Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6621-6630
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6621
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6621
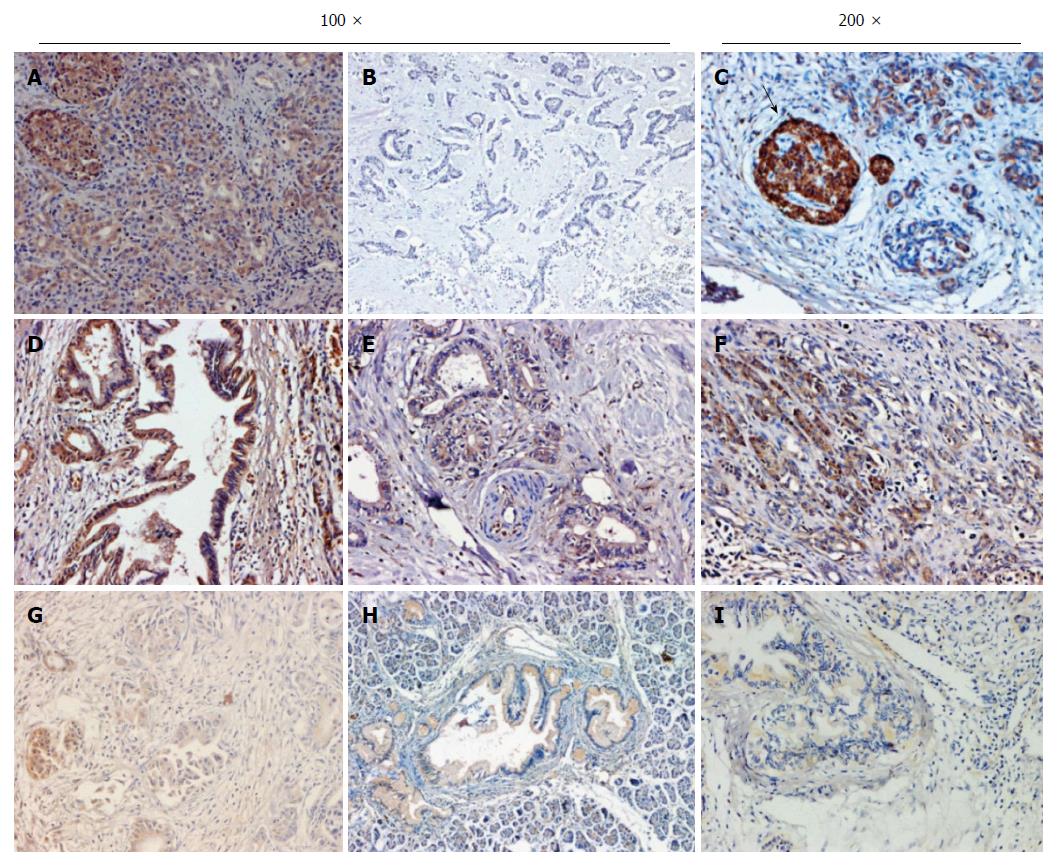
Figure 1 Representative images of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissues immunostained for RASSF6.
Representative micrographs of RASSF6 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cancerous tissues or chronic pancreatitis tissues by immunohistochemistry. A: Diffused cytoplasmic RASSF6 staining in chronic pancreatitis tissues; B: Representative negative staining of RASSF6 in PDAC; C: Extremely strong RASSF6 staining in pancreas islet (black arrow); D-F: Strongly positive RASSF6 staining in PDAC; G-I: Weakly positive RASSF6 staining in PDAC. Magnifications × 100 for A, B, D, E, G and H; × 200 for C, F and I.
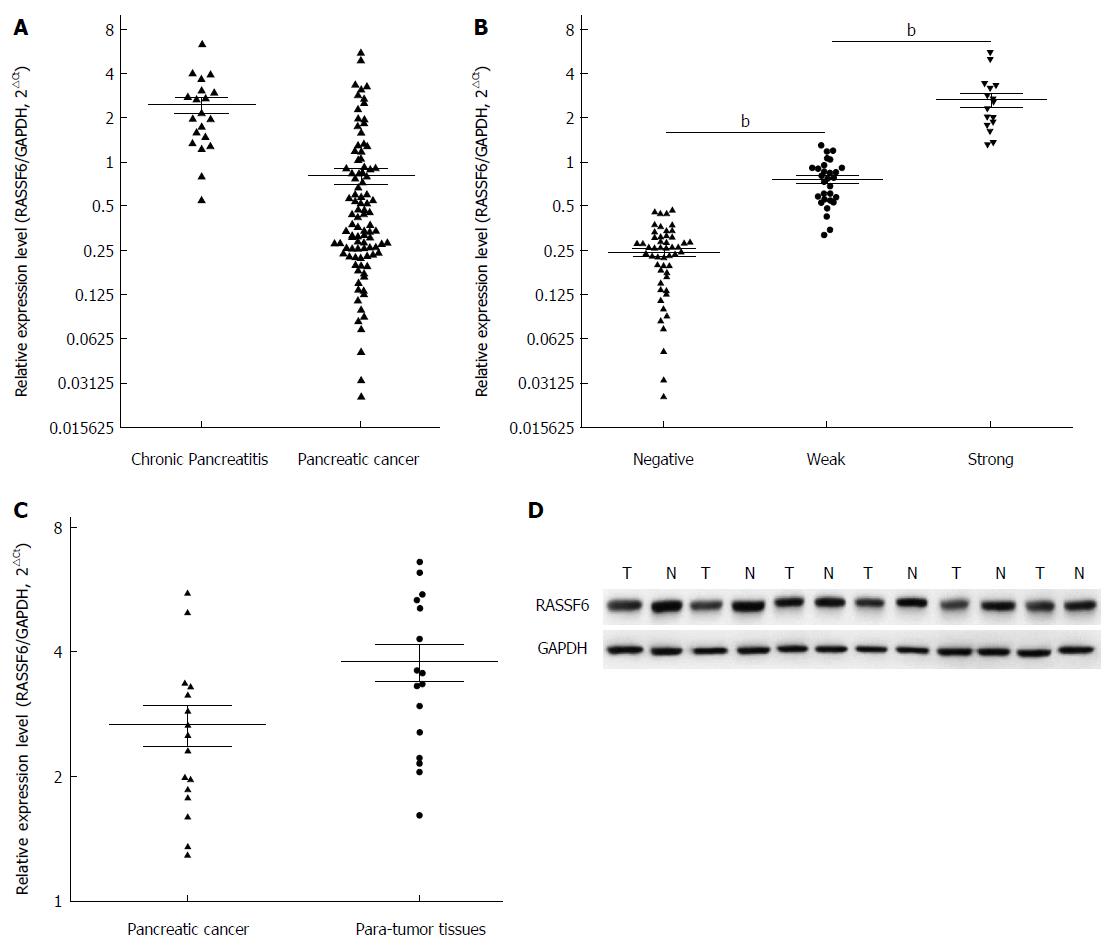
Figure 2 Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction evaluation of RASSF6 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissues.
