Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2015; 21(16): 4817-4828
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4817
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4817
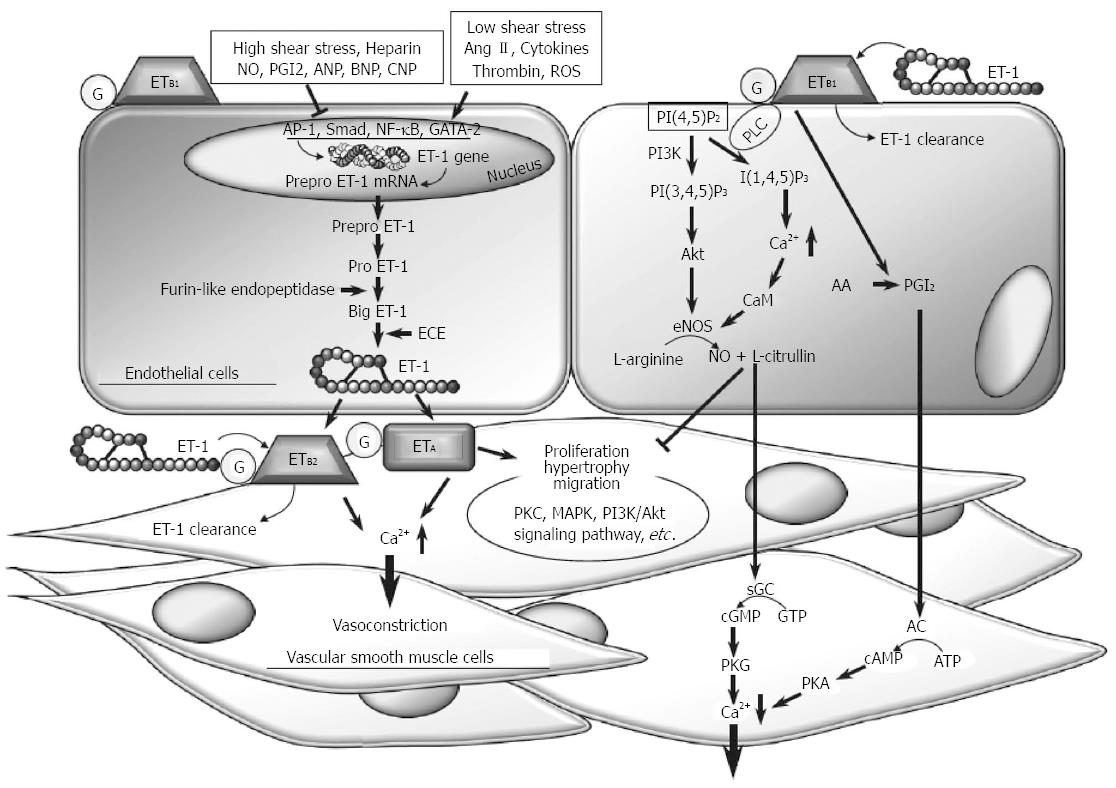
Figure 1 Illustration of interrelationship between Endothelin-1 induced vasoconstriction and nitric oxide mediated vasodilation.
Endothelin-1, PGI2 and NO are closely related in relation to vascular smooth muscle cell tone. (Reprinted with permission Ohkita et al[42] 2002).
