Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2015; 21(2): 453-464
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.453
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.453
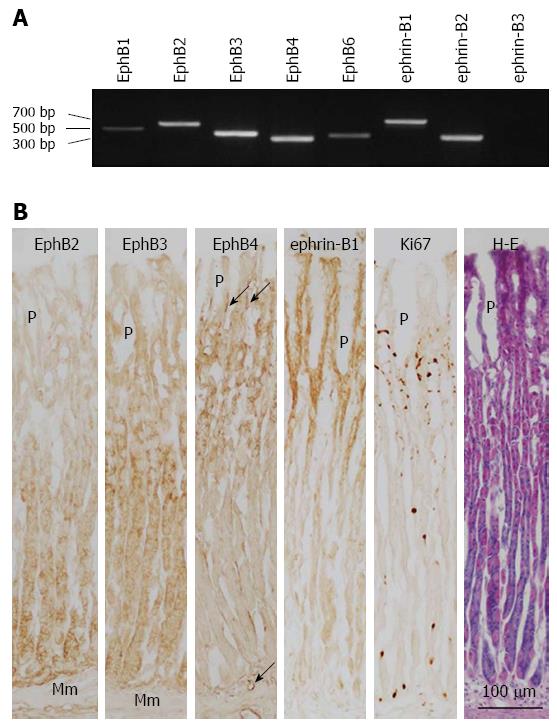
Figure 1 Expression of B-class Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in normal rat gastric corpus mucosa.
A: EphB and ephrin-B mRNA expression was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; B: Expression of EphB2-B4, ephrin-B1, and Ki67 in the gastric corpus mucosa was evaluated by immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin and eosin co-staining of frozen sections. Mm: Muscularis mucosae; P: Gastric pit; arrow: Blood vessel.
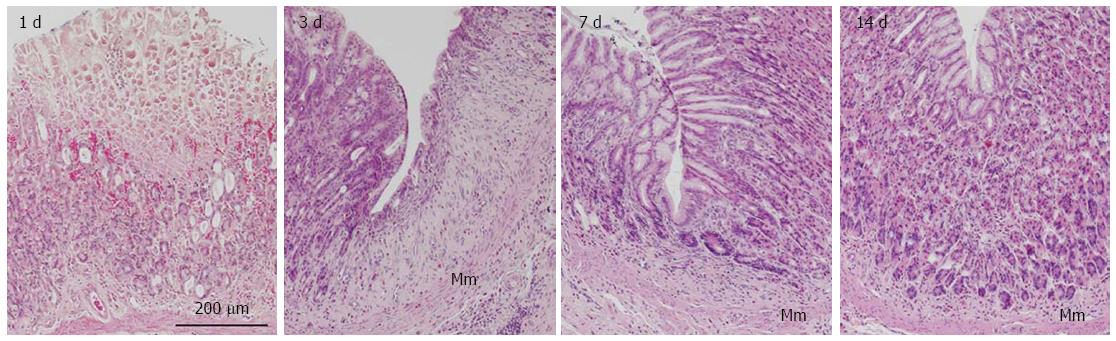
Figure 2 Representative images of rat gastric corpus mucosa showing typical regeneration 1, 3, 7, and 14 d after induction of gastric ulcers by oral administration of acidified ethanol solution (80% ethanol in 0.
15 mol/L HCl). Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Mm: Muscularis mucosae.
Figure 3 Densitometric quantification of EphB1-B4 and B6, and ephrin-B1 and -B2 mRNA expression levels in the gastric corpus mucosa of control (Con) and ulcerated regenerating stomach on day 7 after induction of gastric ulcers (Ulc), as determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
EphB2 expression in the regenerating gastric mucosa was higher than in the control (P = 0.016; unpaired t-test).