A: RASSF6 mRNA levels in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues were significantly decreased compared with its levels in chronic pancreatitis tissues (P < 0.001); B: Groups were made according to the immunohistochemical results, and the consistency between immunohistochemical results and PCR results was evaluated through t test. Result showed that immunohistochemical scores were in keeping with RASSF6 mRNA levels (bP < 0.001); C, D: RASSF6 mRNA and protein expression levels were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot in 16 cases with strong RASSF6 immunohistochemical staining. Even in these PDAC tissues with strongly positive RASSF6 staining, both the mRNA expression (C: P = 0.033) and protein levels (D: P = 0.049) were still less than para-tumor tissues.
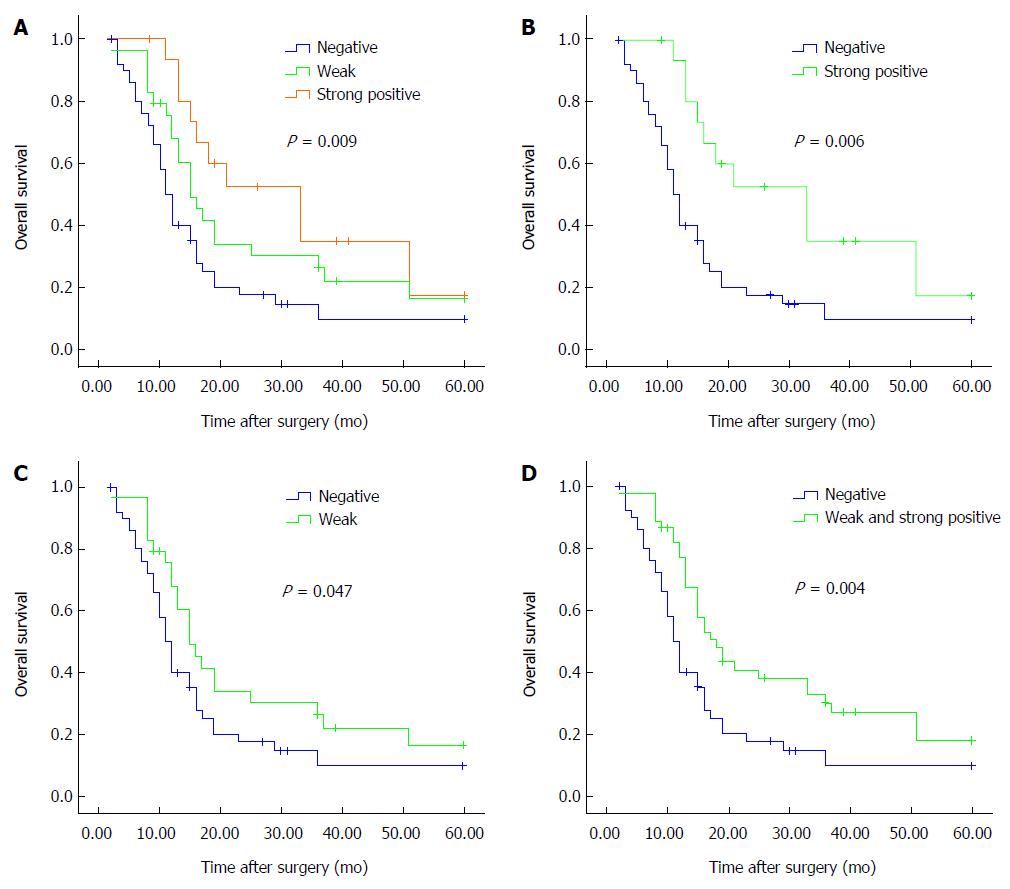
Figure 3 Survival curves of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in regards to RASSF6 expression.
A: There was a significant correlation between RASSF6 expression levels and overall survival (P = 0.009); B: Overall survival of patients with strongly positive RASSF6 staining was significantly higher than overall survival of those whose tumor was negative (P = 0.006); C: Weakly positive staining vs negative staining (P = 0.047); D: Overall survival of patients with positive RASSF6 staining (strongly positive plus weakly positive staining) remained better than survival of patients with negative staining of RASSF6 (P = 0.004).
- Citation: Ye HL, Li DD, Lin Q, Zhou Y, Zhou QB, Zeng B, Fu ZQ, Gao WC, Liu YM, Chen RW, Li ZH, Chen RF. Low RASSF6 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is associated with poor survival. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6621-6630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6621.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6621