Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6572-6581
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6572
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6572
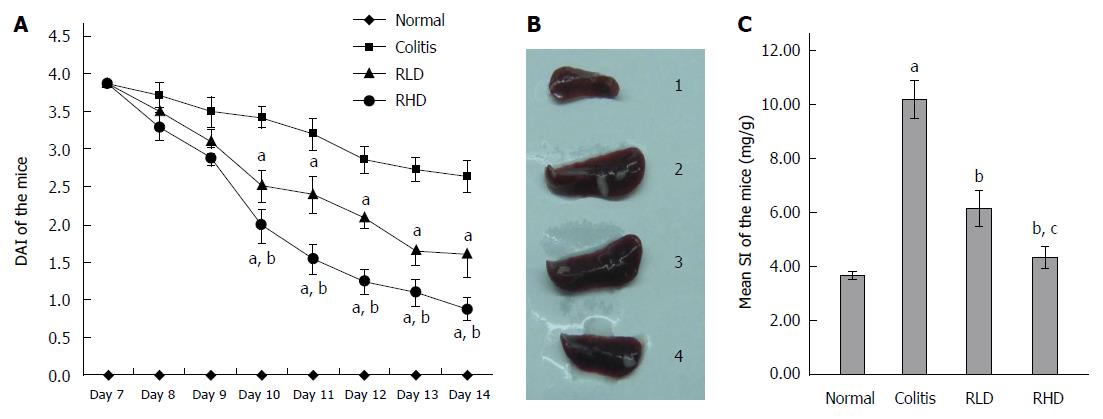
Figure 1 Effect of resveratrol on ulcerative colitis in mice.
A: Disease activity index (DAI); B: Spleens from normal mice (1), mice with colitis (2), mice with colitis treated with low-dose resveratrol (RLD; 3), and mice with colitis treated with high-dose resveratrol (RHD; 4); and C: Spleen index (SI); aP < 0.05 vs normal; bP < 0.05 vs colitis; cP < 0.05 vs RLD.
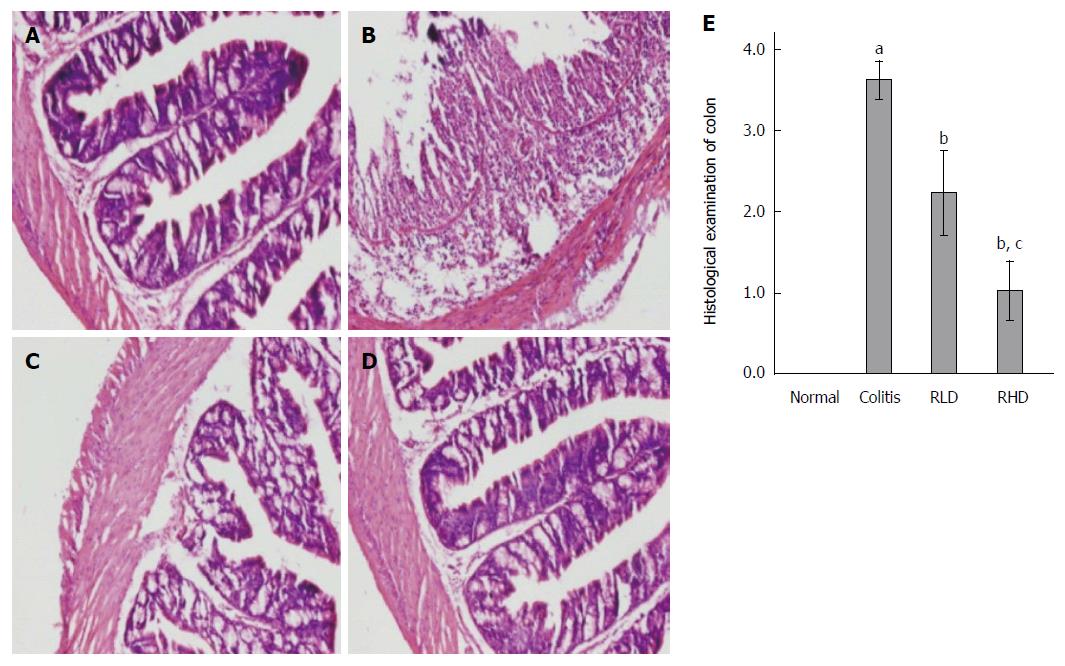
Figure 2 Histologic assessment of resveratrol effects.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining in normal mice (A), mice with colitis (B), mice with colitis treated with low-dose resveratrol (RLD; C), and mice with colitis treated with high-dose resveratrol (RHD; D); E: Histologic scores; aP < 0.05 vs normal; bP < 0.05 vs colitis; cP < 0.05 vs RLD.
