Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2015; 21(19): 5867-5876
Published online May 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5867
Published online May 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5867
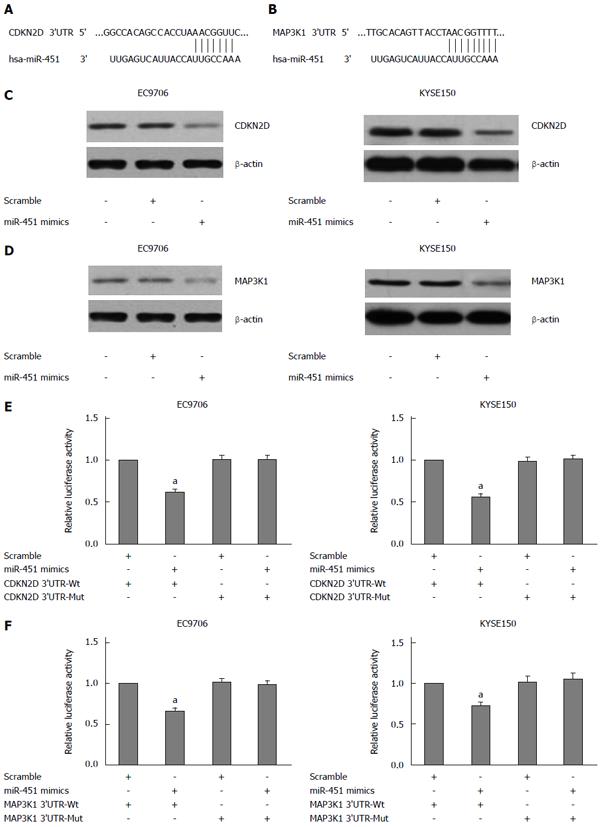
Figure 1 CDKN2D and MAP3K1 are direct targets of miR-451 in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells.
A: The putative miR-451 binding sequence for the CDKN2D 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR). The 3'-UTR of CDKN2D contains a seed region for miR-451; B: The putative miR-451 binding sequence for the MAP3K1 3'-UTR. The 3'-UTR of MAP3K1 contains a seed region for miR-451; C: Western blot analysis of CDKN2D expression in transfected cells. Transfection of miR-451 mimics resulted in a significant reduction of CDKN2D protein expression in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells. β-actin was used as a reference; D: Western blot analysis of MAP3K1 expression in transfected cells. Transfection of miR-451 mimics resulted in a significant reduction of MAP3K1 protein expression in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells. β-actin was used as a reference; E: MiR-451 significantly decreased the luciferase activity of CDKN2D 3’-UTR-Wt in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells; F: MiR-451 significantly decreased the luciferase activity of MAP3K1 3’-UTR-Wt in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells (aP < 0.05 vs control group).
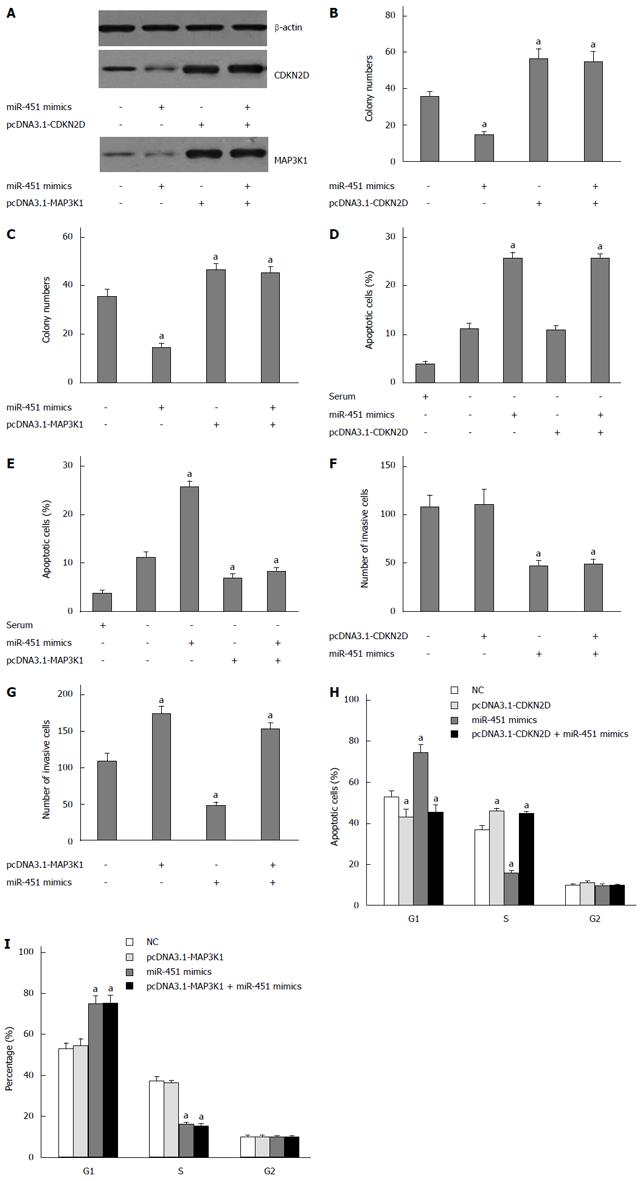
Figure 2 CDKN2D and MAP3K1 overexpression reverses the effect of miR-451.