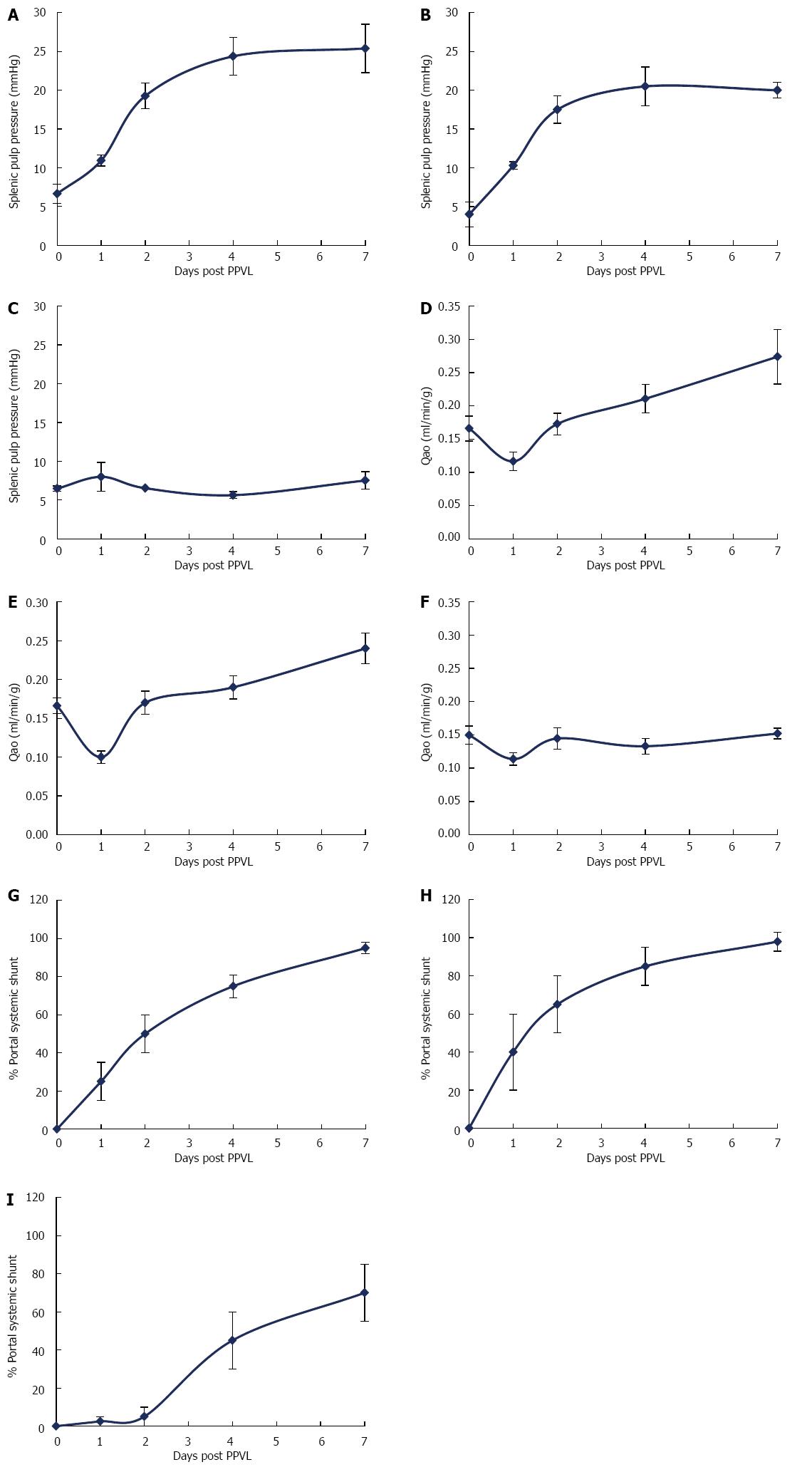
Figure 2 Partial portal vein ligation induces chronic hyperemia and persistent portal hypertension in wild type and iNOS-/- mice but not eNOS-/- mice.
Wild type (A, D, G), iNOS-/- (B, E, H) and eNOS-/- (C, F, I) mice were subjected to partial portal vein ligation surgery. 0-7 d thereafter-splenic pulp pressure (A-C), aortic blood flow (D-F) and portal systemic shunting (G-I) were determined. A-C: Splenic pulp pressure was increased acutely in all mouse groups following ligation (0-1 d). After which pressure was increased further in wild type and iNOS-/- but not in eNOS-/- mice; D, E: Aortic flow was significantly reduced in wild type, iNOS-/- and eNOS-/- mice (0-1 d). In wild type and iNOS-/- mice this low blood flow converted to hyperemia and increased steadily. In eNOS mice flow returned to pre-surgical baseline and was not increased; G-I: Portal systemic shunting increased steadily in wild type and iNOS-/- mice (G, H). There was a significant delay in the development of collateral circulation in eNOS-/- mice (I).
