Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2015; 21(2): 475-483
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.475
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.475
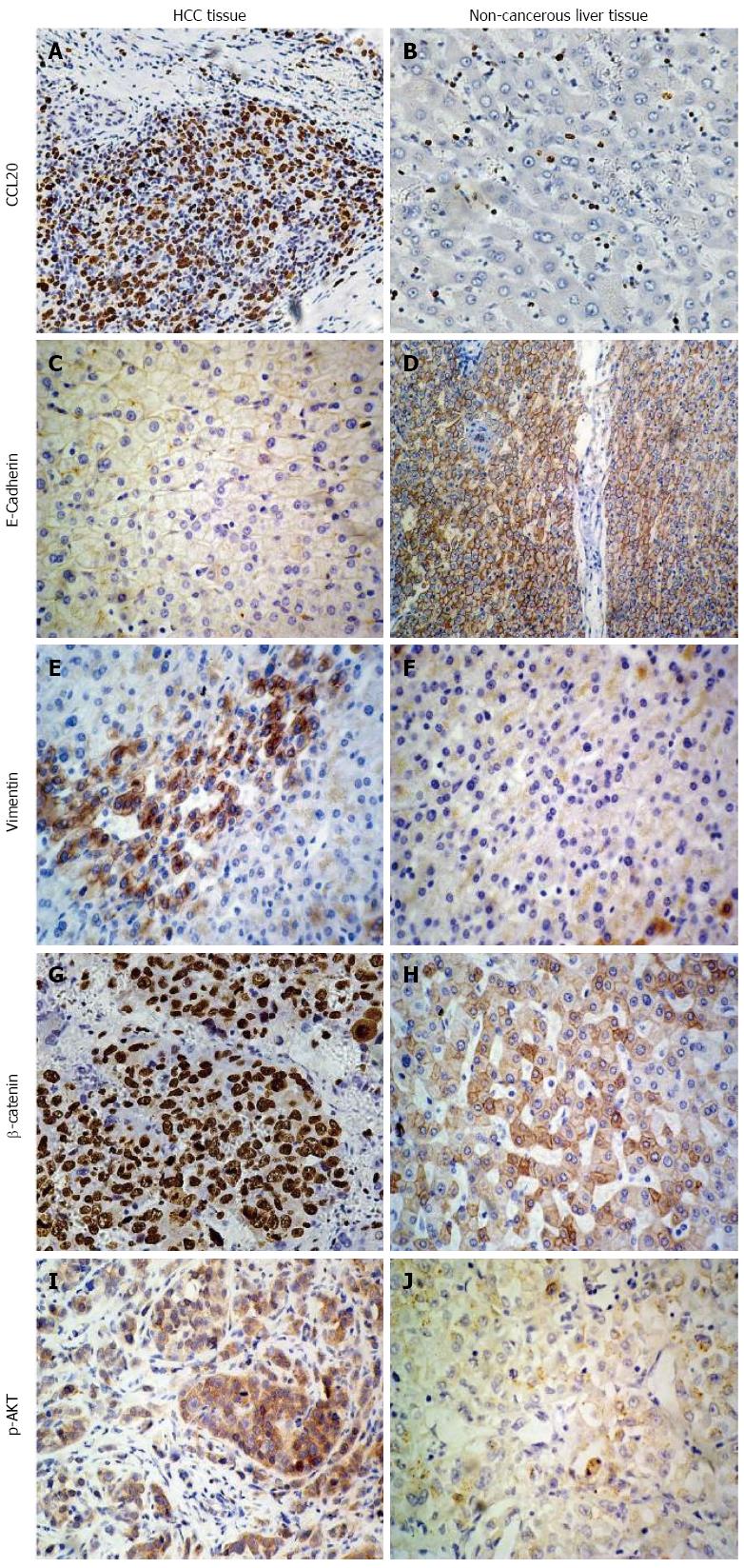
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.