A: CDKN2D and MAP3K1 protein levels were detected by Western blot assay. Western blot assay showed that transfection of miR-451 mimics inhibited the expression of CDKN2D or MAP3K1. Co-transfection of pcDNA3.1-CDKN2D or pcDNA3.1-MAP3K1and miR-451 abrogated the effects of miR-451 on CDKN2D or MAP3K1 expression. β-actin was used as a reference; B: The expression of CDKN2D could partially reverse the anti-proliferation function of miR-451. Colony formation assays were performed. aP < 0.05 vs control group; C: The expression of MAP3K1 could partially reverse the anti-proliferation function of miR-451. Colony formation assays were performed. aP < 0.05 vs control group; D: The expression of CDKN2D did not reverse the pro-apoptotic function of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-CDKN2D (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell apoptosis was assessed using flow cytometry assay; E: The expression of MAP3K1 reversed the pro-apoptotic function of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-MAP3K1 (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell apoptosis was assessed using flow cytometry assay; F: The expression of CDKN2D reversed the anti-migration function of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-CDKN2D (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell invasion was assessed using transwell assay; G: The expression of MAP3K1 reversed the anti-migration function of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-MAP3K1 (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell invasion was assessed using transwell assay; H: The expression of CDKN2D reversed G1 arrest of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-CDKN2D (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell cycle was assessed using flow cytometry assay; I: The expression of MAP3K1 did not reverse G1 arrest of miR-451. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-MAP3K1 (not including 3’-UTR) or (and) miR-451. The cell cycle was assessed using flow cytometry assay (aP < 0.05 vs control group).
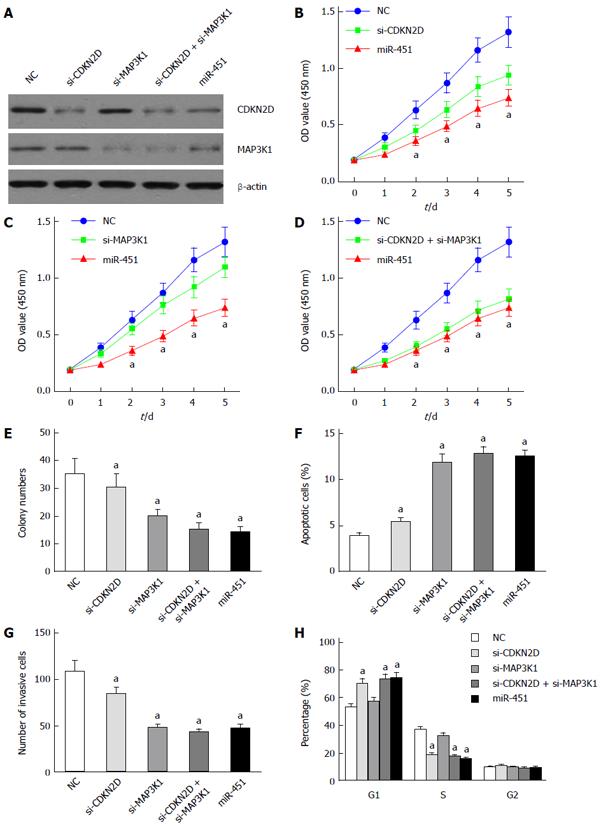
Figure 3 MiR-451 inhibits the proliferation of EC9706 cells by targeting CDKN2D and MAP3K1.
A: CDKN2D and MAP3K1 protein levels were detected by Western blot assay. Western blot assay showed that transfection of CDKN2D-siRNAs, MAP3K1-siRNAs and miR-451 mimics inhibited the expression of CDKN2D and MAP3K1, respectively; B: CDKN2D silencing and miR-451 overexpression inhibited the cell proliferation. CCK8 array was used to assess EC9706 proliferation; C: MAP3K1 silencing and miR-451 overexpression inhibited the cell proliferation. CCK8 array was used to assess EC9706 proliferation; D: Co-transfection of si-CDKN2D and si-MAP3K1 inhibited the proliferation of EC9706 cells. CCK8 array was used to assess EC9706 proliferation; E: CDKN2D, MAP3K1 silencing and miR-451 overexpression reduced the growth of colonies of EC9706 cells. Colony formation assay was used; F: CDKN2D, MAP3K1 silencing and miR-451 overexpression induced EC9706 cell apoptosis. The cell apoptosis was assessed using flow cytometry assay; G: CDKN2D, MAP3K1 silencing and miR-451 overexpression suppressed EC9706 cell invasiveness. The cell invasion was assessed using transwell assay; H: CDKN2D silencing and the overexpression of miR-451 significantly increased the percentage of cells in the G1 phase and decreased the percentage of cells in the S phase (aP < 0.05 vs control group). The cell cycle was assessed using flow cytometry assay.
- Citation: Zang WQ, Yang X, Wang T, Wang YY, Du YW, Chen XN, Li M, Zhao GQ. MiR-451 inhibits proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cell line EC9706 by targeting CDKN2D and MAP3K1. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(19): 5867-5876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i19/5867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5867