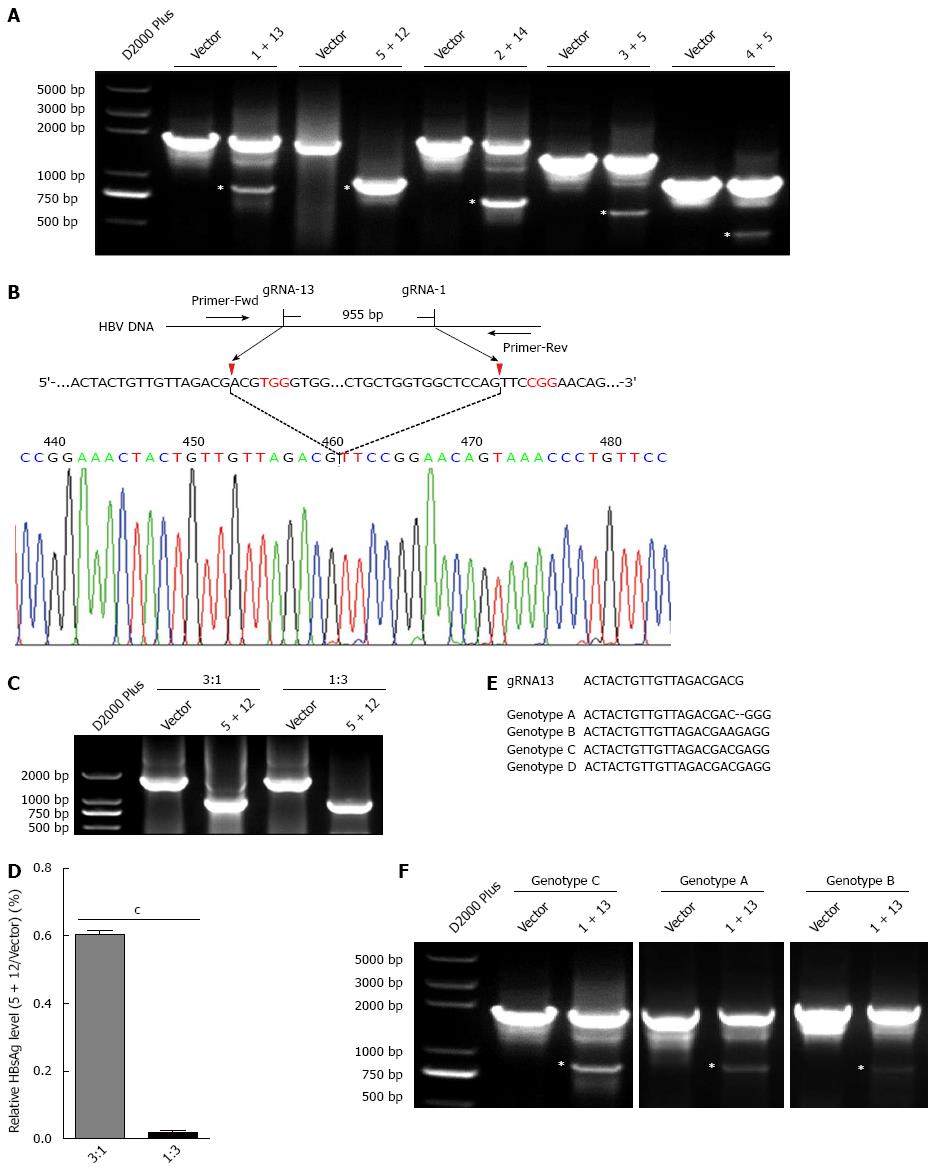
Figure 4 Dual gRNAs could destroy hepatitis B virus genome.