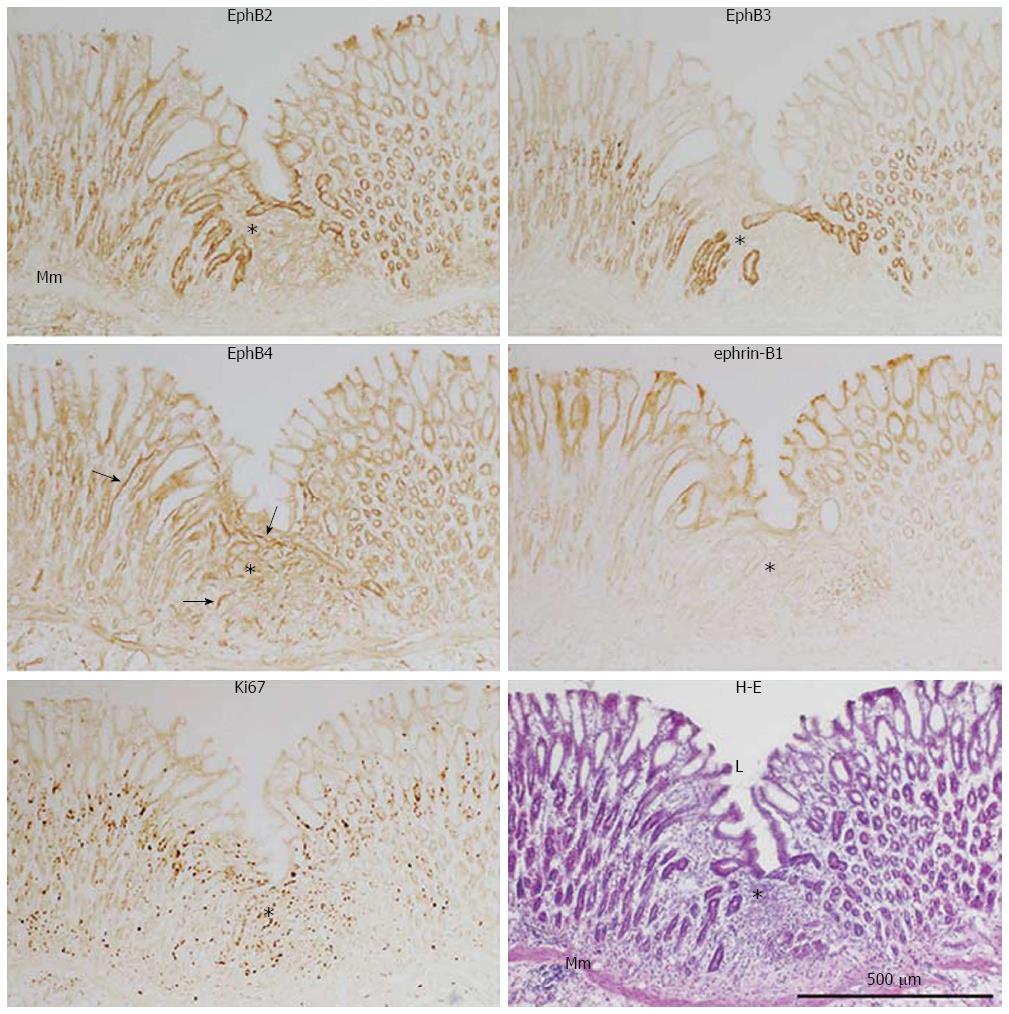
Figure 4 Immunoperoxidase staining of EphB2, B3, and B4, ephrin-B1, and Ki67, with hematoxylin and eosin staining, of frozen sections of the regenerating gastric corpus mucosa 7 d after experimental induction of gastric ulcers (see Figure 2 legend).
Mm: Muscularis mucosae; L: Gastric lumen; Arrow: Blood vessel; Asterisk: Regenerating region.
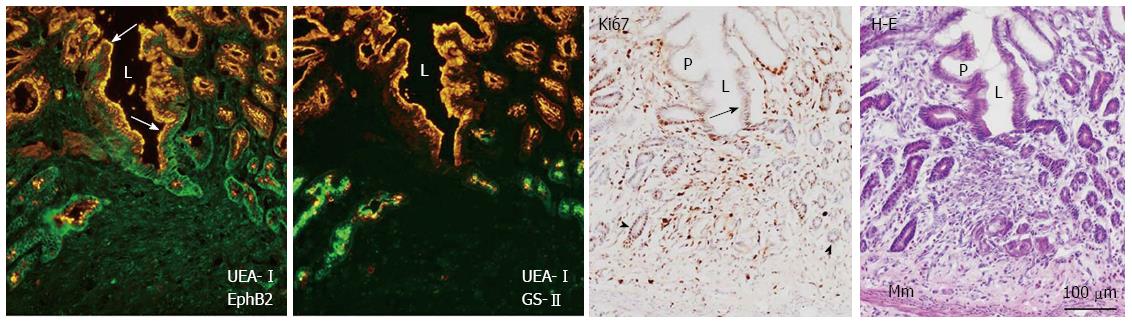
Figure 5 Double immunofluorescence labeling of EphB2 (green) and the pit cell marker Ulex europaeus agglutinin (UEA)-I (orange), and the neck cell marker Griffonia simplicifolia-II (green) and UEA-I, with Ki67 immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin and eosin co-staining in frozen sections of the regenerating gastric corpus mucosa 7 d after induction of gastric ulcers (see Figure 2 legend).