Expression of A, B: Chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20); C, D: E-cadherin; E, F: Vimentin; G, H: β-catenin; I, J: Phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) in HCC and non-cancerous liver tissues (magnification × 200). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
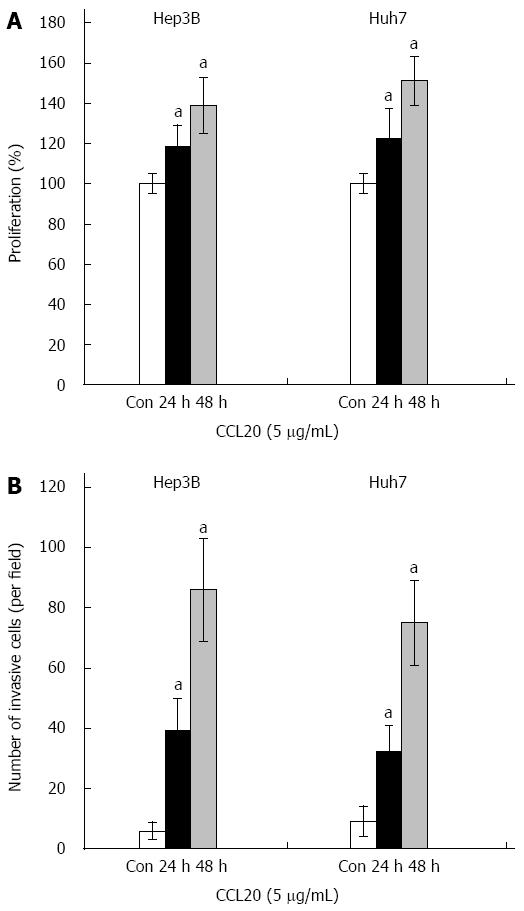
Figure 2 Effects of chemokine ligand 20 on proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hep3B and Huh7 cells were treated with chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) (5 μg/mL) for 24 h and 48 h. A: Cell proliferation was analyzed using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenoltetrazolium bromide (MTT assay); B: Invasion was assessed using a Transwell chamber; aP < 0.05 vs Control. Con: Control.
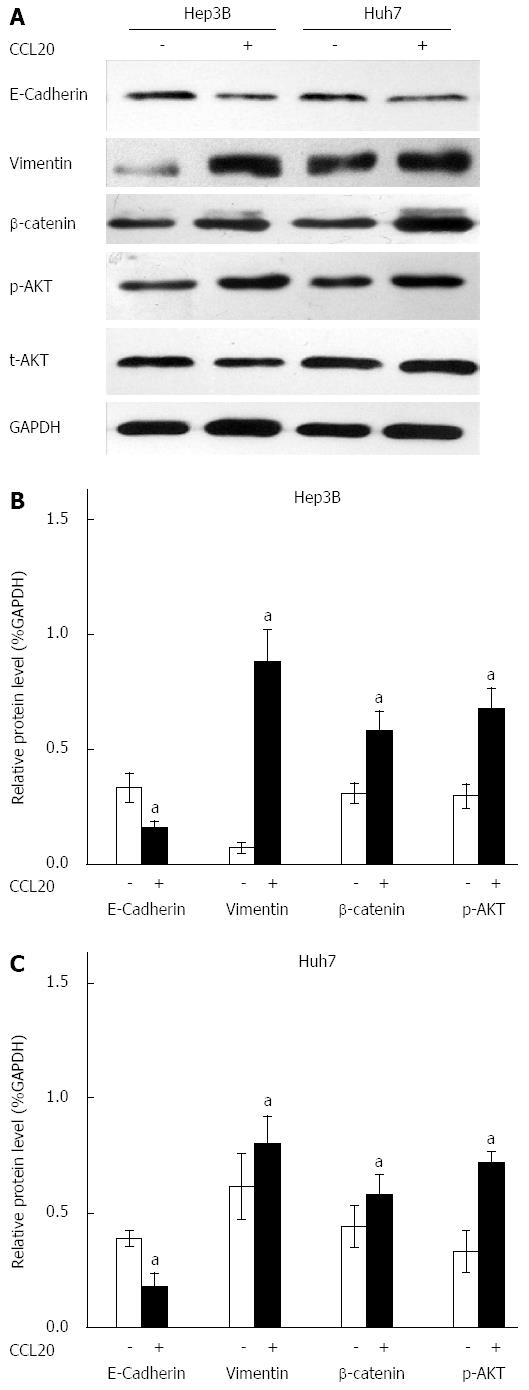
Figure 3 Effects of chemokine ligand 20 on expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins.
A: Representative Western blots for epithelial marker E-cadherin, mesenchymal marker vimentin, total and phosphorylated AKT (t-AKT and p-AKT), and β-catenin in Hep3B and Huh7 cells after treatment with chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) for 48 h. B: Quantification of Western blotting by gray value analysis; aP < 0.05 vs Control.