A: The plasmid pBB4.5-HBV1.2 (0.5 μg) was co-transfected with gRNA-1 and -13, gRNA-5 and -12, gRNA-2 and -14, gRNA-3 and -5, or gRNA-4 and -5 expression vectors (each 0.75 μg) to HuH-7 cells. Cellular DNA was extracted at 72 h post transfection, and PCR amplifications were performed using the primers beyond the cleavage sites of each dual gRNAs; B: Sequencing analysis of the smaller fragment formed by gRNA-5 and -12; C: The plasmid pBB4.5-HBV1.2 was co-transfected with the gRNA-5 and -12 expression vectors at different ratios to HuH-7 cells. The smaller fragment was amplified at 72 h post transfection; D: HBsAg level in culture supernatant was measured using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Data are shown as mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments (Student’s t-test); E: Comparative analysis for the sequences of gRNA13 and HBV genome of genotypes A-D; F: The plasmid pGEM-HBV1.3A or pGEM-HBV1.3B and gRNA-1 and -13 expression vectors were co-transfected into HuH-7 cells, and PCR amplifications were performed at 72 h post transfection as above. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen. The asterisks mean that the digested fragment of the HBV expressing templates.
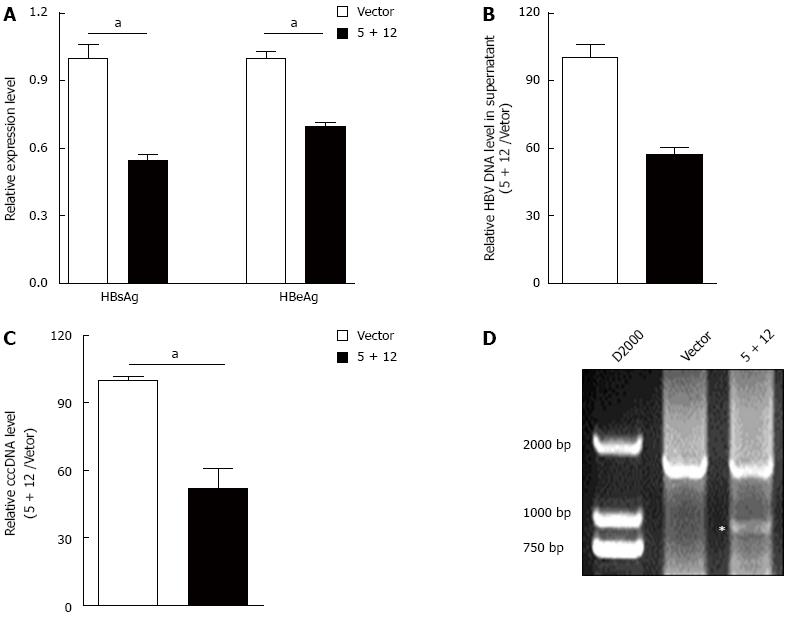
Figure 5 Hepatitis B virus-specific gRNA could suppress the genotype D hepatitis B virus replication and destroy cccDNA.
A: HepAD38 cells were seeded into a 6 well plate. Then, gRNA-5 and -12 expression vectors (each 2 μg) were co-transfected into HepAD38 cells. HBsAg and HBeAg levels in the culture supernatant of HepAD38 cells were measured at 72 h post transfection using a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay; B: HBV DNA levels in the culture supernatant of HepAD38 cells were measured at 72 h post transfection using real-time quantitative PCR; C: HBV cccDNA levels in HepAD38 cells were measured using KCl precipitation, plasmid-safe ATP-dependent DNase (PSAD) digestion, rolling circle amplification and quantitative PCR combined method; D: PCR amplification was performed using the primers beyond the cleavage sites of dual gRNAs following KCl precipitation, PSAD digestion and rolling circle amplification. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen. The asterisk means the digested fragment of cccDNA.
- Citation: Wang J, Xu ZW, Liu S, Zhang RY, Ding SL, Xie XM, Long L, Chen XM, Zhuang H, Lu FM. Dual gRNAs guided CRISPR/Cas9 system inhibits hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(32): 9554-9565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i32/9554.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9554