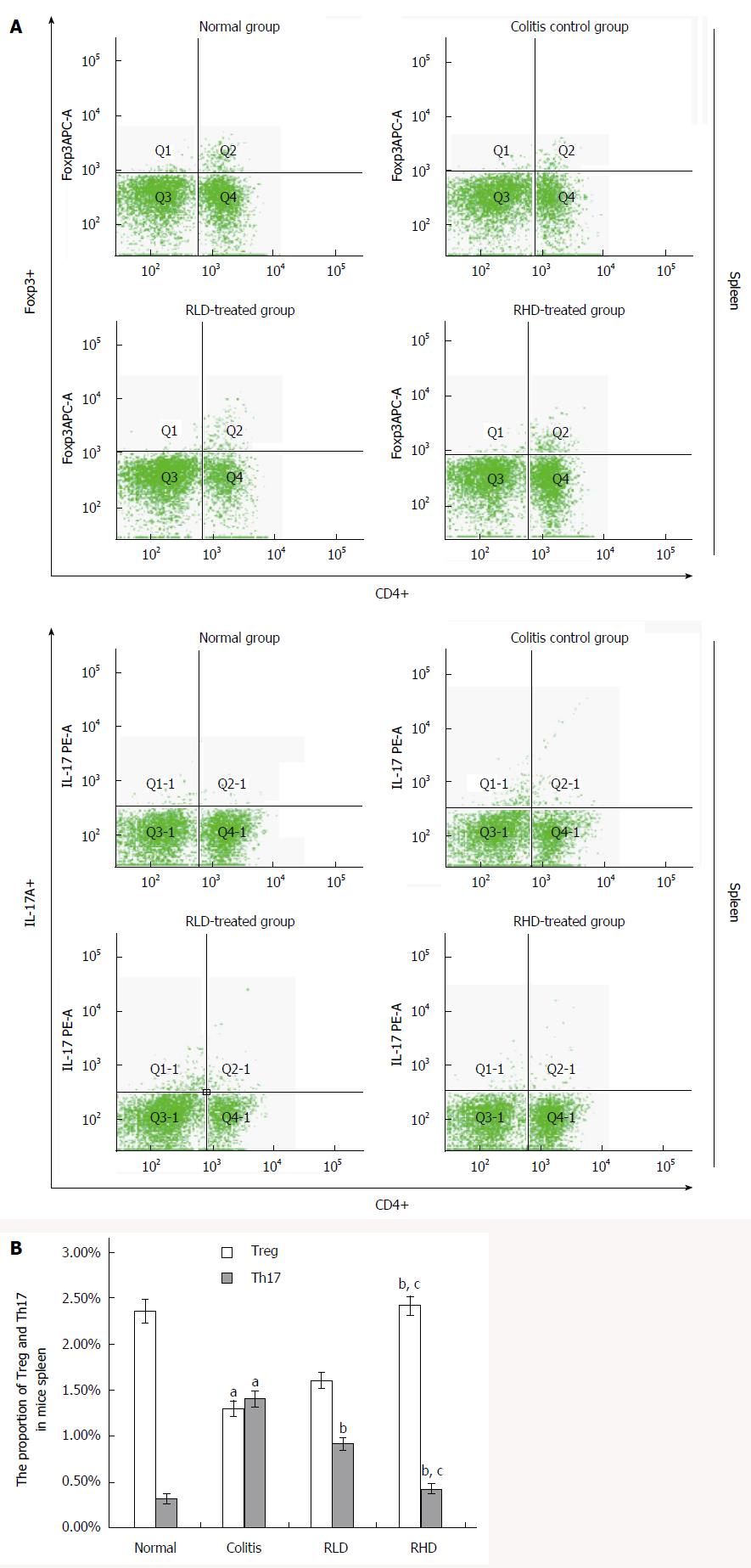
Figure 3 Effect of resveratrol on spleen Treg and Th17 cells.
A: Flow cytometric sorting of Treg and Th17 cells; B: Quantification of flow cytometry. aP < 0.05 vs normal; bP < 0.05 vs colitis; cP < 0.05 vs RLD. RHD: Resveratrol high-dose group; RLD: Resveratrol low-dose group.