L: Gastric lumen; Mm: Muscularis mucosae; P: Gastric pit; Black arrow: Ki67-positive pit cells; Arrowhead: Ki67-positive gland cells; White arrow: UEA-I-positive pit cells.
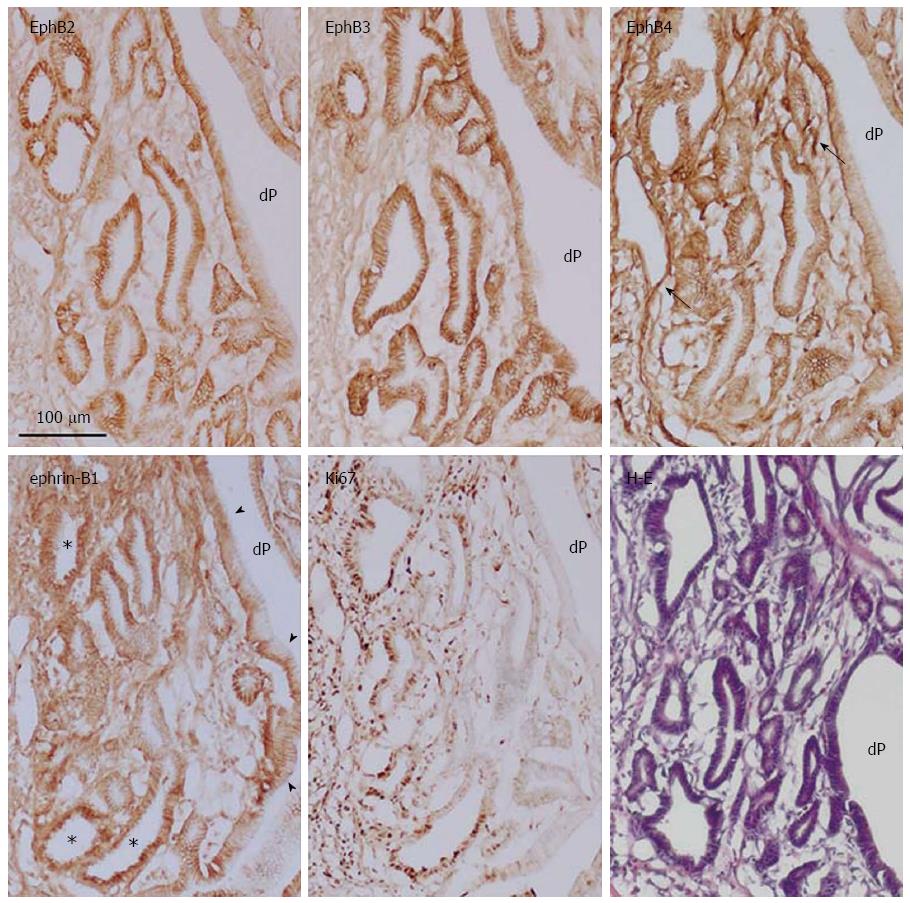
Figure 6 Immunoperoxidase staining of EphB2-B4, ephrin-B1, and Ki67, and hematoxylin and eosin staining of frozen sections of gastric dysplasia in rat induced by oral administration of N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine.
dP: Deep and wide aberrant gastric pit; Arrow: Blood vessel; Arrowhead: Membrane localization of ephrin-B1; Asterisk: Cytoplasmic localization of ephrin-B1.