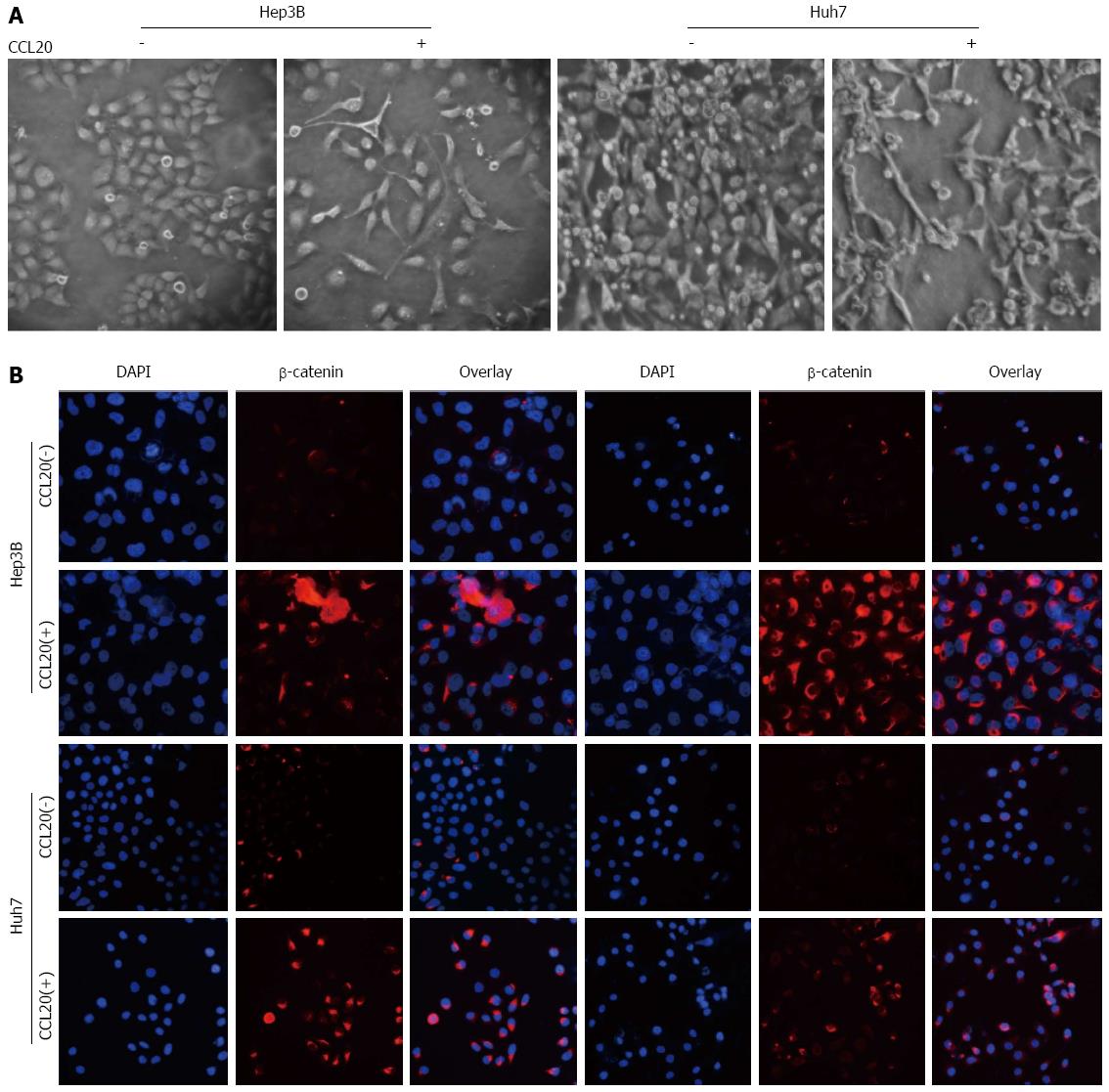
Figure 4 Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like phenotype and upregulation of related markers in hepatocellular carcinoma cells with chemokine ligand 20.
A: Morphologic changes in Hep3B and Huh7 cells after treatment with chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) for 48 h (most cells exhibited an elongated, spindle-shape mesenchymal morphology with treatment); B: Immunocytochemistry for phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) and β-catenin in Hep3B and Huh7 cells after treatment with CCL20 for 48 h (magnification × 200).
-
Citation: Hou KZ, Fu ZQ, Gong H. Chemokine ligand 20 enhances progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(2): 475-483 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i2/475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.475