Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2015; 21(27): 8238-8248
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8238
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8238
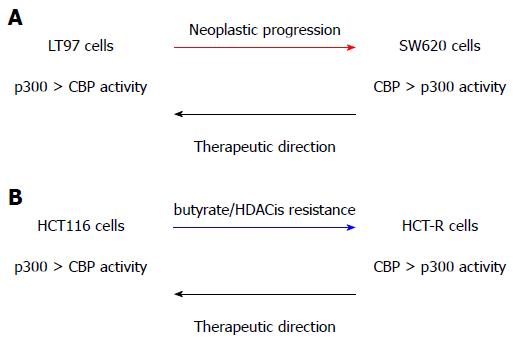
Figure 1 CREB-binding protein/p300 in neoplastic progression and Histone deacetylase inhibitors resistance, and a possible therapeutic approach.
We posit that neoplastic progression (A) and resistance to HDACis (B) are associated with downregulated p300-mediated Wnt activity and relatively increased CBP-mediated Wnt signaling. Gene expression programs dependent upon CBP activity > p300 activity drive cell phenotype changes characteristic of greater neoplastic progression and HDACi resistance. Therefore, therapeutic approaches to prevent and/or reverse progression and resistance will depend upon enhancing p300-mediated Wnt activity at the expense of that mediated by CBP. Adapted from[43]. CBP: CREB-binding protein; HDACis: Histone deacetylase inhibitors.
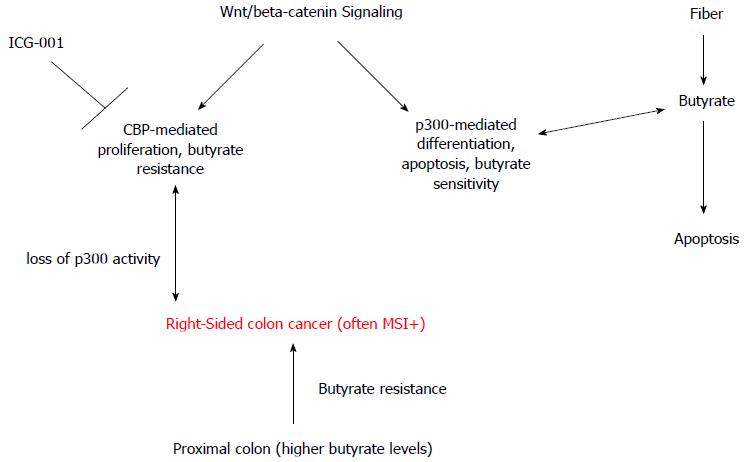
Figure 2 Hypothetical relationship between p300 loss, butyrate-resistance, and right-sided colon cancer.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling has both CBP-mediated and p300-mediated components. CBP-Wnt activity, which is repressed by the clinically relevant agent ICG-001, likely mediates colonic cell proliferation and resistance to butyrate (and other HDACis). In contrast, p300-Wnt activity likely mediates differentiation, apoptosis, and sensitivity to butyrate. Butyrate, derived from dietary fiber, enhances apoptosis of colon cancer cells, possibly acting through the p300-mediated component of Wnt/β-catenin activity. Neoplasms that arise in the proximal colon, where butyrate concentrations are highest, may be resistant to butyrate, and this resistance may arise through loss of p300 expression and activity and a greater reliance on CBP-mediated Wnt signaling. Development of these right-sided colon cancers may be prevented/threated via agents such as ICG-001 and/or other approaches that can promote p300-Wnt > CBP-Wnt activity. CBP: CREB-binding protein; HDACis: Histone deacetylase inhibitors.
- Citation: Bordonaro M, Lazarova DL. CREB-binding protein, p300, butyrate, and Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(27): 8238-8248
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i27/8238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8238