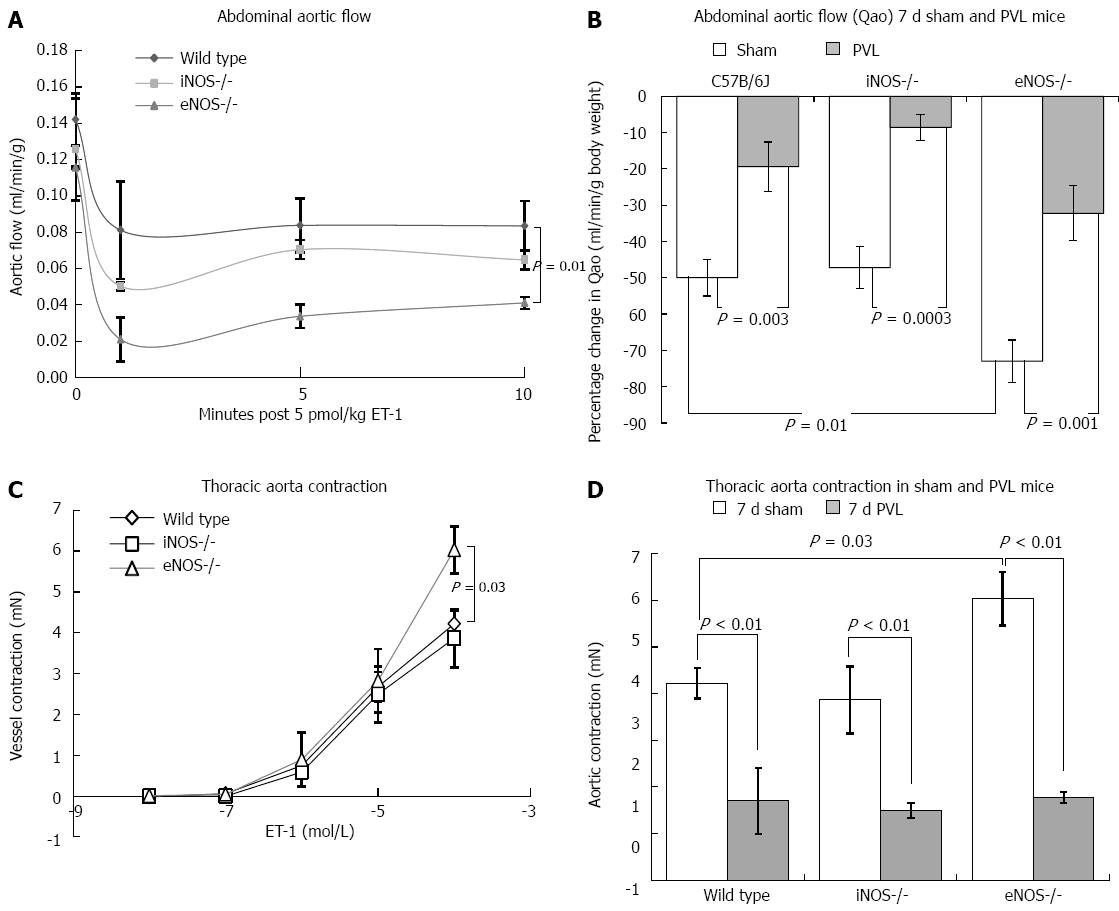
Figure 3 Endothelin-1 hypo-response develops in wild type, iNOS-/- and eNOS-/- mice following portal vein ligation.
A: Aortic blood flow was monitored in unadulterated wild type (squares), iNOS-/- (diamonds) and eNOS-/- (triangle) mice prior to and following IV administration of 5 pmol/kg endothelin-1 (ET1). ET1 induced a rapid vessel contraction and subsequent reduction in flow. Response to ET1 was significantly greater in eNOS-/- when compared to wild type controls; B: Wild type, iNOS-/- and eNOS-/- mice were subjected to sham (open bars) or portal vein ligation surgery (PVL) (shaded bars). After 7 d changes in aortic flow was recorded following IV administration of 5 pmol/kg ET1. In all mouse groups the response to ET1 was markedly reduced following PVL (iNOS > wild type > eNOS-/-); C: ET1 induced contraction of isolated aortic segments from unadulterated wild type (triangle) iNOS-/- (square) and eNOS-/- (triangle) mice were determined using an ADI 610M small animal myograph. Aortic vessel segments contracted to exogenous ET1. At high ET1 dose (10-4 mol/L) aortic vessel segments from eNOS-/- mice contracted significantly greater then segments from wild type controls; D: Wild type, iNOS-/- and eNOS-/- mice were subjected to sham (open bars) or portal vein ligation surgery (shaded bars). After 7 d the aorta was carefully dissected and ET1 contractility was measured. Ex-vivo aorta ET1 (10-4 mol/L) contractility was significantly decreased in vessels from 7 d wild type, iNOS-/- and eNOS-/- PVL mice when compared to shams (PVL vs sham, P < 0.01).
- Citation: Theodorakis N, Maluccio M, Skill N. Murine study of portal hypertension associated endothelin-1 hypo-response. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(16): 4817-4828
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i16/4817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4817