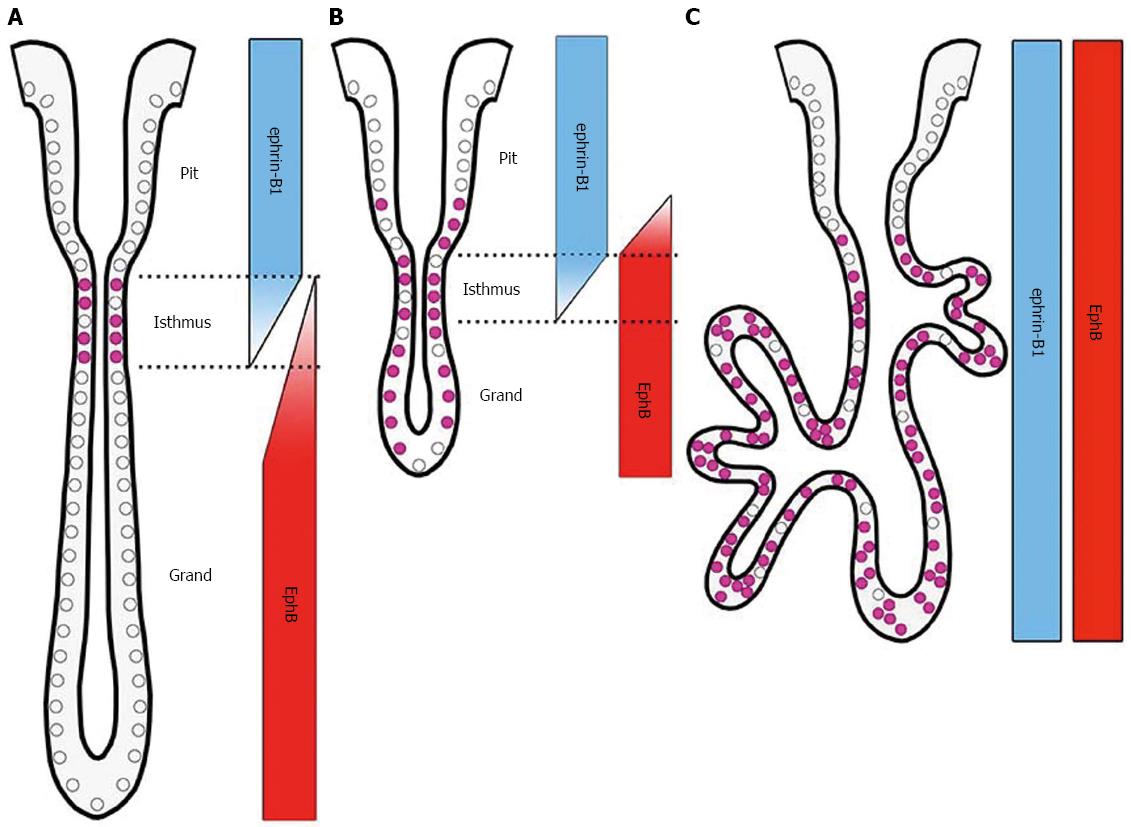
Figure 7 Schematic representation of EphB receptor, ephrin-B1 ligand, and Ki67 expression in normal (A), ulcerated regenerating (B), and dysplastic gastric epithelia (C).
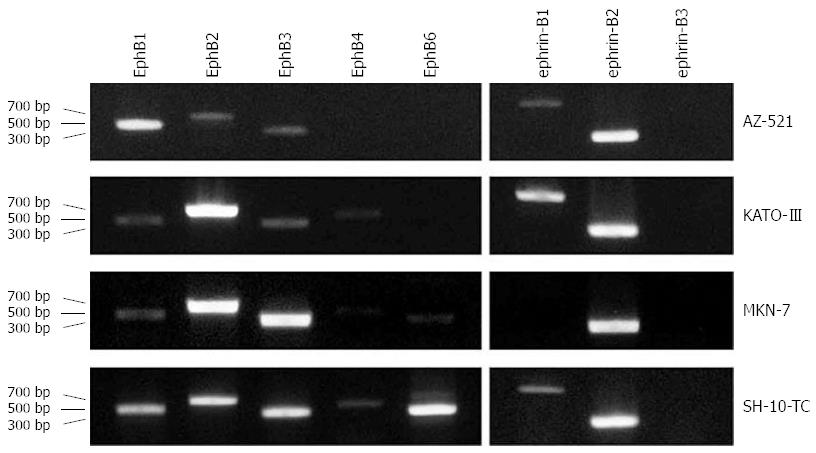
Figure 8 EphB and ephrin-B mRNA expression in human gastric carcinoma cell lines.
Transcript levels in AZ-521, KATO-III, MKN-7, and SH-10-TC cells were determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. All cell lines coexpressed more than one EphB receptor and/or ephrin-B ligand at a high level.
- Citation: Uchiyama S, Saeki N, Ogawa K. Aberrant EphB/ephrin-B expression in experimental gastric lesions and tumor cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(2): 453-464
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i2/453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.453