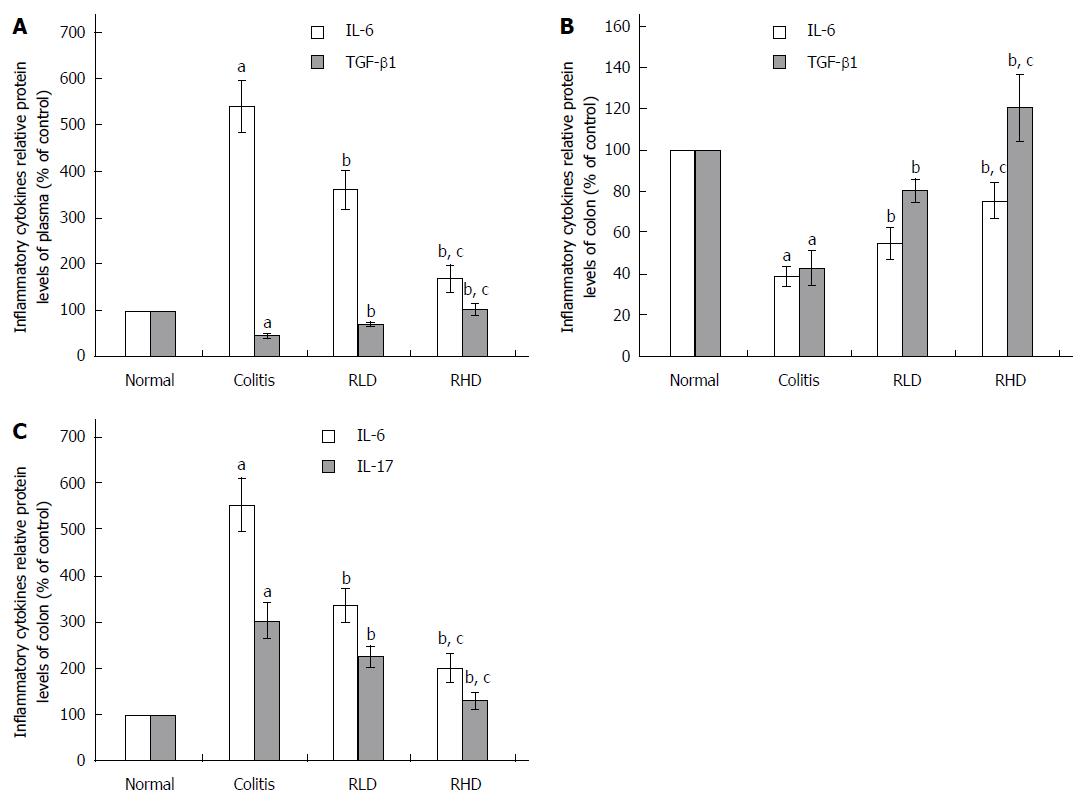
Figure 4 Effect of resveratrol on the cytokines in the plasma and colonic tissues.
The effect of resveratrol on the level of A: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and interleukin (IL)-6 in plasma; B: TGF-β1 and interleukin (IL)-6 in colon tissues; and C: IL-6 and IL-17 in colon tissues. aP < 0.05 vs normal; bP < 0.05 vs colitis; cP < 0.05 vs RLD. RHD: Resveratrol high-dose group; RLD: Resveratrol low-dose group.
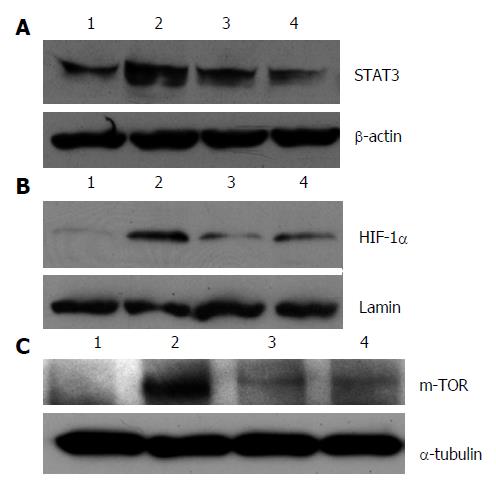
Figure 5 Effect of resveratrol on protein expression of HIF-1α, mTOR, STAT3.
A: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3); B: Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α; and C: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Lane 1: Normal mice; Lane 2: Mice with colitis; Lane 3: Mice with colitis treated with low-dose resveratrol; Lane 4: Mice with colitis treated with high-dose resveratrol.
- Citation: Yao J, Wei C, Wang JY, Zhang R, Li YX, Wang LS. Effect of resveratrol on Treg/Th17 signaling and ulcerative colitis treatment in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6572-6581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6572